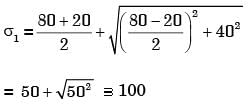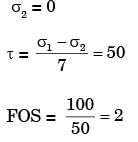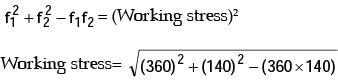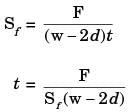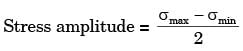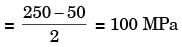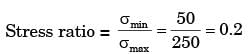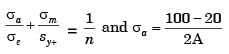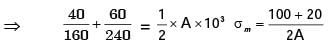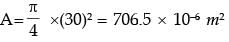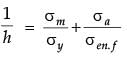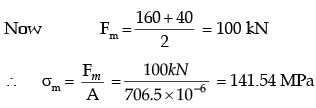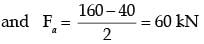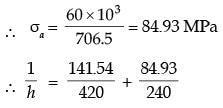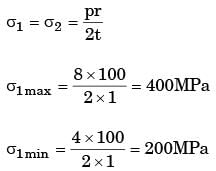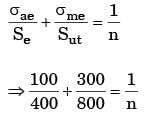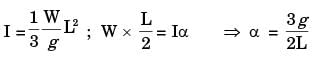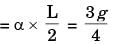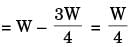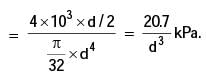GATE Past Year Questions: Static, Dynamic Loading & Failure Theories | Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: Which one of the following failure theories is the most conservative design approach against fatigue failure? [GATE ME 2024]
(a) Soderberg line
(b) Modified Goodman line
(c) Gerber line
(d) Yield line
Ans: (a)
Gerber Line. A parabolic curve joining Se on the ordinate to Sut on the abscissa is called the Gerber line.
Soderberg Line A straight line joining Se on the ordinate to Syt on the abscissas called the Soderberg line.
Goodman Line. A straight line joining Se on the ordinate to Sut on the abscissa is called the Goodman line.
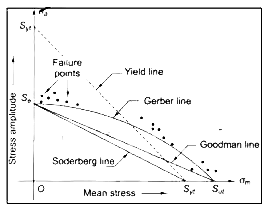 The Gerber parabola fits the failure points of test data in the best possible way. The goodman line fits beneath the scatter of this data. Both Gerber parabola and Goodman line intersect at ( Se ) on the ordinate to ( Sut ) on the abscissa. However, the Goodman line is more safe from design considerations because it is completely inside the Gerber parabola and inside the failure points. The Soderberg line is a more conservative failure criterion and there is no need to consider even yielding in this case.
The Gerber parabola fits the failure points of test data in the best possible way. The goodman line fits beneath the scatter of this data. Both Gerber parabola and Goodman line intersect at ( Se ) on the ordinate to ( Sut ) on the abscissa. However, the Goodman line is more safe from design considerations because it is completely inside the Gerber parabola and inside the failure points. The Soderberg line is a more conservative failure criterion and there is no need to consider even yielding in this case.
Q1: A structural member under loading has a uniform state of plane stress which in usual notations is given by σ x = 3 P, σ y = − 2 P , τ x y = √2 P where P > 0 . The yield strength of the material is 350 MPa. If the member is designed using the maximum distortion energy theory, then the value of P P at which yielding starts (according to the maximum distortion energy theory) is [GATE ME 2022,SET-2]
(a) 70 Mpa
(b) 90 Mpa
(c) 120 Mpa
(d) 75 Mpa
Ans: (a)
σ x = 3
σ y = − 2 P
τ = √2 P
According to maximum distortion energy theory,
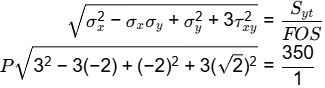
P x 5 = 350
P = 70 Mpa
Q1: The von Mises stress at a point in a body subjected to forces is proportional to the square root of the [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
(a) total strain energy per unit volume
(b) plastic strain energy per unit volume
(c) dilatational strain energy per unit volume
(d) distortional strain energy per unit volume
Ans: (d)
Condition for failure as per M.D.E.T.
Distortion energy per unit volume under tri-axial state of stress > Distortion energy per unit volume under uni-axial state of stress.
Hence, 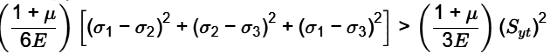
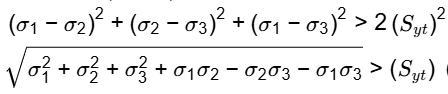 (Von Mises effective stress)
(Von Mises effective stress)
Syt = Von Mises effective stress is defined as the uni-axial yield stress that would create same distortion energy created by the tri-axial state of stress.
Q2: A machine part in the form of cantilever beam is subjected to fluctuating load as shown in the figure. The load varies from 800 N to 1600 N. The modified endurance, yield and ultimate strengths of the material are 200 MPa, 500 MPa and 600 MPa, respectively. [GATE ME 2021, SET-1]
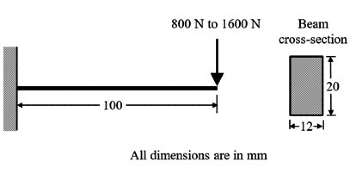
The factor of safety of the beam using modified Goodman criterion is _______ (round off to one decimal place).
Ans: (1.9 to 2.1)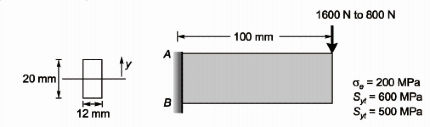 A : Critical Point
A : Critical Point
σmax, A = σb, max at A due to 1600 N = 6M/bd2 = 6 x 1600 x 200/12 x (2σ)2
σ max = 200MPa
σmin, A = σb, max at A due to 800 N
= 6 x 800 x 200/12 x (20)2 = 100MPa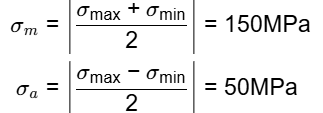
150/600 + 50/200 ≤ 1/N
N ≤ 2
N ≈ 2
Langer Criterion: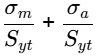 ≤ 1/N
≤ 1/N
150/500 + 50/500 ≤ 1/N (N ≤ 2.5)
N = 2.5
Modified Goodman = Safe result of [Goodman or Langer]
[2015, Set-1]
[2014, Set-2]
From the standpoint of distortion energy (vonMises) criterion, which one of the following statements is true?
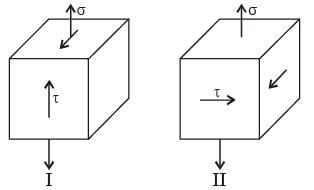
[2014, Set-3]
[1998]
[1997]
[1988]
[2017, Set-1]
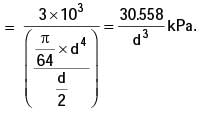
Let d be the diameter of the rivets, and Sf be the maximum permissible tensile stress in the plates. What should be the minimum value for the thickness of the plates to guard against tensile failure of the plates? Assume the plates to be identical.

[2015, Set-3]
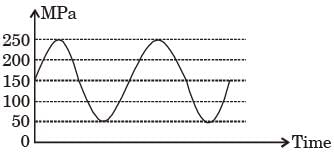
[2013]
[2009]
[2007]
[2007]
[2018, Set-1]
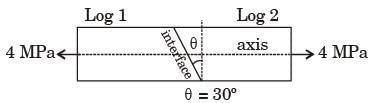
The glue used at the interface fails if
Criterion 1 : the maximum normal stress exceeds 2.5 MPa
Criterion 2 : the maximum shear stress exceeds 1.5 MPa
Assume that the interface fails before the logs fail. When a uniform tensile stress of 4 MPa is applied, the interface
[2018, Set-1]
[2013]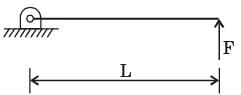
The force F is suddenly removed. At the instant of force removal, the magnitude of vertical reaction developed at the support is
[1996]
[1994]
[1993]
[1992]
The maximum stress in the plate is
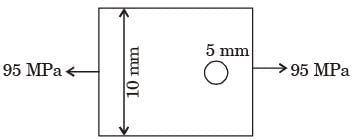
[1991]
|
49 videos|107 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Static, Dynamic Loading & Failure Theories - Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is static loading in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. What is dynamic loading in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 3. What are failure theories in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 4. How does static loading affect the strength of a structure? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of dynamic loading analysis in mechanical engineering? |  |