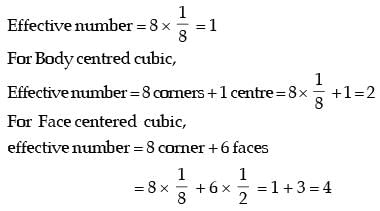GATE Past Year Questions: Structure & Properties of Engineering Materials | Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: The phases present in pearlite are [GATE ME 2024]
(a) austenite and ferrite
(b) cementite and austenite
(c) ferrite and cementite
(d) martensite and ferrite
Ans: (c)
Coarse pearlite →α Ferrite +Fe3C→ Alternating layers of a ferrite and Fe3C that are relatively thick.
Fine pearlite →α Ferrite +Fe3C→ Alternating layers of a ferrite and Fe3C that are relatively thin.
Q1: A steel sample with 1.5 wt. % carbon (no other alloying elements present) is slowly cooled from 1100ºC to just below the eutectoid temperature (723ºC). A part of the iron-cementite phase diagram is shown in the figure. The ratio of the pro-eutectoid cementite content to the total cementite content in the microstructure that develops just below the eutectoid temperature is ________.
(Rounded off to two decimal places) [GATE ME 2023]
Ans: 0.53 to 0.55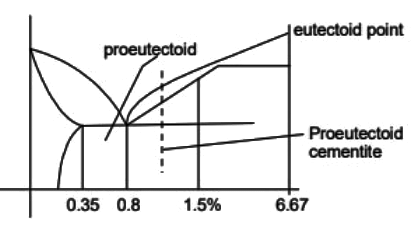 Mass friction of proeutectoid cementite
Mass friction of proeutectoid cementite 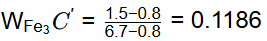
Mass fraction of total cementite
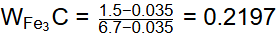
So,
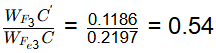
Q2: The atomic radius of a hypothetical face-centered cubic (FCC) metal is (√2/10) nm. The atomic weight of the metal is 24.092 g/mol. Taking Avogadros number to be 6.023 × 1023 atoms/mol, the density of the metal is _______ kg/m3. (Answer in integer) [GATE ME 2023]
Ans: 2490 to 2510
Data given:
r = √2/10 nm
M = 24.092 kg/mol
A = 6.023 x 1013
For FCC structure
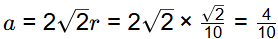
So, volume of unit cell
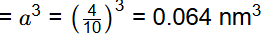
Ne = 4 for FCC
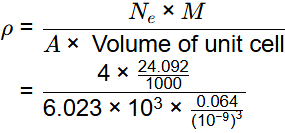
= 2500 kg/m3
Q1: Fluidity of a molten alloy during sand casting depends on its solidification range. The phase diagram of a hypothetical binary alloy of components A and B is shown in the figure with its eutectic composition and temperature. All the lines in this phase diagram, including the solidus and liquidus lines, are straight lines. If this binary alloy with 15 weight % of B is poured into a mould at a pouring temperature of 800ºC, then the solidification range is [GATE ME 2022 SET-2]
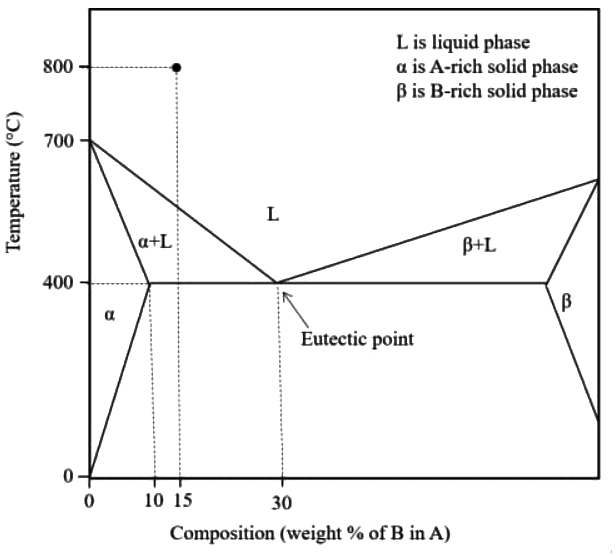
(a) 400ºC
(b) 250ºC
(c) 800ºC
(d) 150ºC
Ans: (d)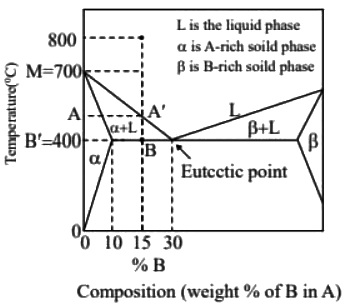 Solidification range = A′B
Solidification range = A′B
△ABC and △MB′C is similar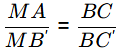
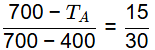
700 - TA = (1/2) x 300
TA = 550ºC
Solidification range = TA − TB = 550 − 400 = 150ºC
Q2: In Fe − Fe3C phase diagram, the eutectoid composition is 0.8 weight % of carbon at 725°C. The maximum solubility of carbon in α-ferrite phase is 0.025 weight % of carbon. A steel sample, having no other alloying element except 0.5 weight % of carbon, is slowly cooled from 1000°C to room temperature. The fraction of pro-eutectoid α-ferrite in the above steel sample at room temperature is [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
(a) 0.387
(b) 0.864
(c) 0.475
(d) 0.775
Ans: (a) Fraction of pro eutectoid α− Ferrite
Fraction of pro eutectoid α− Ferrite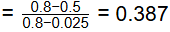
Q3: Which of the following methods can improve the fatigue strength of a circular mild steel (MS) shaft? [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
(a) Enhancing surface finish
(b) Shot peening of the shaft
(c) Increasing relative humidity
(d) Reducing relative humidity
Ans: (a, b, d)
Surface Treatments:
During machining operations,small scratches and grooves are invariably introduced into the workpiece surface by cutting tool action. These surface markings can limit the fatigue life. It has been observed that improving the surface finish by polishing will enhance fatigue life significantly.
One of the most effective methods of increasing fatigue performance is by imposing residual compressive stresses within a thin outer surface layer. Thus, a surface tensile stress of external origin will be partially nullified and reduced in magnitude by the residual compressive stress. The net effect is that the likelihood of crack formation and therefore of fatigue failure is reduced.
Residual compressive stresses are commonly introduced into ductile metals mechanically by localized plastic deformation within the outer surface region. Commercially, this is often accomplished by a process termed shot peening. Small, hard particles (shot) having diameters within the range of 0.1 to 1.0 mm are projected at high velocities onto the surface to be treated. The resulting deformation induces compressive stresses to a depth of between one-quarter and one-half of the shot diameter.
Q4: Which of the following heat treatment processes is/ are used for surface hardening of steels? [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
(a) Carburizing
(b) Cyaniding
(c) Annealing
(d) Carbonitriding
Ans: (a, b, d)
Case-hardening, also referred to as surfacehardening, commonly involves one of four different methods: carburizing, nitriding, cyaniding, or carbonitriding. Case- hardening is used on parts such as gear teeth, cutting wheels, and tools. These case-hardened pieces represent a compromise between the hard, wear-resistant brittleness of high-carbon steel and the softer, more ductile, less wear-resistant low-carbon steels.
Q1: The Cast Iron which possesses all the carbon in the combined form as cementite is known as [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
(a) Grey Cast Iron
(b) Spheroidal Cast Iron
(c) Malleable Cast Iron
(d) White Cast Iron
Ans: (d)
On the basis of nature of carbon present in cast iron, it may be divided into white cast iron and gray cast iron.
In the gray cast iron, carbon is present in free form as graphite. Under very slow rate of cooling during solidification, carbon atoms get sufficient time to separate out in pure form as graphite. In addition, certain elements promote decomposition of cementite. Silicon and nickel are two commonly used graphitizing elements.
In white cast iron, carbon is present in the form of combined form as cementite. In normal conditions, carbon has a tendency to combine with iron to form cementite.
Q1: Which one of the following statements about a phase diagram is INCORRECT? [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]
(a) It indicates the temperature at which different phases start to melt
(b) Relative amount of different phases can be found under given equilibrium conditions
(c) It gives information on transformation rates
(d) Solid solubility limits are depicted by it
Ans: (c)
Phase diagram - Useful information:
Important information, useful in materials development and selection, obtainable from a phase diagram:
It shows phases present at different compositions and temperatures under slow cooling (equilibrium) conditions.
It indicates equilibrium solid solubility of one element/compound in another.
It suggests temperature at which an alloy starts to solidify and the range of solidifcation.
It signals the temperature at which different phases start to melt.
Amount of each phase in a two-phase mixture can be obtained.
Q2: Match The Following [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]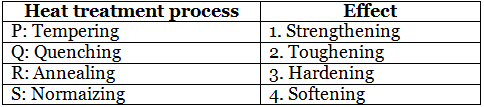 (a) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-1
(a) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-1
(b) P-1, Q-1, R-3, S-2
(c) P-3, Q-3, R-1, S-3
(d) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-1
Ans: (a)
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloys.
Quench hardening is a mechanical process in which steel and cast iron alloys are strengthened and hardened.
Annealing is a process involving heating and cooling, usually applied to produce softening of the metal to facilitate machining or forming operations.
Normalising is used to improve the mechanical properties of, mainly, unalloyed and low-alloy structural steel and cast steel.
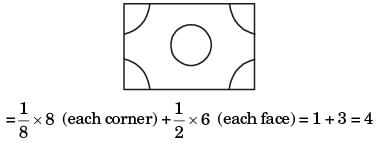
Q2: The crystal structure of γ iron (austenite phase) is [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
(a) BCC
(b) FCC
(c) HCP
(d) BCT
Ans: (b)
Austenite has a cubic-close packed crystal structure, also referred to as a face-centred cubic structure with an atom at each corner and in the centre of each face of the unit cell.
[ME 2018, Set-1]
[ME 2017, Set-2]
[ME 2010]
[ME 2009]
[ME 2009]
[PI 1992]
|
15 videos|35 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Structure & Properties of Engineering Materials - Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are the key properties of engineering materials that are important for mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How does the microstructure of materials affect their properties? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of phase diagrams in material selection? |  |
| 4. How can mechanical properties of materials be tested in the laboratory? |  |
| 5. What role does temperature play in the properties of engineering materials? |  |