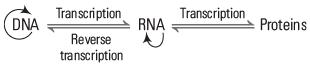Genetics | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Inheritance of One Gene |

|
| Inheritance of Two Genes |

|
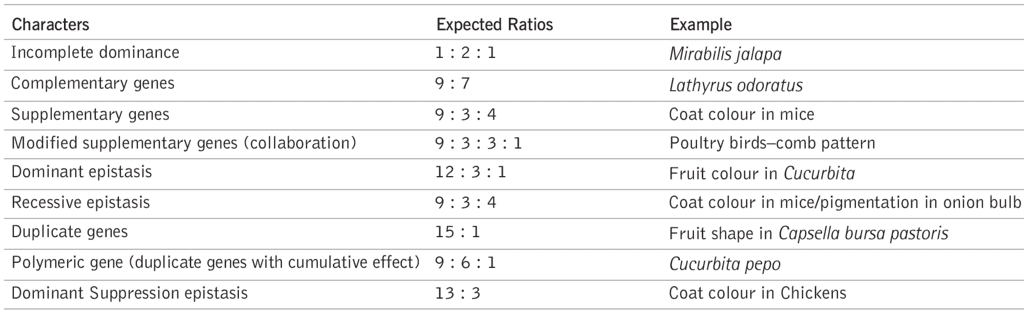
| Exceptions to Mendelism |

|
| Genetic Disorders |

|
| Genetic Code |

|
Introduction
- Genetics is the study of how parents pass their traits to their offspring, a process known as the inheritance of traits.
- The traits that are passed down are called inherited traits.
- The study of these inherited traits and their variations is called genetics.
- Gregor Mendel, known as the Father of Genetics, conducted experiments on pea plants due to their self-pollinating nature and short life cycle.
- He introduced the term "factor" to describe what we now call genes, the functional units of DNA.
- Genes exist in pairs of similar forms called alleles.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884)
Mendel, a scientist and monastery worker, is famous for his groundbreaking work on pea plants, which led to the formulation of fundamental laws of genetics, now known as Mendel’s laws of inheritance. Although his work was not initially recognized, it later became the cornerstone of modern genetics.
Inheritance of One Gene
- Mendel discovered that some alleles are dominant over others.
- These dominant alleles are represented by capital letters, while recessive alleles are represented by lowercase letters.
- When only one trait is observed, this is known as the inheritance of one gene, and the cross is called a monohybrid cross.
- The inheritance of one gene can be explained through monohybrid cross, which is represented in the following diagram.
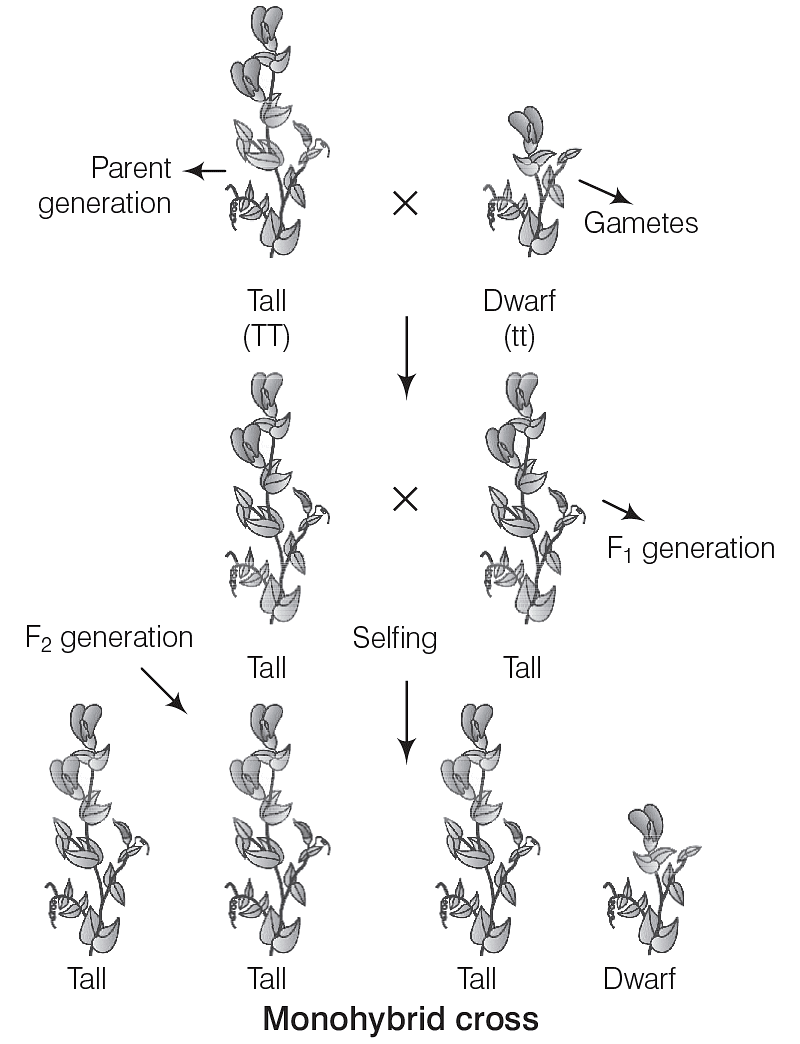
Mendel’s Law of Dominance
One allele can be dominant over another, and this dominant allele will be expressed in the offspring.
- Phenotypic ratio: 3:1
- Genotypic ratio: 1:2:1
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
During gamete formation, alleles separate so that each gamete carries only one allele for each trait.
- P Generation: The parental generation includes tall plants (TT) and dwarf plants (tt).
- F1 Generation: The first filial generation consists entirely of tall plants (Tt).
- F2 Generation: The second generation shows a ratio of three tall plants to one dwarf plant, illustrating the dominance of the tall trait and the segregation of alleles.
Inheritance of Two Genes
When observing two traits simultaneously, this is called the inheritance of two genes, and the cross is a dihybrid cross. Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment explains this type of inheritance.
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
Allele pairs separate independently during gamete formation, meaning the inheritance of one trait does not affect the inheritance of another. Mendel deduced this principle from dihybrid crosses, such as those involving seed color and pod color, which produced an F2 generation ratio of 9:3:3:1.
- P Generation: Seeds with round (dominant) and wrinkled shapes, and yellow (dominant) and green colors.
- F1 Generation: Both dominant traits are represented.
- F2 Generation: Shows a 9:3:3:1 ratio, with nine round yellow, three round green, three wrinkled yellow, and one wrinkled green. This demonstrates that the inheritance of seed shape is independent of seed color.
Mendel’s observations and laws illustrate that the inheritance of one character does not influence the inheritance of another, confirming the independent assortment of traits.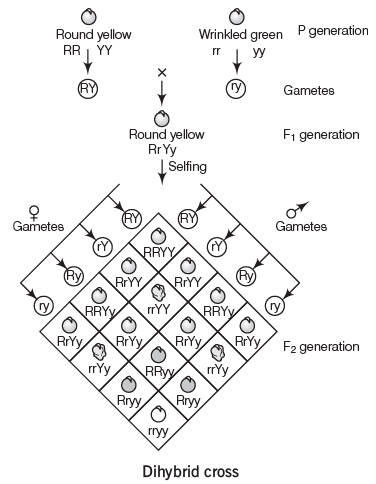
Exceptions to Mendelism
Following table will give the idea of different crosses and their expected ratios
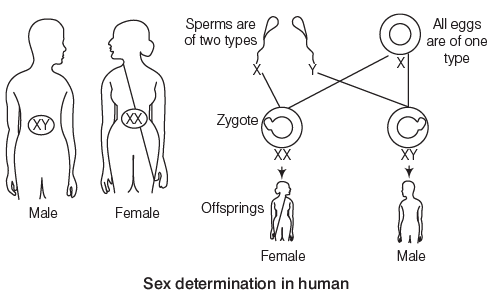
Sex Determination in Humans
- Humans have 46 chromosomes, of which 44 form 22 pairs known as autosomes.
- The remaining two are sex chromosomes.
- In females, these are identical and are called X chromosomes (XX).
- In males, they differ and are known as the X and Y chromosomes.
- During reproduction, females produce gametes with 22 autosomes and one X chromosome.
- While males produce two types of gametes: one with 22 autosomes and an X chromosome (22 X),
- And another with 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome (22 Y).
Gene and Gene Concept
A gene is a small segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a polypeptide. This concept, known as the one gene-one polypeptide theory, was proposed by Lederberg and Tatum. During inheritance, genes tend to stay together, a phenomenon known as linkage. The formation of new combinations of genes different from those of the parents is called recombination.
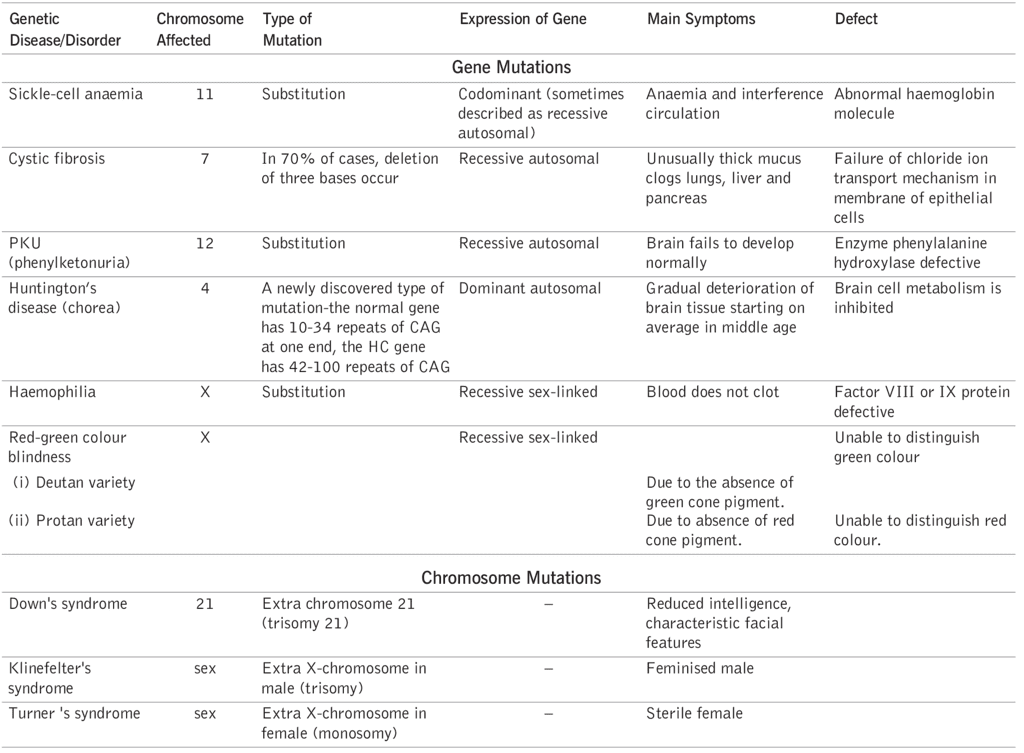
Genetic Disorders
At the time of inheritance, due to various complexities, some genetic disorders can occur in progeny organisms lead to various diseases. A list of these disorders, with their details in given below:
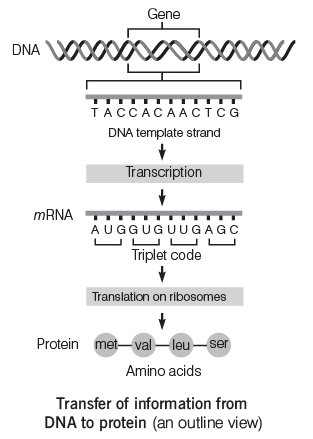
Genetic Code
Genetic codes are sequences of three nitrogenous bases, such as AUG, GUG, and UUG, which correspond to specific amino acids and play a crucial role in protein synthesis (translation). The central dogma explains the utility of the genetic code.
D Baltimore (1970) also described the presence of reverse transcriptase enzyme in RNA tumour viruses. Its presence changed the central dogma of protein synthesis into central dogma reverse, which looks like
According to data from the Human Genome Project (HGP), the human genome comprises approximately 40,000 genes, each responsible for various functions in the human body.
|
474 videos|1733 docs|394 tests
|
FAQs on Genetics - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the inheritance pattern of genetic disorders? |  |
| 2. How many genes are typically involved in determining a specific trait? |  |
| 3. Can exceptions to Mendel's laws occur in genetic inheritance? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the genetic code in understanding inheritance patterns? |  |
| 5. How do genetic disorders impact human health and well-being? |  |