HPSC (Haryana) Exam > HPSC (Haryana) Notes > HPSC Preparation: All subjects > Geographical location of Haryana
Geographical location of Haryana | HPSC Preparation: All subjects - HPSC (Haryana) PDF Download
An Overview of Haryana: India's Prosperous North Indian State
- Haryana, a state situated in the northwest of India, was formed on 1st November 1966 by separating from the Indian State of Punjab. The state's capital is Chandigarh, which is administered as a Union Territory.
- Despite having just 1.37% of the total geographical area and less than 2% of India's population, Haryana occupies a strategic location between 27º 39′ and 30º 35’N latitude and between 74º27′ and 77º36′ E longitude. Furthermore, almost one-third of the state's total area falls in the National Capital Region.
- Haryana's economy is predominantly agrarian, with 85% of its land under cultivation. Agriculture engages about 78% of the population, making it a significant contributor to the state's economic growth.
- Haryana has made significant progress in various sectors such as agriculture, industry, canal irrigation, and rural electrification over the past three decades. This progress has allowed the state to carve out a place of distinction for itself in India.
- Haryana is known for its prosperity, with one of the highest per capita incomes in the country. The state's success can be attributed to its progressive policies and efficient governance, making it an attractive destination for business and investment.
Geography of Haryana
Here are four points that provide an overview of the primary geographical features of Haryana:
- Haryana is characterized by the presence of the Shivalik Hills in the northeast.
- The Ghaggar Yamuna Plain is the largest geographical feature of the state.
- The southwest of Haryana is home to a semi-desert sandy plain.
- The southern part of Haryana is marked by the presence of the Aravalli hills.
Shivalik Hills
- The Shivalik Hills in Haryana serve as the origin of several rivers, including Saraswati, Ghaggar, Tangri, and Markanda.
- The districts of Panchkula, Ambala, and Yamunanagar in Haryana are located in proximity to these hills.
Aravali Hills
- The Aravalli Hills are a range of mountains that extend from Gujarat in western India to Delhi in the north.
- In Haryana, these hills are situated in the southern part of the state. The Aravalli range is one of the oldest mountain ranges in the world, with some estimates suggesting that it is around 350 million years old.
- In Haryana, the Aravalli hills are a significant geographical feature and serve as a major source of minerals such as quartz and feldspar. These hills also play a crucial role in regulating the local climate and preserving the biodiversity of the region.
- The Aravalli hills in Haryana are home to several wildlife species, including leopards, hyenas, and Indian hares. Additionally, the hills also have archaeological and historical significance, with several ancient temples and monuments located in the region.
Semi-Desert Sandy Plain
- The semi-desert sandy plain is a geographical feature located in the southwest region of Haryana. It is an area characterized by sandy soil and sparse vegetation. This region receives limited rainfall, and the arid climate makes it challenging to sustain agriculture.
- However, farmers in this region have adapted to these conditions and practice agriculture through the use of innovative techniques such as drip irrigation and water harvesting.
- The semi-desert sandy plain in Haryana is home to several wildlife species such as blackbuck, chinkara, and desert fox.
- Additionally, the region is also known for its unique flora, including the khejri tree, which is considered sacred by the local community and is a vital source of food and fuel for the residents of this region.
Ghaggar Yamuna Plain
- The Ghaggar Yamuna Plain is the largest geographical feature of Haryana, covering a significant portion of the state. This plain is formed by the Ghaggar and Yamuna rivers and their tributaries, which flow through the region.
- The Ghaggar Yamuna Plain is an important agricultural area and is home to several crops such as wheat, rice, and sugarcane. The region also has significant mineral deposits, including limestone, dolomite, and quartzite.
- Additionally, the Ghaggar Yamuna Plain has historical significance, with several ancient civilizations, including the Indus Valley civilization, having flourished in this region. Today, the plain is dotted with several historical sites and monuments, attracting tourists from across the world.
- The Ghaggar Yamuna Plain is also home to several wildlife species such as blackbuck, blue bull, and Indian fox.
Physiographic Profile of Haryana
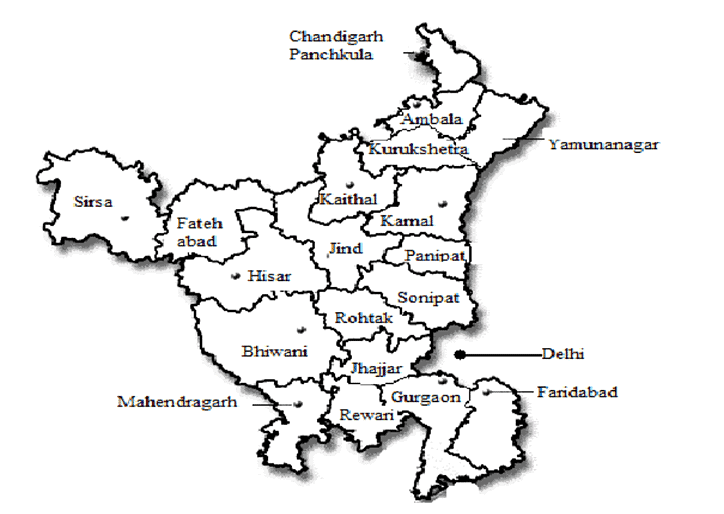
- The physiography of the Haryana sub-region is primarily composed of flat plains formed by the Yamuna River's alluvial deposits, with some areas of Aravali foothills.
- With the exception of the Aravali-dominated areas, most districts in the sub-region have comparable characteristics.
Panipat District
- The alluvial plain of the Yamuna River encompasses Panipat district.
- The area slopes from west to east, and its water flows towards the Yamuna.
- The flood plains, which are one of two major physiographic units in the area, are ideal for growing rice and sugarcane.
- The other unit, the older alluvial plain located in the western part of the district, slopes towards the south and southwest and is irrigated by tube wells and canals, making it a prosperous agricultural area.
Sonipat District
- Sonipat district is located in the Indian state of Haryana, and it is situated in the eastern part of the state. The district shares its boundaries with other districts like Panipat, Rohtak, Jind, and Delhi. Sonipat is an important agricultural district with a variety of crops being grown, including wheat, sugarcane, and vegetables.
- The district has a diverse landscape, with the Khadar region being the fertile floodplain of the Yamuna river, the upland plain region comprising of elevated terrain, and the sandy region being characterized by sandy soils. Apart from agriculture, Sonipat is also home to several industries, with the district housing a number of large manufacturing plants.
- The district is also known for its educational institutions, with a number of prestigious universities and colleges being located in and around the region. Overall, Sonipat district is an important economic and cultural center in the state of Haryana.
Rohtak District
- The Rohtak district is primarily composed of the extensive Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains referred to as the older alluvial plain.
- This older alluvial plain is subdivided into sand, which originated from the old alluvial plains that is predominantly composed of a diverse composition derived from the Himalayan rivers.
Jhajjar District
- Jhajjar district is made up of extensive Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains.
- The primary physiographic components include:
(a) The upland plains, which are located in the northeastern part of the district and are covered with old alluvial soil that has high productivity characteristics.
(b) The alluvial plains, which have productive soils and good irrigation facilities, including canals and tube-wells.
Rewari District
- Rewari district can be categorized into four landscapes that include:
(a) Rocky and stony barren land
(b) Sandy plains with sand dunes
(c) Older flood plains
(d) Undulating uplands with or without scrub and occasional hillocks. - The Aravali hills in the district are presently undergoing weathering and denudation.
Gurgaon District
- The topography of Gurgaon district is varied, with both hills and depressions, creating an irregular and diverse landscape.
- There are two ridges in the district - the Firozepur-Jhirka Delhi ridge forms the district's western boundary, while the Delhi ridge forms the eastern boundary.
Mewat District
- The topography of Mewat district is unique, with mostly flat alluvial plains covering the region.
- The area is also characterized by long, narrow pediments and slight elevations caused by sand deposits blown by the wind in the foothill areas and on the plains.
Faridabad and Palwal Districts
- Faridabad and Palwal districts exhibit mountainous topography with deposits of alluvium.
- The alluvial plains in the region have been segregated into two categories.
- The first one is the Khadar which is the flood plain of newer alluvium and is located at a lower altitude. The second one is called Banger, which is an upland plain composed of older alluvial deposits and is spread towards the west.
- Additionally, the region is home to several artificial lakes, such as Surajkund, Badhkal, Peacock, and Dhauj Lake.
The document Geographical location of Haryana | HPSC Preparation: All subjects - HPSC (Haryana) is a part of the HPSC (Haryana) Course HPSC Preparation: All subjects.
All you need of HPSC (Haryana) at this link: HPSC (Haryana)
|
91 videos|318 docs|111 tests
|
Related Searches
















