Geography of Asia | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
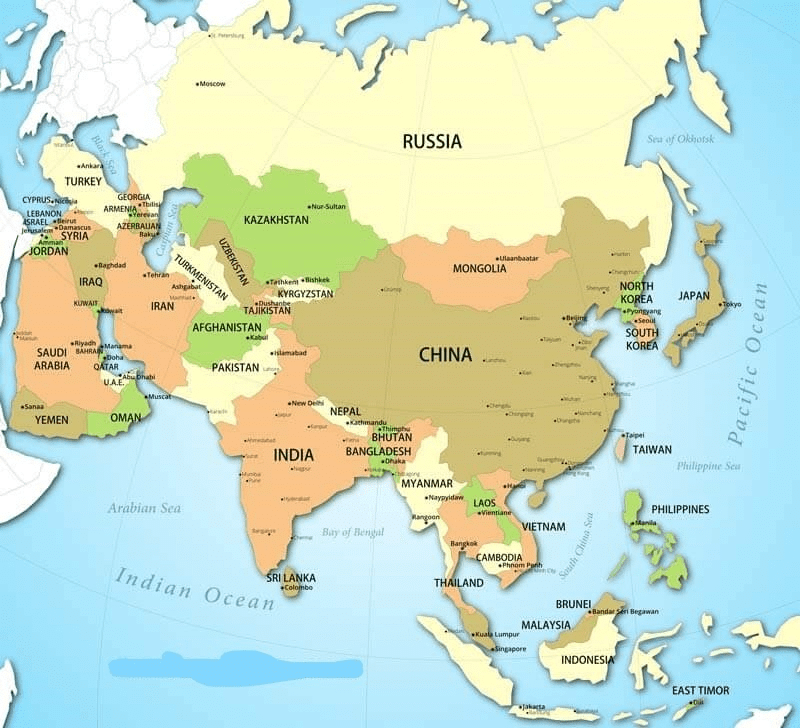
Area: 43,608,000 million sq. km (30% of the total laud surface of the earth.)
Latitudes: 10°11’S to 81°12'N
Longitude: 26°2' E to 169°40' W in the east crossing 180' longitude.
North-South Extent: 6,440 km
East-West Extent: 9,650 km
Only some of the Indonesian group of islands is located to the south of the equator in the southern hemisphere.
The largest continent in the world.
13 times larger than India
Most Northernmost point: Mys Dezhneva Russia
Most Southernmost point: Pulau Pamana
Most Easternmost point: Mys Dezhneva Russia
Most Westernmost point: Bozca Adasi Turkey.
Highest point: Mt Everest Nepal
Lowest point: Dead sea Israel/Jordan
Highest temperature: Tirat Tsvi Israel
Lowest temperature: Verhoyansk Russia
Regional Divisions of Asia
Asia can be divided into six physiographic divisions: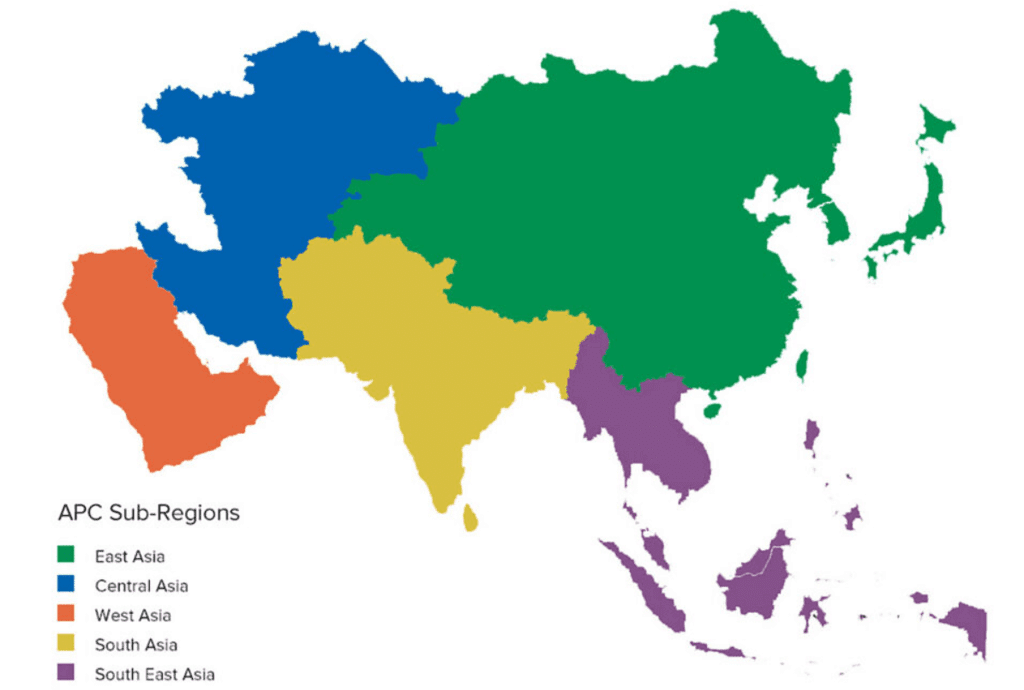
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
- Eastern Asia: China, Hong Kong, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Macau, Mongolia, Taiwan
- Northern Asia: Russia
- South-eastern Asia: Brunei, Myanmar, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Vietnam.
- Southern Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka.
- Western Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cyprus, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, State of Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Yemen.
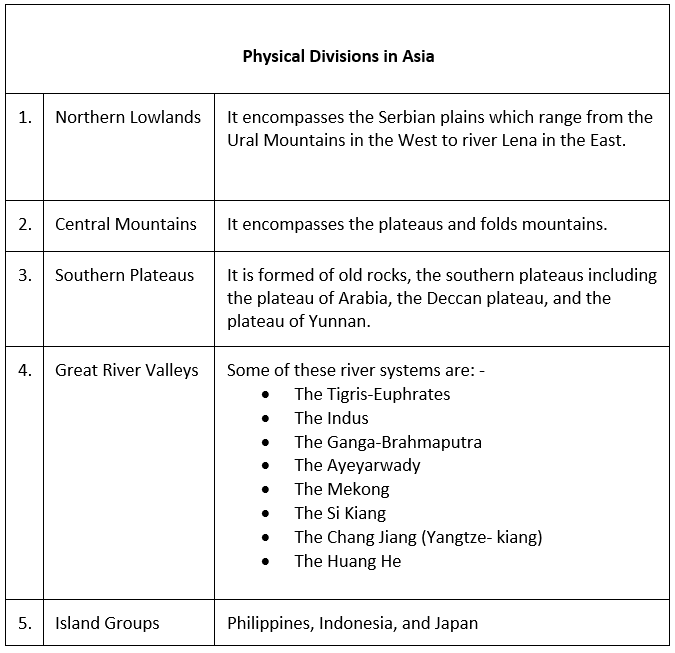
Major Physical Divisions of Asia
The Northern Lowlands
The Central Mountains
The Central and Southern Plateaus
The Peninsulas
Deserts
The Great River Plains
Island Groups
The Northern Lowlands
The Northern Lowlands are the extensive plain areas that comprise of several patches of lowlands of this large continent.
The major lowlands are:
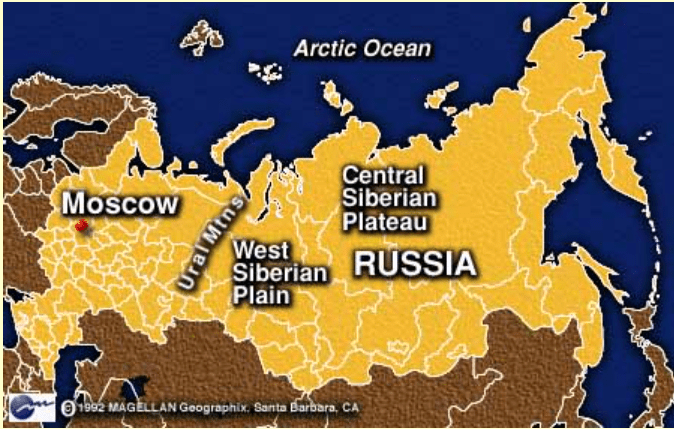
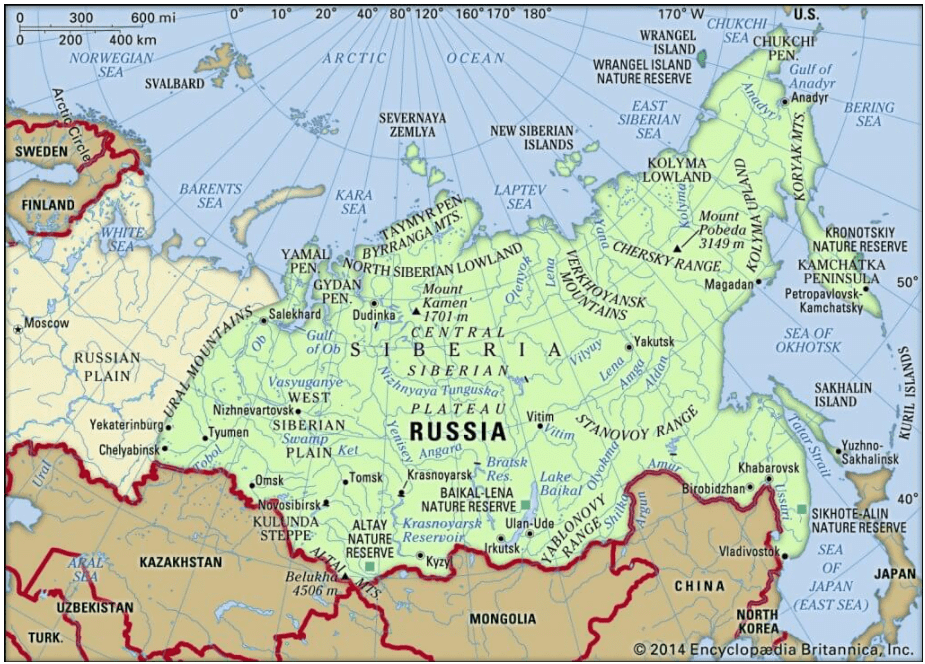
Great Siberian plain
It extends between the Ural Mountains in the west and the river Lena in the east. It is the largest lowland in the world covering an area of 1,200,000 square miles approx.
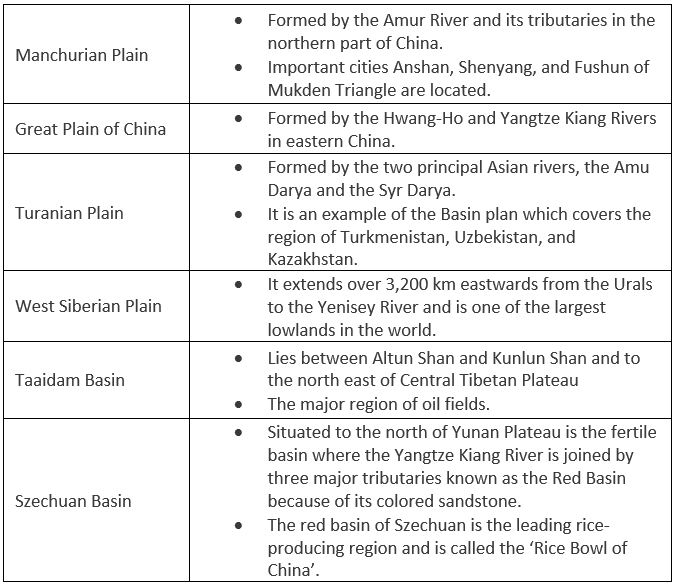
 Manchurian Plain
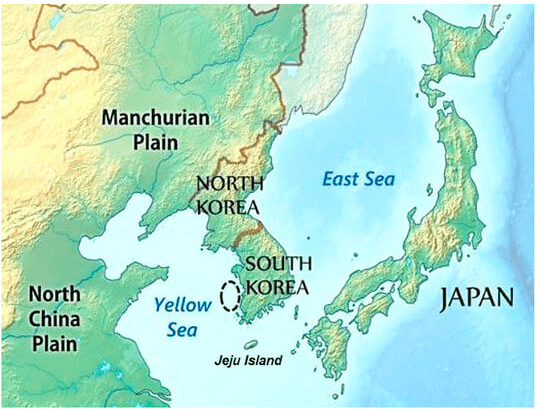
Manchurian Plain
It is the area adjoining the Amur river and its tributaries of the northern part of China with an area of 135,000 square miles approx.
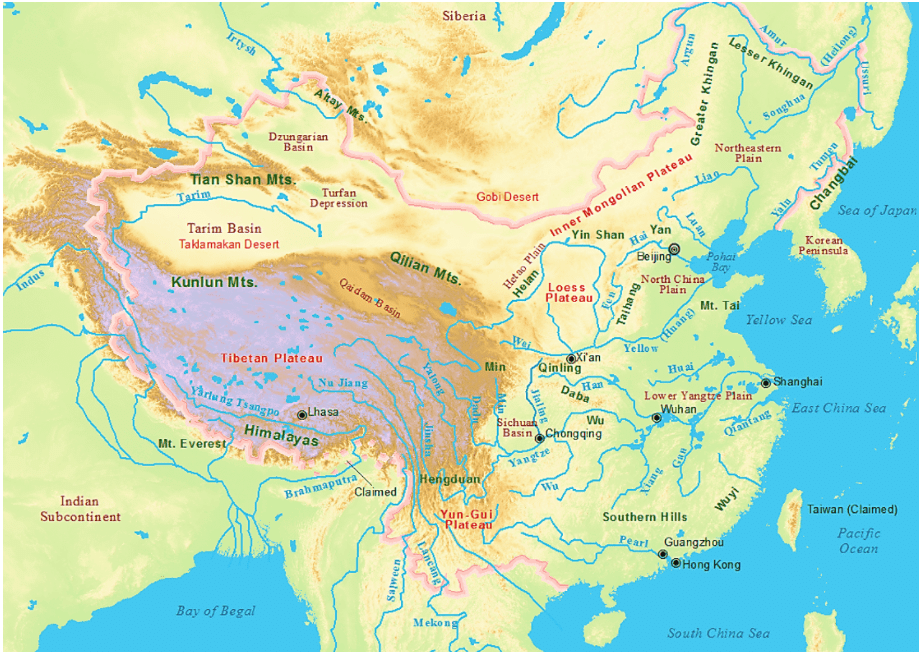
Great Plains of China
It is contributed by two major rivers of China, Hwang Ho, and Yangtze river, which covers an area of 158,000 square miles approx.
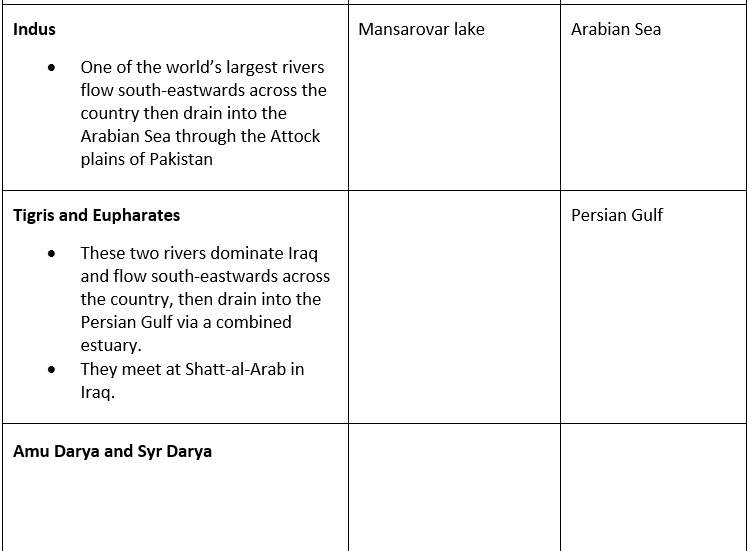
Tigris-Euphrates plains
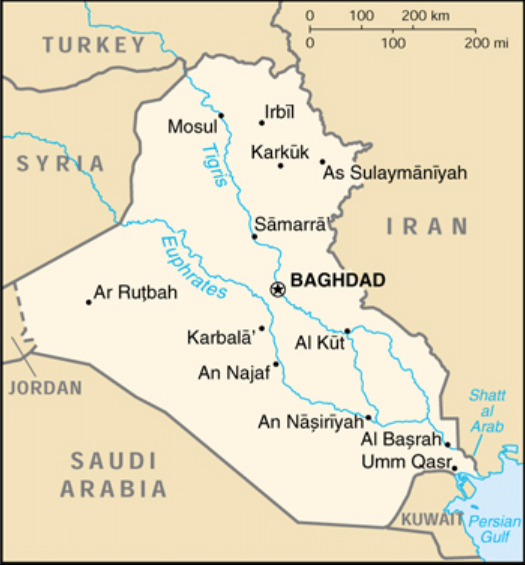
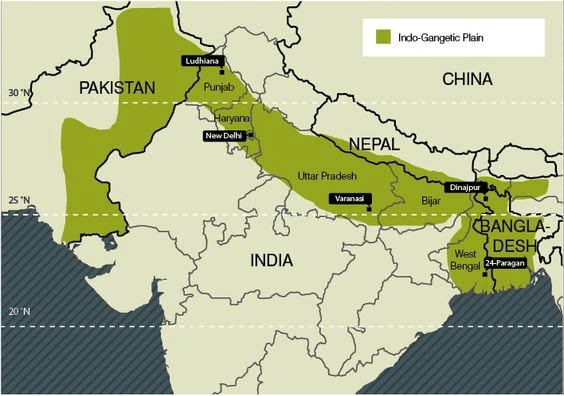
Ganga plains
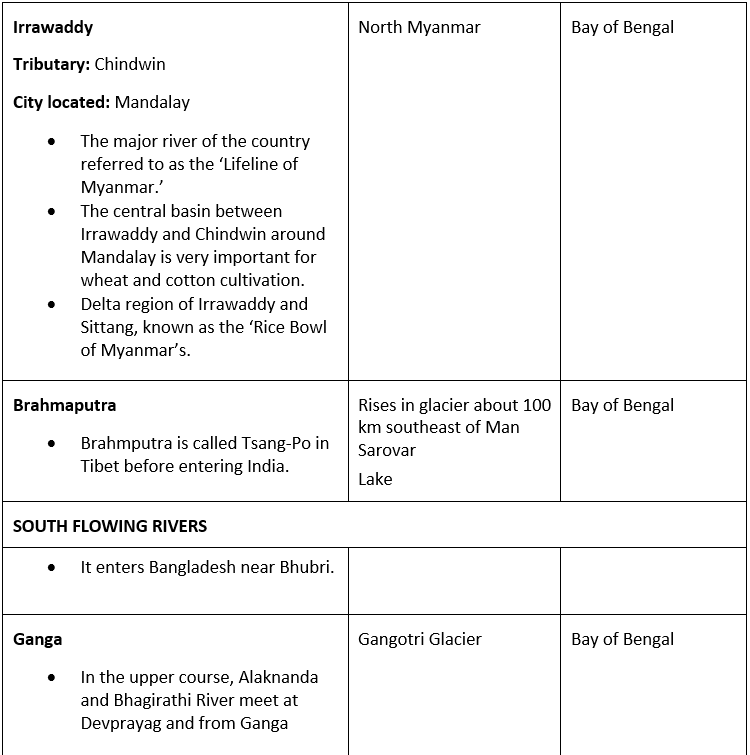
The river Ganga is the most important river which flows through India and Bangladesh.
The river Ganga rises in the Indian state of Uttarkhand and flows south and east through Gangetic plains, and finally discharges itself into the Bay of Bengal.
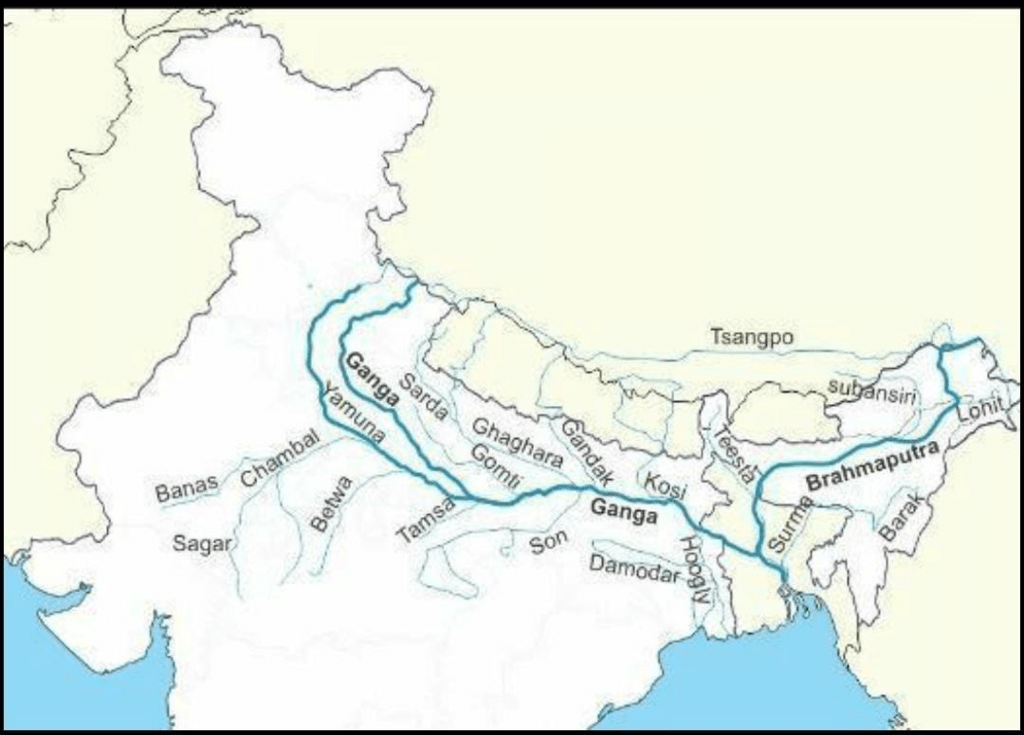
It is the largest river in India, and it is the most sacred river to Hindus.
The most important tributaries of Ganga are the Yamuna, Chambal, the Gomati, the Ghaghara, the Ramganga, the Mahanadi, the Kosi, the Gandak.
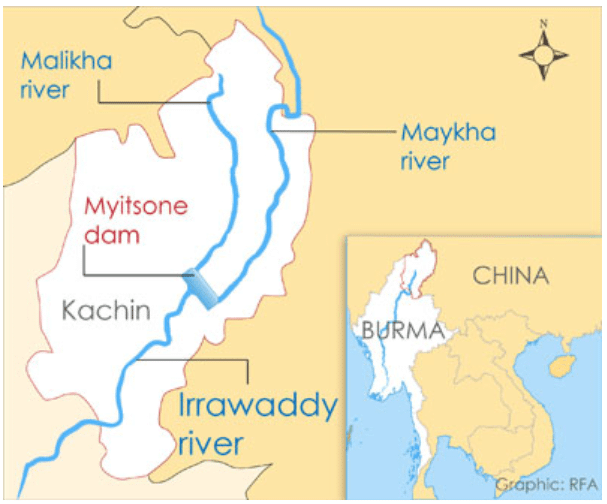
Irrawaddy plains
At 2,170 kilometers (1,340 miles), the Irrawaddy river is the largest in Myanmar (Burma).
Most of the 47 million in the country live on or near the Irrawaddy.
Its tributaries flow from the eastern margins of the Tibetan plateau and, although not directly fed by glaciers, originates high in the same mountains as the other rivers we have described here.
Important Land Regions
The Central Mountains
These are the prominent and extensive mountain ranges that cover the parts of Central Asia.
They consist of Pamir and Tian Shan ranges and extending across portions of Afghanistan, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
These mountain ranges are designated as biodiversity hot spots by Conservation International, which covers several montanes and alpine ecoregions of Central Asia.
It encompasses several habitat types, including montane grasslands and shrublands, temperate coniferous forests, and alpine tundra.
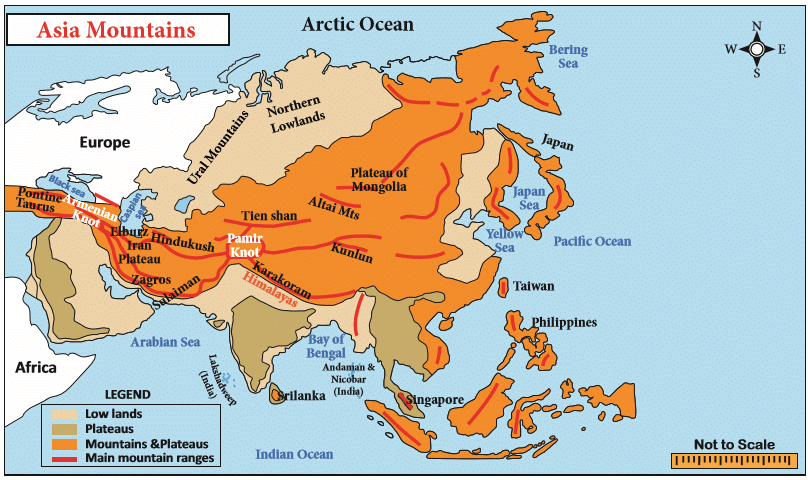
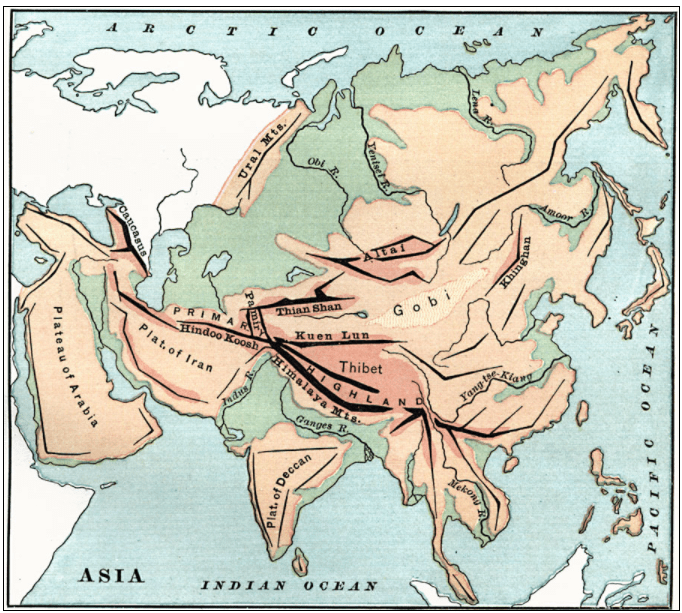
A mountain knot is a junction of two or more mountain ranges.
The two main mountain knots in Asia are:
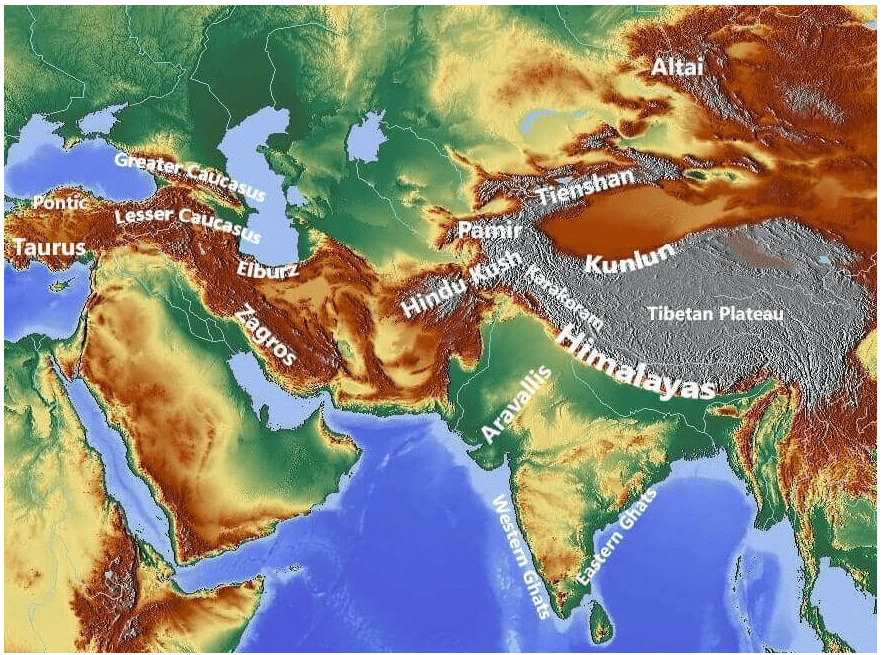
The Pamir Knot is the junction of five mountain ranges they are the Sulaiman, the Hindu Kush, the Kunlun, the Karakoram, and the Himalayan ranges. Mount Everest, the highest peak in the world in the Himalayan range.
The Armenian Knot is connected to the Pamir Knot by the Elburz and the Zagros Ranges that originate in the Armenian Knot. The Tien Shan and the Altai are other mountain ranges in Asia.
Peaks of Asia
Mount Everest (8848 m), Nepal-Tibet, China border
K2 (8,61,1 m), Pakistan-China
Kangchenjunga (8,586 m), Nepal-Sikkim (India).
Lhotse (8,516 m), Nepal-Tibet, China
Makalu (8,462 m), Nepal-Tibet, China
Cho Oyu (8,201 m), Nepal
Important Mountains

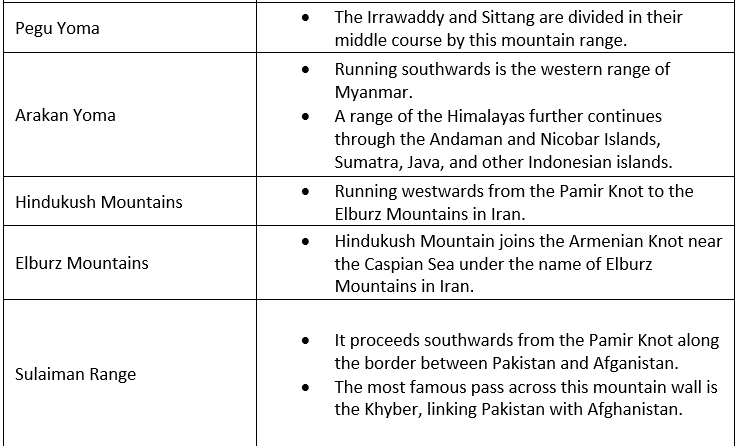
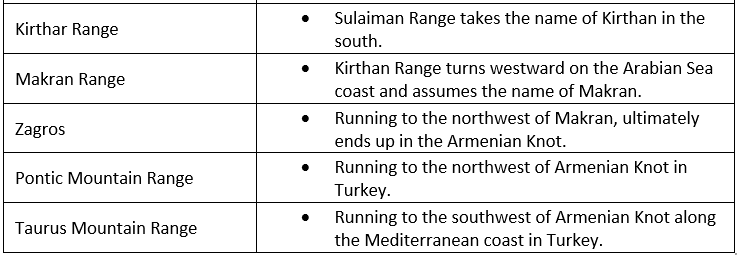
The Central and Southern Plateaus
Plateaus are the land areas having a relatively surface considerably raised above adjoining land on at least one side and often cut by a deep canyon.
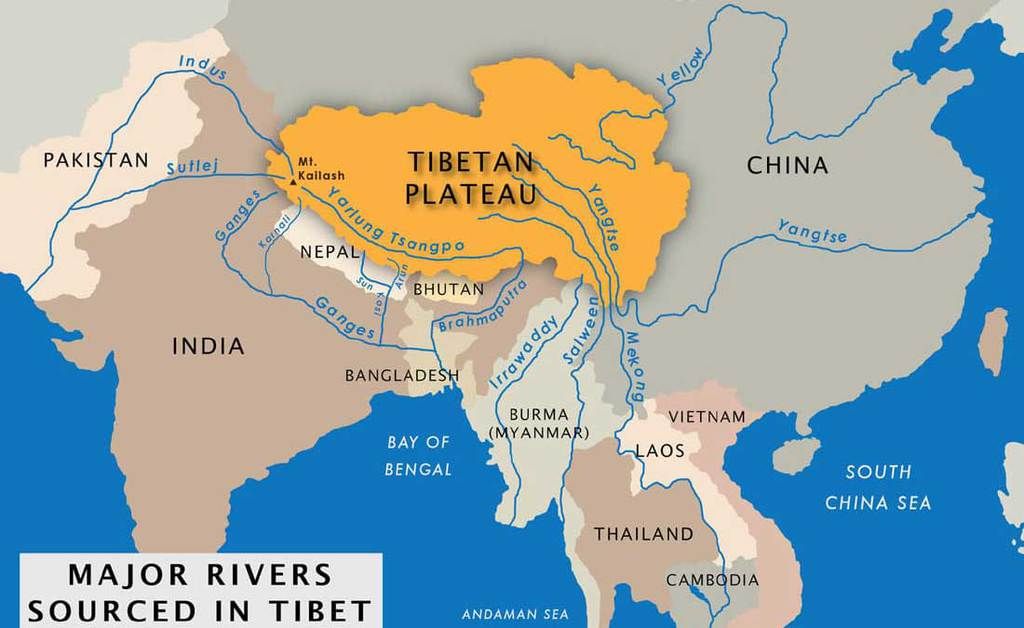
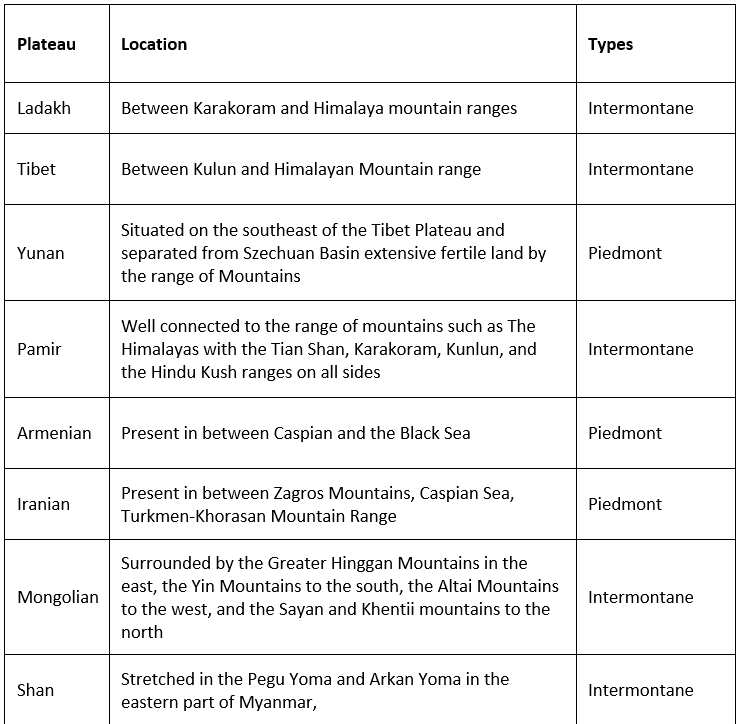
Tibetan Plateau
- The highest and largest plateau in the world and hence called the ‘roof of the world’.
- Formed due to collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- The plateau is sufficiently high enough to reverse the Hadley cell convection cycles and to drive the monsoons of India towards the south.
- It covers most of the Autonomous Tibetan Region, Qinghai Province of Western China, and a part of Ladakh in Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is surrounded by mountains to the south by the Himalayan Range, to the northeast by the Kunlun Range, and to the west by the Karakoram Range.
Columbia- Snake Plateau
- River Columbia and its tributary Snake meet in this plateau.
- It is bordered by the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains and divided by the Columbia River.
- This plateau has been formed as the result of volcanic eruptions with a consequent coating of basalt lava (Flood Basalt Plateau).
Colorado Plateau
- It is lying to the western part of U.S.A. It is the largest plateau in America.
- It is divided by the Colorado River and the Grand Canyon.
- This plateau is an example of the intermontane plateau. Mesas and buttes are found here at many places [Arid Landforms].
- The plateau is known for the groundwater which is under positive pressure and causes the emergence of springs called Artesian wells.
Deccan Plateau
- Deccan Plateau is a large plateau that forms most of the southern part of India.
- It is bordered by two mountain ranges, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats.
- The plateau includes the Deccan Traps which is the largest volcanic feature on Earth.
- Made of multiple basalt layers or lava flows, the Deccan Traps covers 500,000 square kilometers in area.
- The Deccan Traps are known for containing some unique fossils.
- The Deccan is rich in minerals. Primary mineral ores found in this region are mica and iron ore in the Chotanagpur region, and diamonds, gold, and other metals in the Golconda region.
Kimberley Plateau
- Lies in the northern part of Australia.
- This plateau is made of volcanic eruptions.
- Many minerals like iron, gold, lead, zinc, silver, and diamond are found here.
- Diamond is also found here.
Katanga Plateau
- It is lying in Congo.
- It is famous for copper production.
- Other minerals like Cobalt, Uranium, Zinc, Silver, Gold, and Tin are also mined here.
Mascarene Plateau
- Plateaus also form in the ocean, such as the Mascarene Plateau in the Indian Ocean.
- It extends between the Seychelles and Mauritius Islands.
Laurentian Plateau
- Lying in the eastern part of Canada, it is a part of the Canadian Shield.
- The fine quality of iron ore is found here.
Mexican Plateau
- It is called as ‘Mineral Store’. Different types of metallic minerals like silver, copper, etc. are obtained from here.
- World’s biggest silver mine Chihuahua is situated on the plateau.
Patagonian Plateau
- It is a Piedmont plateau (Arid Landforms) lying in the southern part of Argentina.
- It is a rain shadow desert plateau.
- It is an important region for sheep rearing.
Bolivian Plateau
- It is an intermontane plateau which is located between two ranges of Andes Mountain.
- It is a major area of Tin reserves.
Anatolian Plateau
- Also known as Asia Minor, most of Turkey lies on this plateau.
- It is an intermontane plateau lying between Pontiac and Taurus Mountain ranges.
- Tigris – Euphrates Rivers flow through this plateau.
- Precious wool-producing Angora goats are found here.
Others
- Spanish Plateau or Iberian Plateau: It is situated in the middle of Spain. It is a lava plateau. It is rich in minerals like Iron.
- Loess Plateau: It is in China. The soil here is made of fine particles brought by the wind. This fine loamy soil is extremely productive. Crops grown in this soil along the Yellow River give great yields.
Arid Landforms – Erosional, Depositional – Wind, Water Eroded
- Potwar Plateau: It is situated in northern plateau (Punjab) region of Pakistan. Its average ‘Salt Range’ is located to the south-west of the plateau.
- Bavarian Plateau: Southern part of Germany.
- Ahaggar Plateau: A small plateau located in Algeria, Sahara.
Major Plateaus of Asian Continent

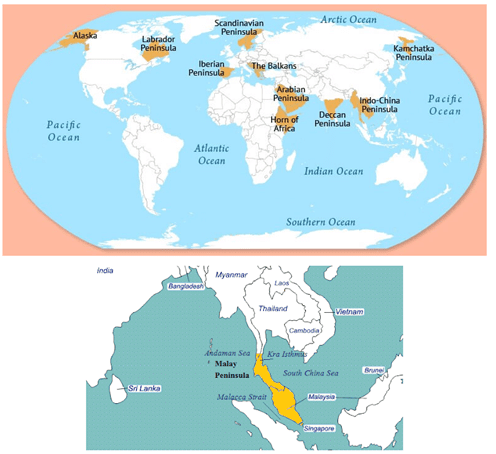
Peninsulas
- A peninsula is a mass of land surrounded by water but attached to the mainland. The Deccan plateau region is also a peninsula.
- The major peninsulas of Arabia, India, and Malay are in southern Asia. The Kamchatka peninsula lies in northeastern Asia.
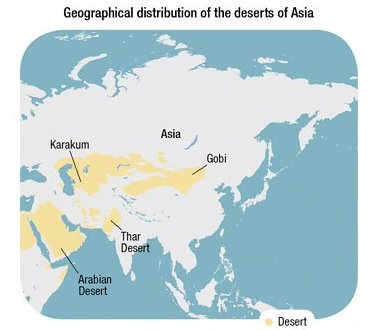
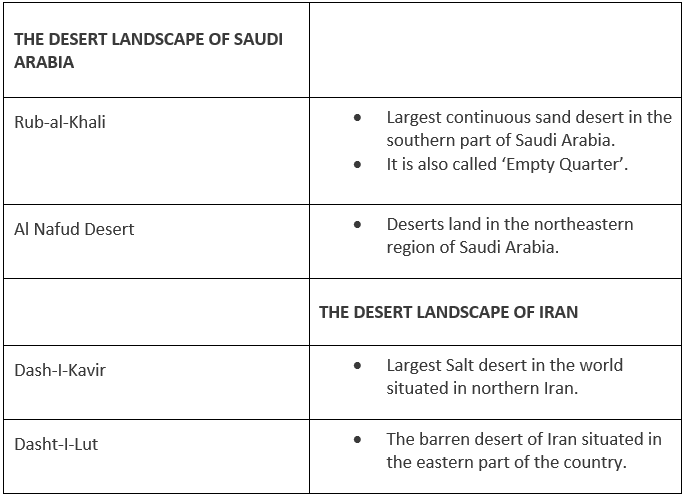
Deserts
- Asia has some big deserts such as the Gobi, the Takla Makan, the Thar, the Kara-Kum, and the Rub-al-Khali Deserts.
- The Rub’ al Khali desert, considered the world’s largest sand sea, covers an area larger than France across Saudi Arabia, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.
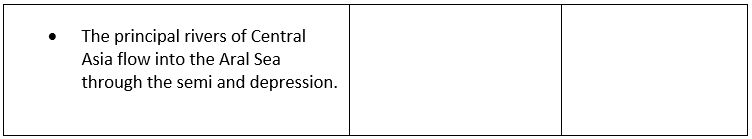
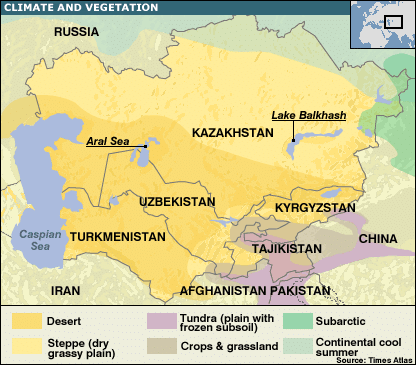 Deserts of Central Asia
Deserts of Central Asia
Islands of Asia
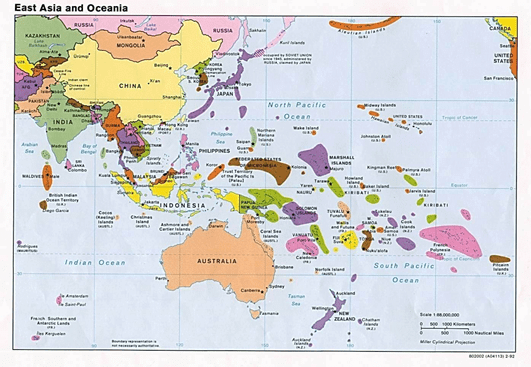
- Asia also has a cluster of islands, also called an archipelago.
- An archipelago sometimes called an island group or island chain is formed close to each other in large clusters.
- Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, Andaman, and Nicobar are some examples of archipelagos.
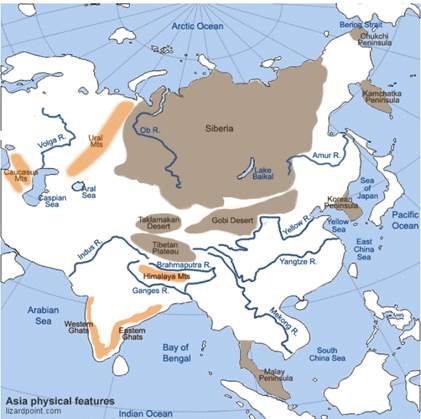
Drainage of Asia
- The drainage of Asia consists of mighty oceans, extensive seas, lengthy rivers, and their tributaries and distributaries, major lakes, etc.
- Oceans: Asian continent is surrounded by three major ocean from three sides such as
- The Pacific Ocean: It covers the eastern part of Asia where major rivers of eastern Asia drain, such as Menam Mekong, Xi Jiang, Chang Xiang, Huang Ho, and Amur.
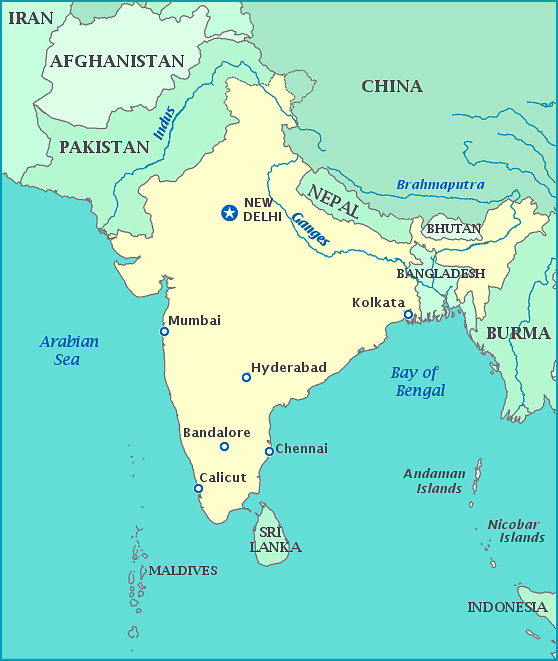
- The Indian Ocean: It covers the southern part of Asia and the major rivers that flow into the Indian Ocean are Tigris, Euphrates, the Indus, the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Irrawaddy, Salween.
- The Arctic Ocean: It covers the North east part of Asia and consists of three major rivers such as Ob, Yenisei, and Lena.
Drainage Patterns
The patterns formed by the streams, rivers and lakes in a particular drainage basin which are governed by the topography of the land constitute the drainage patterns of an area.
There are 7 types of drainage patterns:
- Dendritic drainage pattern: looks like the branching of a tree, found in regions with homogenous material.
- Parallel drainage pattern: forms where there is a slope.
- Trellis Drainage Pattern: patterns look similar to the common garden trellis.
- Rectangular Drainage Pattern: found in regions that have undergone faulting.
- Radial Drainage Pattern develops: around a central elevated point.
- Centripetal Drainage Pattern: flows towards a central depression.
- Deranged Drainage Pattern: develop from the disruption of a pre-existing drainage pattern.
 Drainage Patterns
Drainage Patterns
Rivers
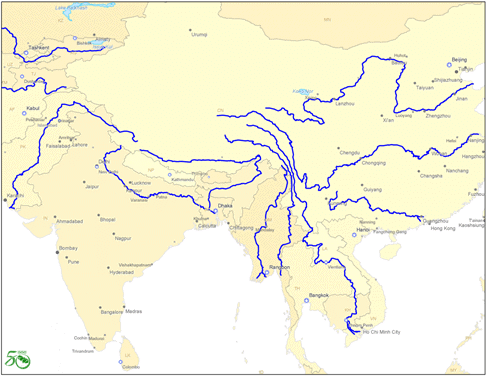 Rivers of Asia
Rivers of Asia
Important Rivers
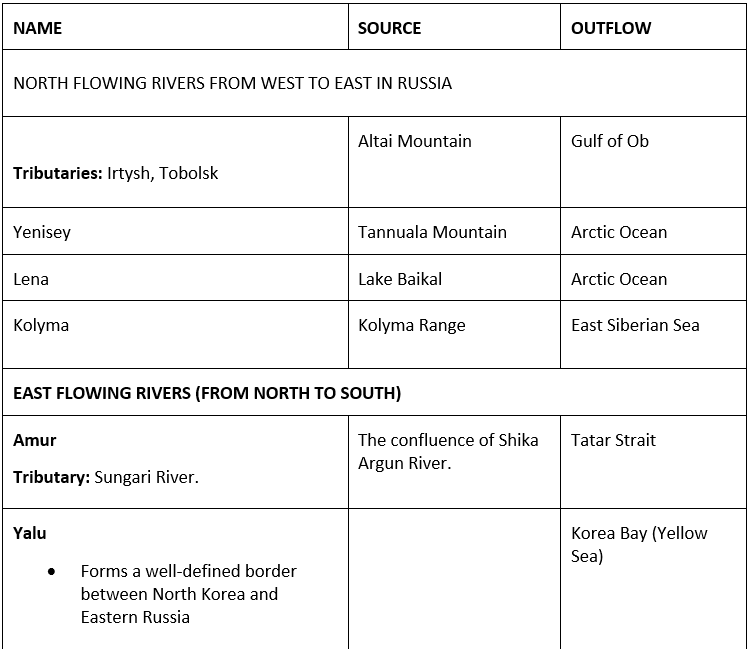



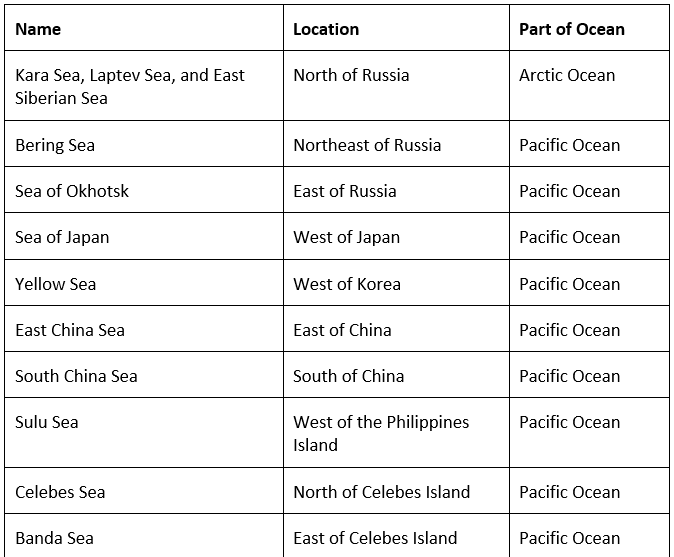
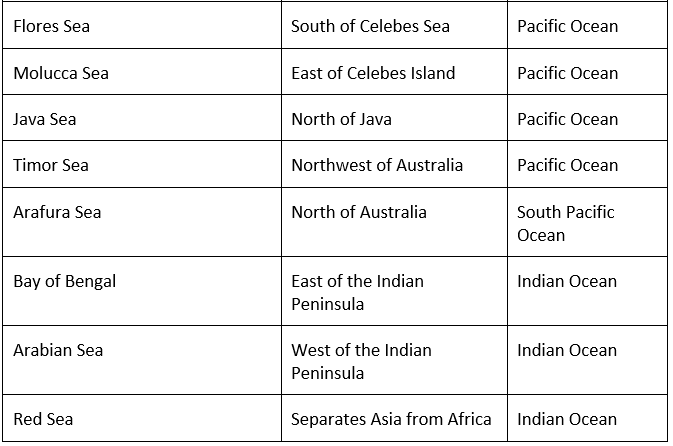
Seas
- As the continent is covered by sea from its three sides, It has also characterized by the long stretch of bay and gulf.
- Major seas contributing to Asian Drainage are Andaman Sea, Arabian Sea, Banda Sea, Barents Sea, Bering Sea, Black Sea, Caspian Sea, East Siberian Sea, Java Sea, Kara Sea, Laccadive Sea, Sea of Japan, Sea of Okhotsk. The South China Sea and the Yellow Sea.
Important Seas
Lakes
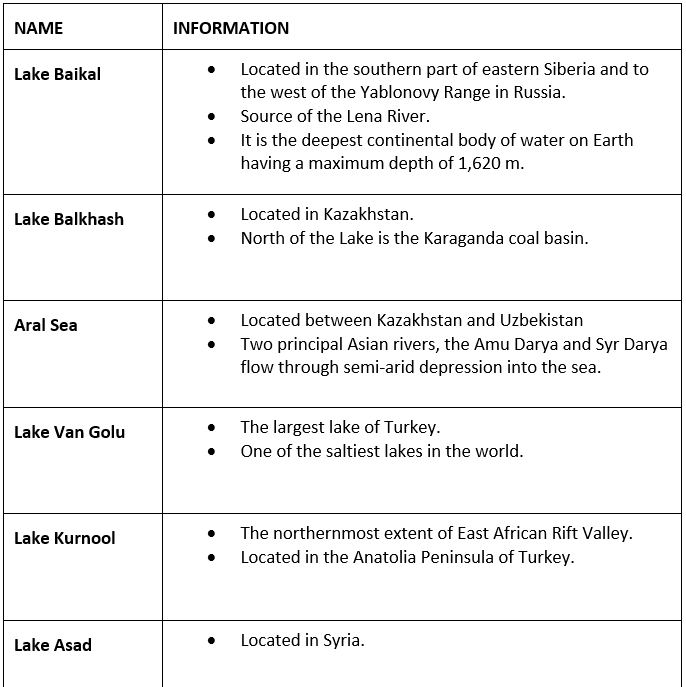
Major lakes of Asia are
- Lake Baikal, Onega, Ladoga, and Peipus in Russia;
- Lake Akan, Mashu, Biwa, Shikotsu in Japan;
- Qinghai Lake, Lake Khanka in China;
- Dal Lake, Chilka, Vembanada, Pullicat and Sukhna in India;
- Lake Matano and Toba in Indonesia, etc.
Baikal is the deepest lake in the world. It is in Southern Siberia, Russia.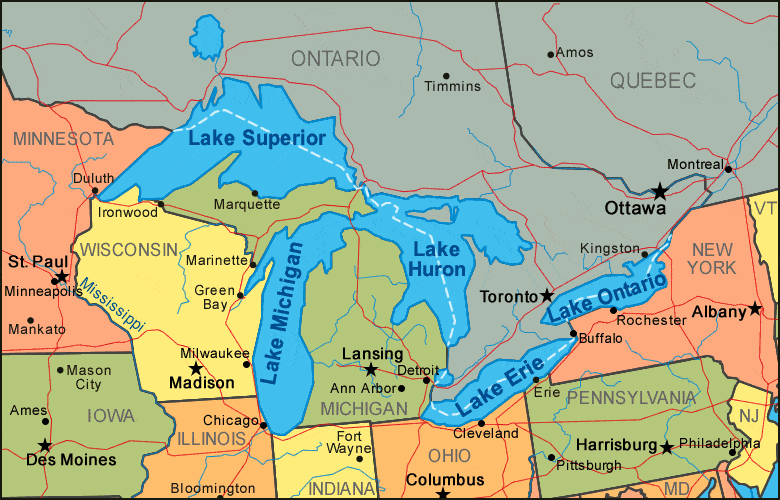
Important Lakes
Freshwater
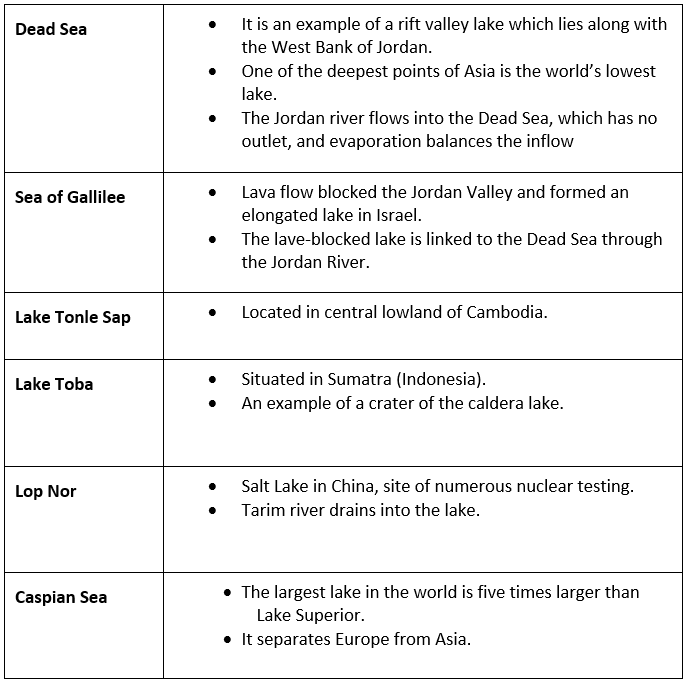
- Lake Baikal, located in southern Russia, is the deepest lake in the world, reaching a depth of 1,620 meters (5,315 feet). The lake contains 20 percent of the world’s unfrozen freshwater, making it the largest reservoir on Earth. It is also the world’s oldest lake, at 25 million years old.
- The Yangtze is the longest river in Asia and the third-longest in the world (behind the Amazon of South America and the Nile of Africa). Reaching 6,300 kilometers (3,915 miles) in length, the Yangtze moves east from the glaciers of the Tibetan Plateau to the river’s mouth on the East China Sea. The Yangtze is considered the lifeblood of China.
- The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers begin in the highlands of eastern Turkey and flow through Syria and Iraq, joining in the city of Qurna, Iraq, before emptying into the Persian Gulf. The land between the two rivers, known as Mesopotamia, was the center of the earliest civilizations, including Sumer and the Akkadian Empire.
Saltwater
- The Persian Gulf has an area of more than 234,000 square kilometers (90,000 square miles). It borders Iran, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, and Iraq. The gulf is subject to high rates of evaporation, making it shallow and extremely salty.
- The Sea of Okhotsk covers 1.5 million square kilometers (611,000 square miles) between the Russian mainland and the Kamchatka Peninsula.
- The Bay of Bengal is the largest bay in the world, covering almost 2.2 million square kilometers (839,000 square miles) and bordering Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Burma. Many large rivers, including the Ganges and Brahmaputra, empty into the bay.
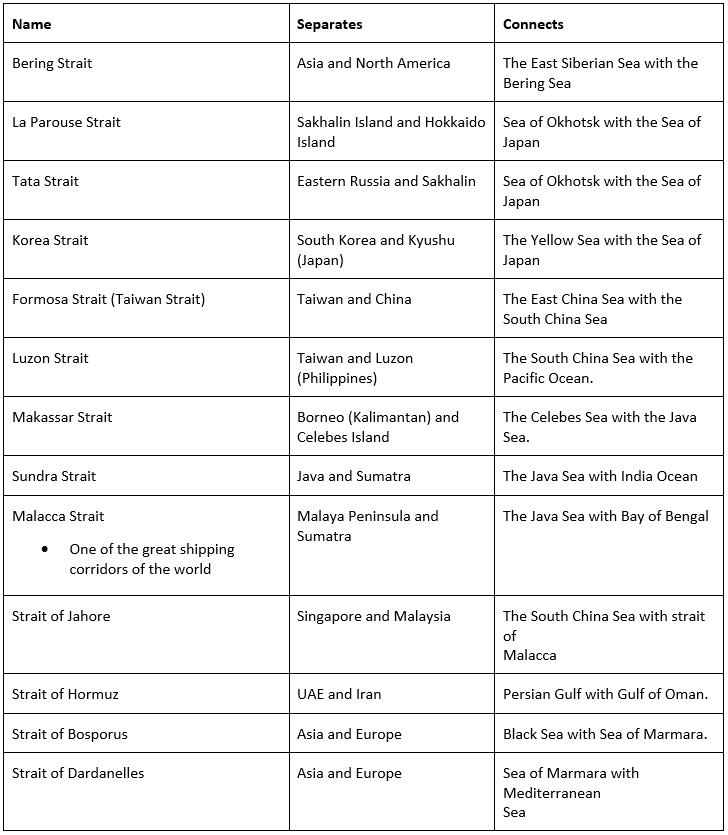
Straits
The important straits in Asia are the Strait of Malacca, Bering Strait, etc.
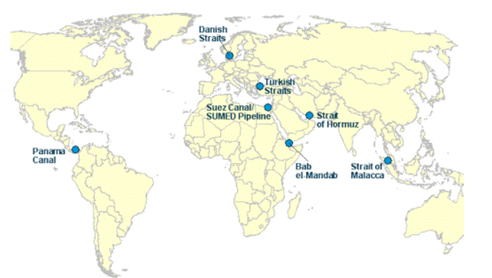
Important Straits
Resources
Asia’s climate can be most generally divided into three zones:
- North/central,
- Southwest
- Southeast
North/Central Zone
- The continent’s north/central zone is affected by cold and dry Arctic winds, especially in the Siberia region of Russia.
- Hardier grains, such as barley, buckwheat, millet, oats, and wheat, are grown in the central and southern areas of this zone, where permanent frosts inhibit plant growth.
- Animal husbandry is also very important in this zone. In Mongolia, for example, 75 percent of agricultural land is allocated to the rearing of livestock, such as sheep, goats, and cattle.
Southwest
- The southwest zone is a dry, hot region that stretches from the Gobi Desert in Mongolia through Pakistan, Iran, and into the Arabian Peninsula.
- This zone has very few areas with enough moisture and precipitation to produce crops. Grains, such as barley and corn, are the principal irrigated crops of some countries.
- Dates, figs, apricots, olives, onions, grapes, and cherries are the most important of these fruit and vegetable crops.
Southeast
- The southeast zone is greatly affected by the summer monsoon season.
- Rice is one of Asia’s most important agricultural commodities and a major food staple of the entire continent.
- Many regions where rainfall is less, grow a large amount of wheat.
- Southeast Asia is also a major producer of tropical fruits, such as mango, papaya, and pineapple. India is the world’s largest mango-producing nation, accounting for roughly 40 percent of total global output.
Mining
- China, India, Russia, and Indonesia are the continent’s most productive mining economies. These countries extract many of the same minerals.
- China is the world’s largest producer of aluminum, gold, tin, and coal.
- India is also a major producer of aluminum and iron ore, along with other minerals such as barite (used in drilling fluids), chromium (used in steel production and dyes), and manganese (used in steel production).
- Russia is a major producer of coal, tungsten (used in steel production), diamonds, iron, and steel.
- Indonesia is a major producer of coal, gold, copper, and tin.
Drilling
- Countries on the Arabian Peninsula have the world’s largest deposits of oil and natural gas. These fossil fuels are drilled for energy and fuel.
- The oil found throughout the Arabian Peninsula and the Middle East is of the highest quality: light sweet crude.
- Light sweet crude oil is used to make gasoline, kerosene, and diesel fuels.
- In 2010, Saudi Arabia was the world’s largest manufacturer of petroleum liquids, producing 10.07 million barrels of liquid fuels every day. (An oil barrel is 159 liters or 42 gallons.) It also has the world’s largest oil reserves, at roughly 250 billion barrels.
- Russia has oil reserves in Siberia and massive natural gas reserves throughout the Arctic.
- Russia and Iran have the world’s largest reserves of natural gas, while the US produces the most
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of Asia - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the major characteristics of the Central and Southern Plateaus in Asia? |  |
| 2. How do the Central and Southern Plateaus contribute to the geography of Asia? |  |
| 3. What countries in Asia are located on the Central and Southern Plateaus? |  |
| 4. How do the Central and Southern Plateaus impact the local communities living in the region? |  |
| 5. What are some of the challenges faced in the Central and Southern Plateaus region of Asia? |  |

















