Geography of Europe | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Europe
- Europe is the second smallest continent, the smallest being Australia.
- Its area, including the islands around the coast, is about 10 million square kilometers.
- Europe is often described as a “peninsula of peninsulas.”
- A peninsula is a piece of land surrounded by water on three sides.
- It is roughly three times the size of India and smaller than China.
Location of Europe
- A large part lies in the temperate zone as it stretches from 35°N to 80°N latitude.
- Longitudinally, it stretches from 10°W to 60°E
- The Prime Meridian passes through London. Prime Meridian passes through the UK, France, and Spain in Europe and Algeria, Mali, Burkina, Faso, Tongo, and Ghana in Africa.
- In the north, though it stretches into the Arctic Circle, the Warm Gulf Stream keeps the ports ice-free.
- The broad continent shelf on its west provides good fishing grounds and there are sheltered harbors along the indented coastline.
- It has the longest coastline in proportion to size.
Boundaries of Europe
- To the east, it is separated from Asia by the Ural Mountain, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountain, and the Black Sea.
- To the south is the Mediterranean Sea. The Aegean Sea and the Adriatic Sea are two of their branches.
- To the west is the Strait of Gibraltar separating Europe from Africa and joining the Mediterranean to the Atlantic Ocean. The Bay of Biscay, the English Channel, and the North Sea are parts of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Baltic Sea with two branches – the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland is an inlet in the north. The Arctic Ocean to the north has a bay called the White Sea.
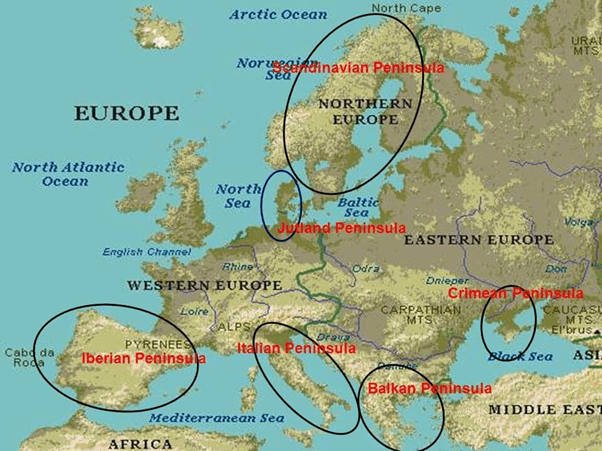
- The peninsula of Greece, known as the Balkan Peninsula, and Italy extends into the Mediterranean Sea.
- In the southwest is the Iberian Peninsula which is made up of Spain and Portugal.
- In the northwest is the Scandinavian, Peninsula consisting of Norway and Sweden.
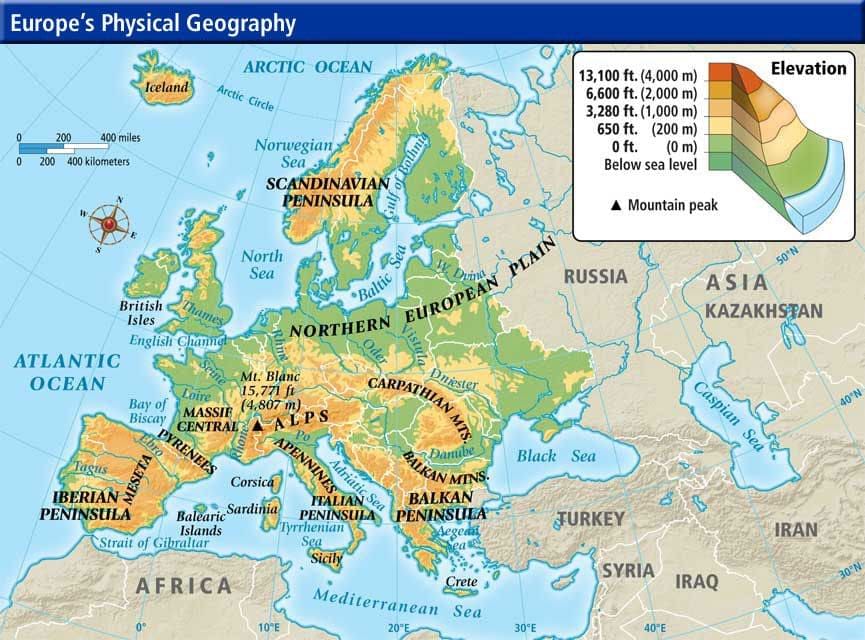
Physical Divisions of Europe
- Western Upland
- North European Plain
- Central Uplands or Plateau
- Alpine Mountain Systems
- Islands of Europe
- Drainage Pattern
- Gulfs and Bays
➤ Western Upland
- It is also known as the Northern Highlands, delineates the western edge of Europe and defines the physical landscape of Scandinavia (Norway, Sweden, and Denmark), Finland, Iceland, Scotland, Ireland, the Brittany region of France, Spain, and Portugal.
- These landforms are result of glaciations of hard rock in ancient times.
- Distinct physical features such as marshlands, lakes, and fjords have been emerged with the recession of glaciers form the highland areas.
- The famous Norwegian Fjords are Lyse fjord, the Geiranger fjord.
- A fjord is a long, deep, narrow body of water that reaches far inland. Fjords are often set in a U-shaped valley with steep walls of rock on either side.
➤ North European Plain
- It is the extensive low land spread along the bank of various mighty rivers such as Rhine, Weser, Elbe, Oder, and Vistula.
- These river valleys are favorable for growing seasonal crops.
- It covers all most half of Europe.
- Bordered by Baltican White sea from north and Black and Azov from the south the plain is gradually narrowed down towards the west.
- The northern part of the land is characterized by diversified glacial landforms such as Pipet Marshland, Valdai hills of western Russia, glacial lakes, etc.
➤ Central Uplands or Plateau
- These are the collection of distinctive landscapes of summits, steep slopes, valleys, and depression which stretches across central Europe.
- It extends from Belgium in the East to France in the West and from the Czech Republic and south Germany in south to Switzerland and Austria in the North.
- Except for some river valleys such as the Rhine, Rhone, Elbe, and Danube river valleys all other areas of this division is sparsely populated.
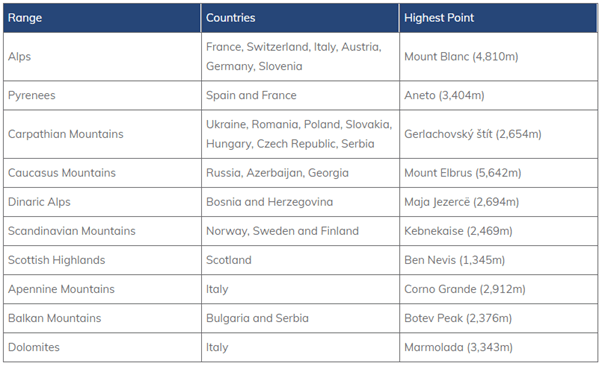
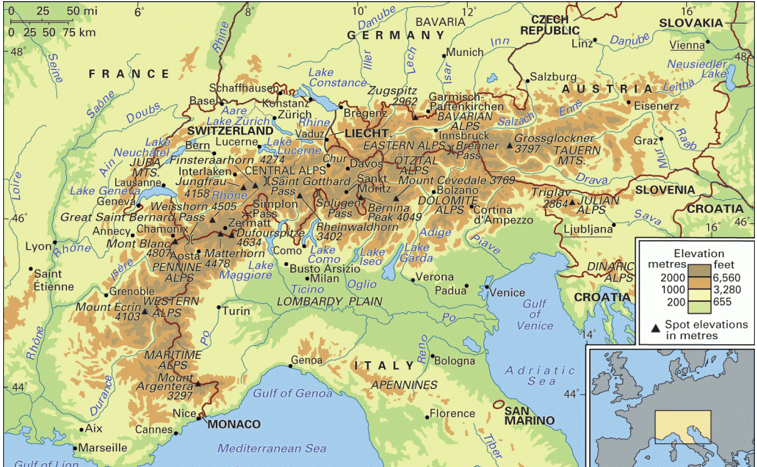
➤ Alpine Mountain Systems
- These are located in south-central Europe, immediately north of the Mediterranean Sea.
- They extend for almost 700 miles in a crescent shape from the coastline of southern France (near Monaco) into Switzerland, then through northern Italy and into Austria, and down through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro – then ending in Albania on the rugged coastline of the Adriatic Sea.
- The highest point is Mont Blanc at 15,771 ft. (4,807m).
(i) Mountains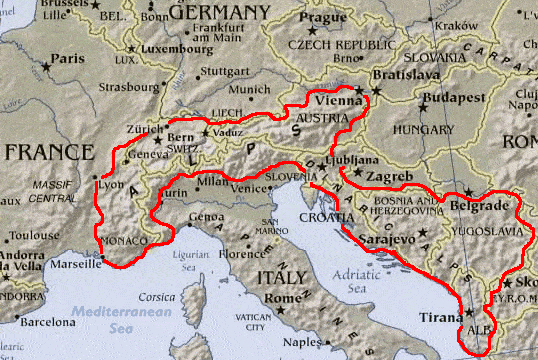
(a) The Ural Mountains
- The Ural Mountains are a mountain range that forms part of the natural boundary between Europe and Asia.
- The mountains run through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and Kazakhstan.
- From north to south, these are 2,200 km long and 80-120 km broad with many parallel valleys.
- Several islands, such as Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya, are a continuation of the Ural Mountains that run below the sea and emerge again on the islands.
- The Ural Mountains are a rich source of minerals including coal, metal ores, and precious stones, and mining in the region significantly contributes to Russia’s economy.
- The highest peak in the range is Mount Narodnaya, which has an elevation of 1,894 m.
(b) The Scandinavian Mountains
- Scandinavia consists of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark.
- In fact, Scandinavia exists or Fenno-Scandia which continues into the east through Finland to the Kola Peninsula in Russia.
(c) The Old Mountain Blocks
- These are Hercynian and Caledonian mountain chains.
- In the west, the Meseta of Spain, the Central Plateau of France, the Britanny Peninsula, the Rhine Upland, the Block Forest, Vosges, Bohemian Plateau, and Rhodope Mt, etc, are examples of these old mountains.
(ii) The Alpine Mountain Ranges
- The highest peak is (Mount Blanc 5,000 m).
- The mountain range runs in many branches.
- The main ones are the Alps, the Carpathians, the Balkans, the Caucasus, etc.
- Another branch is the Apennines (Italy, the Atlas (Africa, and the Sierra Nevada Spain).
- Still another branch is the Dinaric and the Pindus mountain (Yugoslavia and Greece) and enters through the Crete island into Asia.
(a) Apennines
- The Apennine Mountains are a range consisting of several sub-ranges that run parallel to each other for approximately 1,200 km, along the length of peninsular Italy.
- Como Grande is the tallest peak in the Apennines, with an elevation of 2,912 m.
- The Apennine Mountains contain pristine forests and montane grasslands, many of which are protected by national parks.
(b) The Pyrenees
- The Pyrenees are half as long and broad as the Alps and separate broadly France from Spain.
- The highest peak is Pice de Aneto (3,404 m).
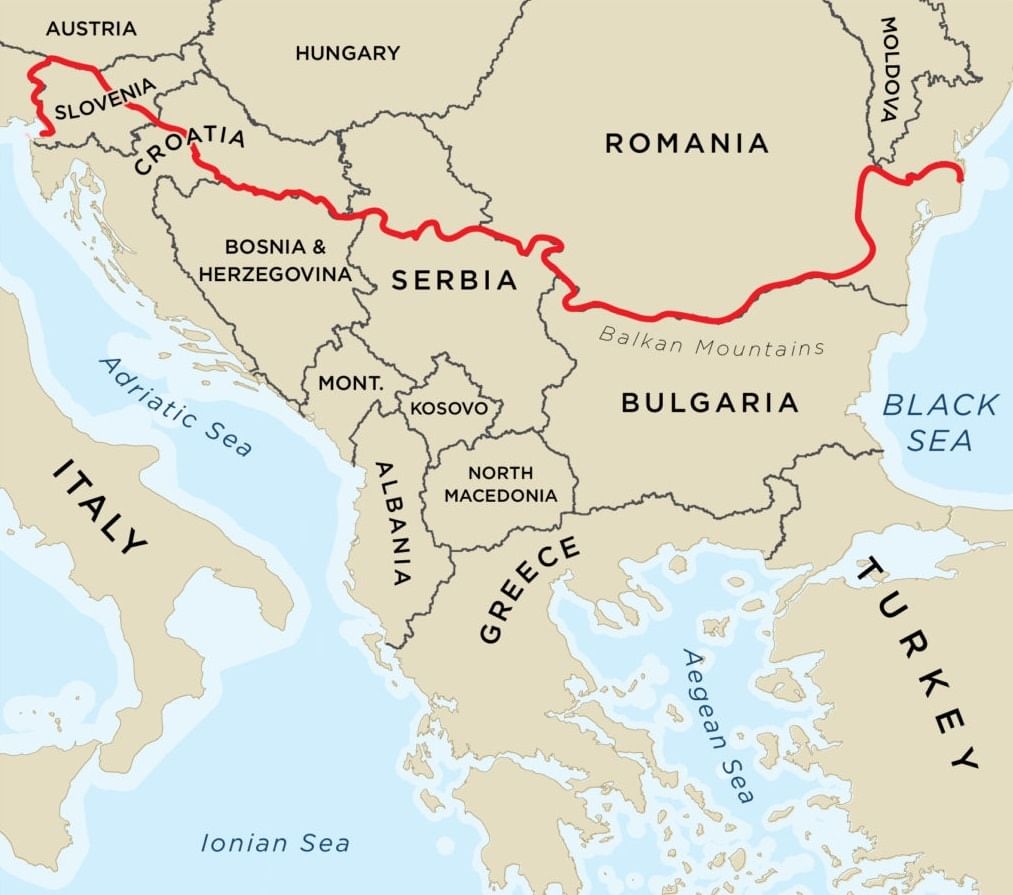
(c) Balkan Mountains
- The Balkan Mountain is a mountain range is located in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula, stretching for approximately 557 km from the Vrashka Chuka Peak near the Bulgaria-Siberia border to Cape Emine along the coast of the Black Sea.
- The highest peaks of the Balkan Mountains are located in the central part of Bulgaria, the tallest of which is Botev Peak, with an elevation of 2,376 m.
- Several protected areas, such as Central Balkan National Park and Bulgarka Nature Park, help conserve the ecosystem and landscapes within the Balkan Mountains. Additionally, numerous caves within the range are a significant tourist attraction in the region.
- The Balkan Mountains are closely connected to the history of Bulgaria and are considered to have the nation and its people.
(d) Caucasus Mountains
- Like the Urals, the Caucasus Mountains also form part of the boundary between Europe and Asia. The mountain range has a length of approximately 1,200 km and stretches between the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea.
- Europe’s highest peak, Mount Elbrus, which has an elevation of 5,642 m, is located in the Caucasus Mountains. Additionally, all 10 of the tallest peaks in Europe are located in the Caucasus Mountains, particularly in Russia, Georgia, or along the Russia-Georgia border.
➤ Islands of Europe
- As surrounded by a number of seas from all sides, Europe is an island-rich continent.
- The British Isles is the largest and the most important group of islands consisting of England, Scotland, and Ireland.
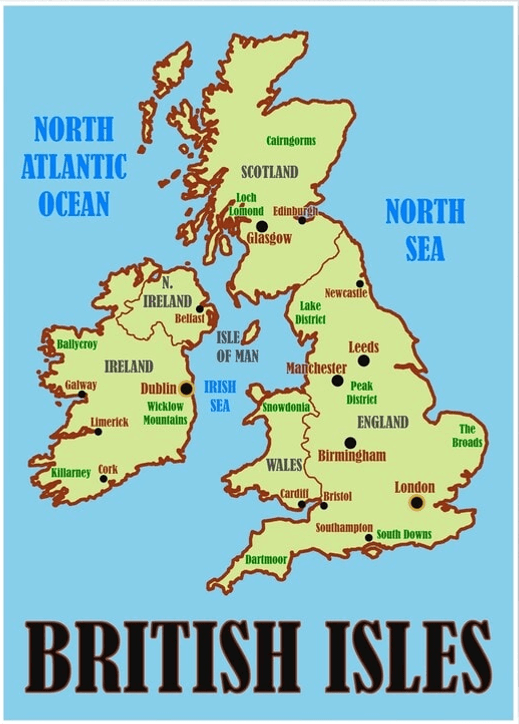
The largest European islands by area are as follows:
- Great Britain
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Severny Island
- Spitsbergen
- Yuzhny Island
- Sicily
- Sardinia
- Nordaustlandet
- Cyprus
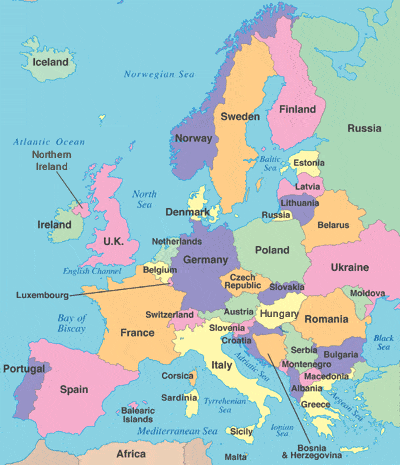 (i) Peninsula
(i) Peninsula
- Europe’s main peninsulas are the Iberian, Italian, and Balkan, located in southern Europe, and the Scandinavian and Jutland, located in northern Europe.
➤ Drainage Pattern
- The rivers of Europe are perennial being fed by melting snow or by the rain brought by the Westerlies.
- Many of them have their origin in the Alps.
- Rivers that flow into the Mediterranean Sea are Rhone (France) and Ebro (Spain).
- River Po of Italy flows into the Adriatic Sea.
- The Danube, Dnieper, and Don flow into the Black Sea.
- Rivers that flow into the Atlantic Ocean are – Guadalquivir (Spain), Tagus and Douro (Portugal), Loire and Seine (France), The Rhine Weser and Elbe (Germany).
- Many rivers flow into the Baltic Sea.
- The Thames, the chief river of England, flows into the English Channel.
- Rhine and Danube are international rivers because they pass through many countries.
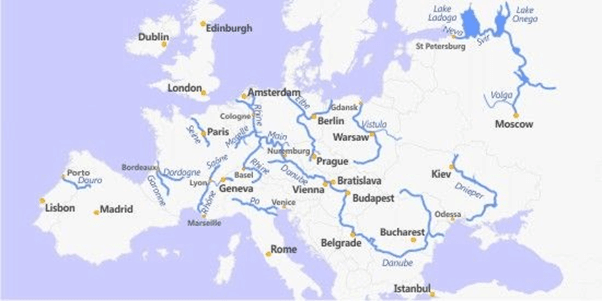
- The Rhine starts from the Alps in Switzerland and flows northwards through Germany and enters the sea through Holland.
- It passes through heavily industrialized regions and is used for transporting heavy goods.
- It is the busiest waterway in Europe. Rotterdam, the largest part of Europe, is on its delta.
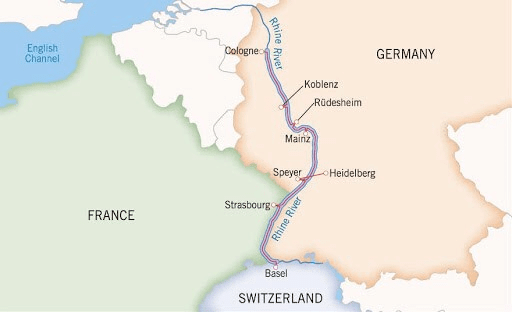
- The Danube is also an international river.
- It rises from the Alps in Germany and flows through Australia, Hungary, Serbia, and enters the Black Sea in Romania.
- It is not as important as the Rhine for international trade because of the Black Sea in the interior.
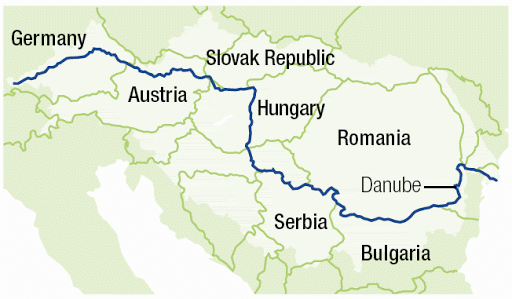
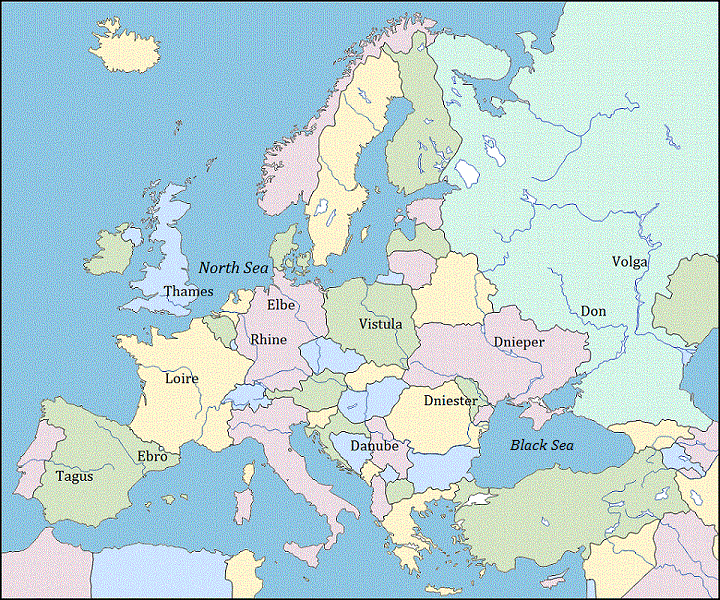 Major river of Europe
Major river of Europe
➤ Gulfs and Bays
These are the parts of large water bodies which are adjacent to a massive land may it be continents or countries which are of economic importance for any human civilization, As Europe is surrounded by
A number of large water bodies such as the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, The North Sea, etc. there are a lot of Gulfs, Bay, and straits.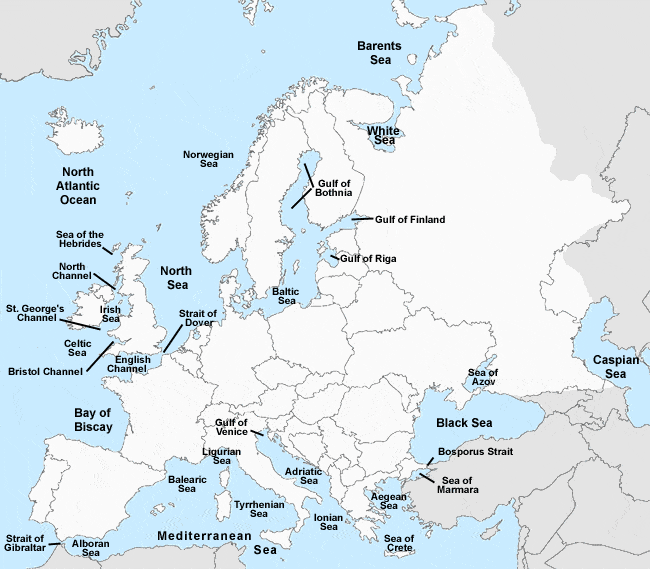 Europe Bodies of Water
Europe Bodies of Water
(i) The Gulf of Finland
- It is situated in the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea and extends between Finland (to the north) and Estonia (to the south) all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it.
- Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn.
- The eastern parts of the Gulf of Finland belong to Russia, and some of Russia’s most important oil harbors are located farthest in, near Saint Petersburg.
(ii) The Gulf of Bothnia
- It is situated in the northernmost part of the Baltic Sea and bordered by Sweden at its western side and Finland at the eastern side
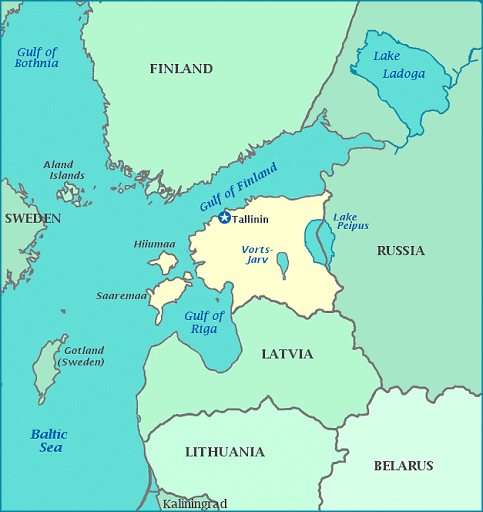
(iii) The Gulf of Riga
- It is a brackish water body that is considered as a sub-basin of the Baltic Sea.
- The areal extent of the Gulf of Riga is approximately 16,300 km².
- It is also called the Bay of Riga which is a very shallow water sea with a maximum depth of 67metres.
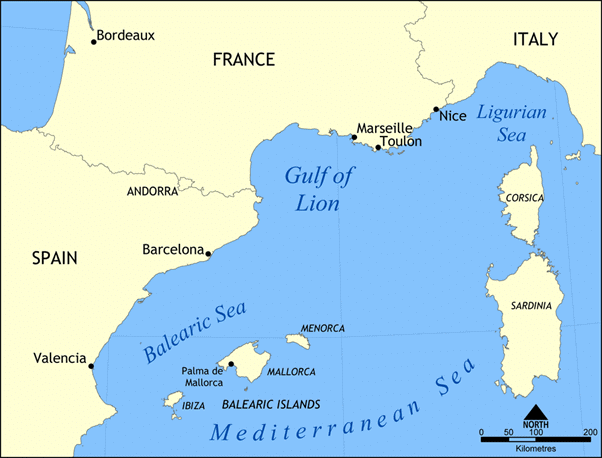
(iv) The Gulf of Lions
- It extends from the easternmost spurs of Pyrenees and covers various lagoons, the Rhone River delta, limestone hills of Marseille.
- It’s an embayment of the Mediterranean coastline of Languedoc-Roussillon and Provence in France.
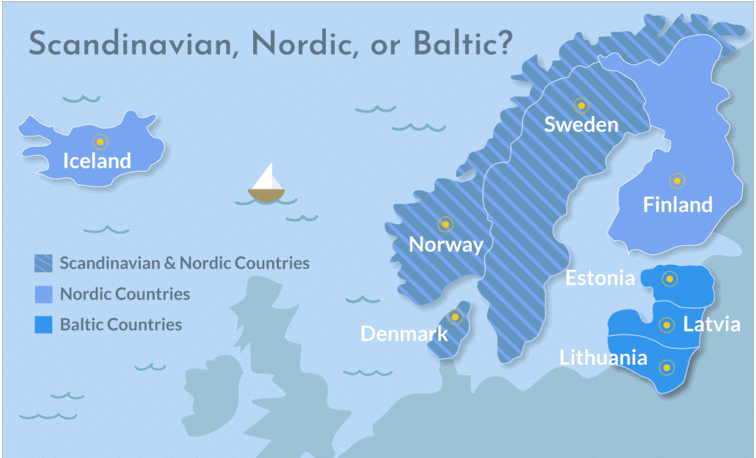
Scandinavian and Nordic countries
- ‘Scandinavia‘ is commonly used for Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, the term “Nordic countries” is vaguely used for Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland, including their associated territories of Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the Åland Islands.
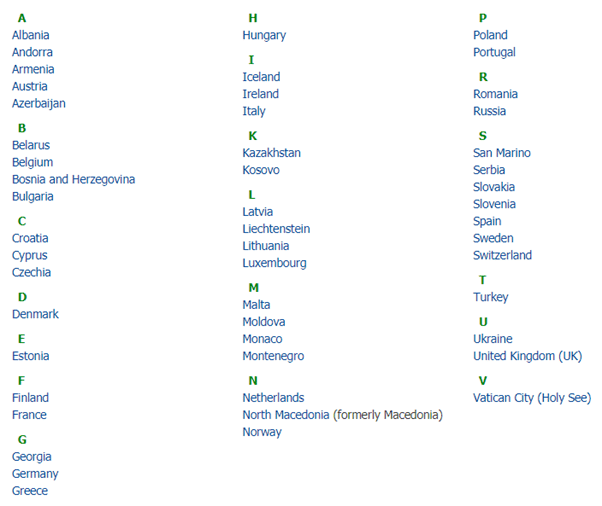
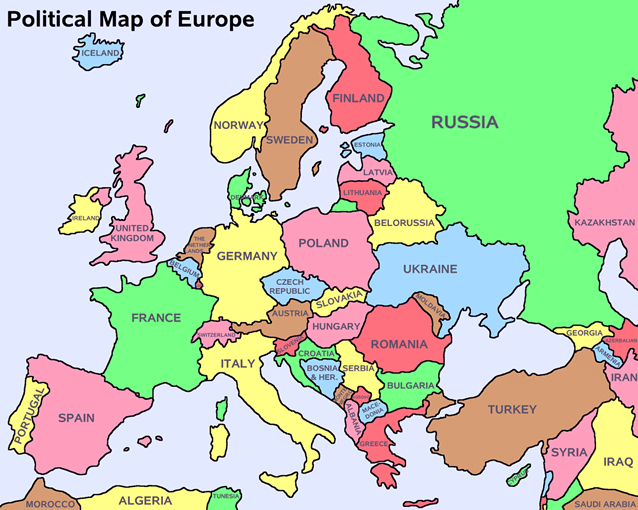
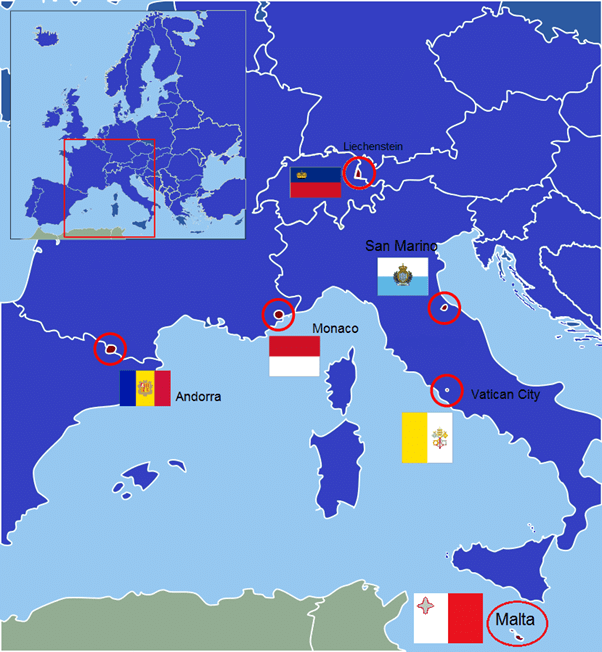
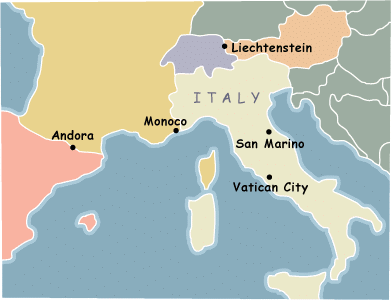
Smallest countries in Europe
- The European microstates or European ministates are a set of very small sovereign states in Europe.
- The term is typically used to refer to the six smallest states in Europe by area: Andorra, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.
Great Britain
- Great Britain, also called Britain, island lying off the western coast of Europe and consisting of England, Scotland, and Wales.
- The term is often used as a synonym for the United Kingdom, which also includes Northern Ireland and a number of offshore islands.
Smallest country in the world
- Based on the landmass, Vatican City is the smallest country in the world, measuring just 0.2 square miles, almost 120 times smaller than the island of Manhattan.
- Situated on the western bank of the Tiber River, Vatican City’s 2-mile border is landlocked by Italy.
French islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of Europe - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the major physical features of Europe? |  |
| 2. How many countries are there in Europe? |  |
| 3. What is the climate like in Europe? |  |
| 4. What are some famous landmarks in Europe? |  |
| 5. How does Europe's geography influence its economy? |  |
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Bank Exams exam
|

|


















