Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 9 > Glossary and Important Information - Drainage
Glossary and Important Information - Drainage | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
- Drainage - A flowing water system from the higher to the lower level.
- River – A natural stream of flowing water from a mountain/ lake/ spring to the sea, lake, or another water body.
- Lake – A deep and vast depression on the earth's surface filled with water.
- Dendritic Pattern – The stream and its tributaries resemble the branches of trees.
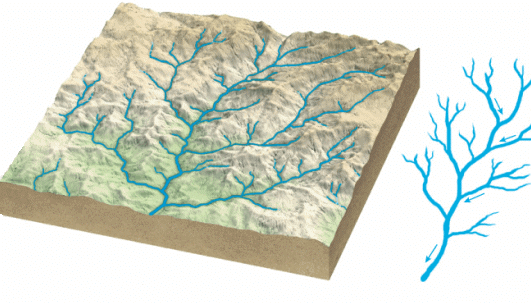 Dendritic Pattern
Dendritic Pattern - Trellis Pattern – The tributaries were joining the mainstream at the right angles.
- Radial Pattern–the streams flowing in different directions from a central peak.
- Centrifugal Pattern - Streams emerging from all sides towards the central depression.
- Perennial Rivers - Rivers that flow throughout the year.
- Tributary – A smaller stream or river that flows into a larger river. The Zaskar, the Nubra, the Shyok, and the Hunza, join it in the Kashmir region
- Distributary - A channel which branches off from the main river and carries away a part of its water.Question for Glossary and Important Information - DrainageTry yourself:Which pattern of drainage resembles the branches of trees?View Solution
- Meanders – Winding sections or loops of river that swing from side to side as it flows over a level tract normally along its lower course.
 Meanders
Meanders - Delta - A more or less triangular and level tract of alluvium formed at the mouth of a river entering a relatively quiet body of water.
- Estuary – Tidal mouth of a river where sweet and salty waters freely mix.
- Source of the River – The place where the river originates.
- Mouth of the river – The place where the river empties itself into the sea or the lake.
- River valley – The path followed by the river to its mouth.
- Drainage Basin – The entire area in which the river and its tributaries flow.
- Water divide or watershed – The higher area separating two drainage basins.
- Catchment area – The upland area from which the river draws its water.
- The Indus River System - It rises in Tibet (near the lake Mansarovar).
Features: Gentle slope, one of the longest rivers in the world. Indus basin –in Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Pakistan.Question for Glossary and Important Information - DrainageTry yourself:What is the term used to describe the place where a river originates?View Solution - The Ganga River System - Headwaters of Ganga-Bhagirathi (source –Gangotri Glacier) and Alaknanda (source –Alkapuri Glacier) join at Devprayag.
- The Brahmaputra Basin–It rises in Tibet east of Lake Mansarovar Features: longer course, in Tibet there is less volume of water, and less silt as it is a cold, dry area. In India, the river passes through a region of heavy rainfall, carries large amounts of water and a lot of silt (layer of fine particles, carried and deposited by rivers).
 The Brahmaputra Basin
The Brahmaputra Basin - The Narmada Basin –Rises in Amarkantak hills in Madhya Pradesh.Features: It flows in a rift valley (trough), and drains into the Gulf of Khambhat by an estuary (a funnel-shaped mouth of a river, river joins the sea directly without depositing the silt)
- The Tapi Basin – It rises in Satpurarange in Madhya Pradesh. Flows in Rift Valley parallel to Narmada basin-Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- The Godavari Basin – It rises from the slope of the Western Ghats in Nasik. Largest peninsular river. Basin –Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh. It is commonly referred to as the Dakshin Ganga due to its length and the area it covers.
- The Mahanadi Basin – It rises in the hills of Chhattisgarh. Drainage basin –Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Orissa.
- The Krishna Basin – It rises from the spring in Mahabaleshwar. Basin –Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh
- The Kaveri Basin – It rises in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats. Basin –Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu.
- Gorge – A narrow steep-sided valley formed by the erosive action of a river cutting through hard rock.
- V-shaped valleys – They are formed in areas of sufficient rainfall where the rocks are not hard. Down cutting, and side cutting is done simultaneously.Question for Glossary and Important Information - DrainageTry yourself:Which river is commonly referred to as the Dakshin Ganga?View Solution
- Waterfalls – When the river cascades vertically from a significant height along its course, it forms waterfalls.
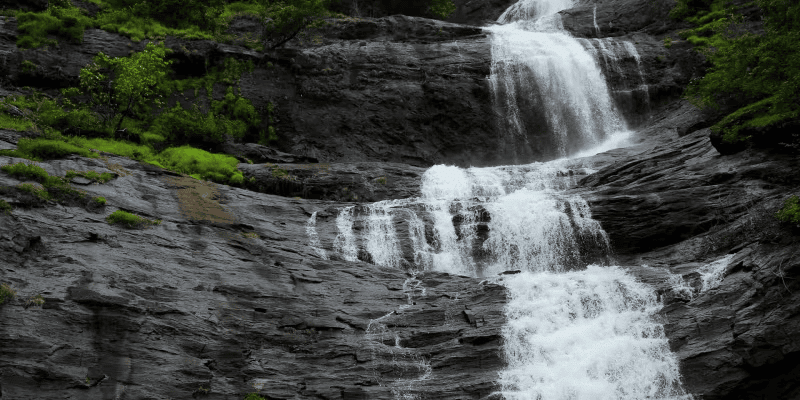 Waterfalls
Waterfalls - Alluvial plains - It is a fan-shaped deposit formed where a fast-flowing stream flattens, slows, and spreads typically at the exit of a canyon onto a flatter plain.
- Floodplain – The flat land next to a river that is prone to flooding during heavy rains."
- Braided Channels – Streams that split into multiple paths and rejoin, often due to varying water levels and sediment deposits. Question for Glossary and Important Information - DrainageTry yourself:Which landform is formed when a fast-flowing stream flattens, slows, and spreads typically at the exit of a canyon onto a flatter plain?View Solution
The document Glossary and Important Information - Drainage | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information - Drainage - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is drainage and why is it important in agriculture? |  |
Ans.Drainage refers to the process of removing excess water from the soil to prevent waterlogging and improve soil aeration. It is important in agriculture because it helps maintain optimal moisture levels for crops, enhances root growth, and prevents the development of diseases related to excessive moisture.
| 2. What are the different types of drainage systems used in agriculture? |  |
Ans.The different types of drainage systems used in agriculture include surface drainage, subsurface drainage, and artificial drainage systems such as tile drainage. Surface drainage involves the removal of excess water from the soil surface, while subsurface drainage involves the installation of underground pipes to collect and convey excess water away from the root zone of crops.
| 3. How does poor drainage affect crop yield? |  |
Ans.Poor drainage can lead to waterlogged conditions, which can suffocate plant roots, hinder nutrient uptake, and create an environment conducive to pests and diseases. As a result, crop yield can be significantly reduced due to stunted growth, poor quality produce, and increased mortality rates among plants.
| 4. What are the signs of poor drainage in a field? |  |
Ans.Signs of poor drainage in a field include standing water after rainfall, overly wet soil that remains saturated for extended periods, stunted plant growth, yellowing leaves, and the presence of weeds that thrive in wet conditions. These indicators suggest that the soil is not draining properly and may require intervention.
| 5. How can farmers improve drainage in their fields? |  |
Ans.Farmers can improve drainage in their fields by implementing various methods such as installing drainage tiles, creating ditches or channels to redirect water, planting cover crops to enhance soil structure, and employing contour farming techniques to manage water flow more effectively. Regular soil testing and management practices can also help maintain adequate drainage.
Related Searches






















