Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 9 > Glossary and Important Information - Working of Institutions
Glossary and Important Information - Working of Institutions | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Glossary and Important Information
- Council of Ministers: A group of ministers who are collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
- Cabinet: A group of senior ministers who manage key ministries. It is the main part of the Council of Ministers and often meets to make important decisions for the entire Council.
- Impeachment: A special procedure in Parliament to prosecute or remove the President and Judges for breaking the Constitution.
- Money Bills: Bills that deal with financial matters such as taxes, income, spending, and grants.
- Lok Sabha: The lower house of the Indian Parliament, made up of elected representatives of the people.
- Rajya Sabha: The upper house of Parliament that represents the interests of states and Union Territories.

- Speaker: The presiding officer of the Lok Sabha, responsible for ensuring smooth conduct of its business.
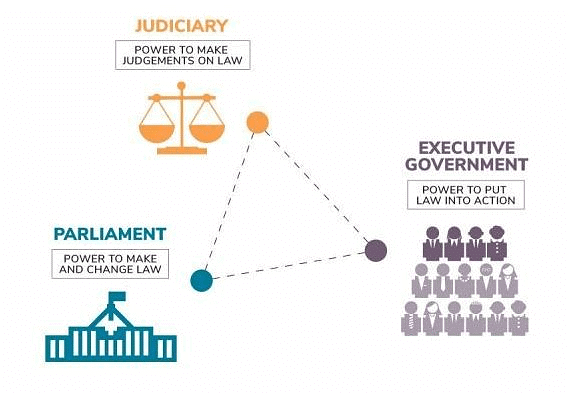
- Executive: The part of government that puts laws into action. It consists of people with the authority to create major policies, make decisions, and implement them according to the Constitution and laws.
- Legislative: The part of government that creates laws and monitors the executive branch.
- Judiciary: The system that administers justice and resolves legal disputes. All courts in the country are part of the judiciary.
- Criminal Cases: Cases involving breaking criminal laws, such as murder, theft, and assault.
- Independence of the Judiciary: The Constitution ensures that the judiciary operates independently from the executive to avoid bias in favour of the government.
- Coalition Government: A government formed when multiple political parties come together to rule, usually when no single party has a majority.
- Government: The organisation responsible for managing a country, state, or community, exercising authority over various aspects of public life.
- Office Memorandum: A communication from an authority stating the government’s policy or decision.
- Political Institutions: Formal structures like government bodies and political parties that regulate political processes and hold authority in society.
- Reservation: A policy aimed at offering special opportunities to disadvantaged groups, often through quotas in education and employment.
- State: A political entity with a defined territory, organised government, and the ability to make domestic and foreign policies. The state remains constant, even if government leaders change. The terms country, nation, and state are often used interchangeably.
- Legislative Assembly: A governing body that is responsible for making laws in a specific region.

- Parliament: The highest legislative body in a country, made up of elected representatives who create laws and oversee the government.
- Political Executive: The branch of government that implements laws and policies, led by elected officials like the president or prime minister.
- Public Interest Litigation: Legal action taken in the interest of the public, aimed at addressing social justice, human rights, or welfare issues.
The document Glossary and Important Information - Working of Institutions | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary and Important Information - Working of Institutions - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the role of the Parliament in a democracy? |  |
Ans. The Parliament is the supreme legislative body in a democracy. It is responsible for making laws, discussing important national issues, and representing the interests of the citizens. The Parliament consists of two houses: the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). Members of the Lok Sabha are directly elected by the people, while members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by the state legislatures. The Parliament also holds the government accountable by questioning its decisions and policies.
| 2. How do elections work in a democracy? |  |
Ans. Elections in a democracy are conducted to choose representatives who will make decisions on behalf of the citizens. In India, elections are held at multiple levels, including national, state, and local. The Election Commission oversees the election process to ensure fairness and transparency. Citizens have the right to vote for their preferred candidates, and those who receive the majority of votes are elected. Regular elections help maintain the democratic process and allow citizens to voice their opinions.
| 3. What is the significance of the Constitution in India? |  |
Ans. The Constitution is the fundamental law of India and serves as the guiding document for the country's governance. It establishes the framework for the political system, defines the roles and powers of various institutions, and guarantees fundamental rights to all citizens. The Constitution also lays down the principles of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity, which are essential for a democratic society. It is a living document that can be amended as needed to address changing societal needs.
| 4. What are the different types of government institutions in India? |  |
Ans. In India, government institutions can be broadly classified into three categories: legislative, executive, and judiciary. The legislative institutions, primarily the Parliament, make laws. The executive institutions, which include the President, Prime Minister, and Council of Ministers, implement these laws and govern the country. The judiciary, comprising the Supreme Court and other courts, interprets the laws and ensures justice. Together, these institutions function to uphold democracy and protect citizens' rights.
| 5. How does the system of checks and balances work in Indian democracy? |  |
Ans. The system of checks and balances in Indian democracy ensures that no single branch of government becomes too powerful. Each branch—legislative, executive, and judiciary—has distinct functions and powers, and they can check each other’s authority. For example, the Parliament can make laws, but the President has the power to give assent or withhold it. The judiciary can review laws and declare them unconstitutional if they violate the Constitution. This system promotes accountability and prevents the misuse of power.
Related Searches






















