Gold Leaf Electroscope | Physics for JAMB PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Electroscope? |

|
| Working of Electroscope |

|
| Types of electroscope |

|
| Uses of Electroscope |

|
What is an Electroscope?
An electroscope is a scientific device that is used to detect the presence of an electric charge on a body.
- In the year 1600, British physician William Gilbert invented the first electroscope with a pivoted needle called versorium.
- The electroscope detects the charge based on the Coulomb electrostatic force which causes the motion of the test charge.
- An electroscope can be regarded as a crude voltmeter as the electric charge of an object is equal to its capacitance.
- An instrument that is used to measure the charge quantitatively is known as an electrometer.
Working of Electroscope
The working principle of an electroscope is based on the atomic structure of elements, charge induction, the internal structure of metal elements and the idea that like charges repel each other while unlike charges attract each other.
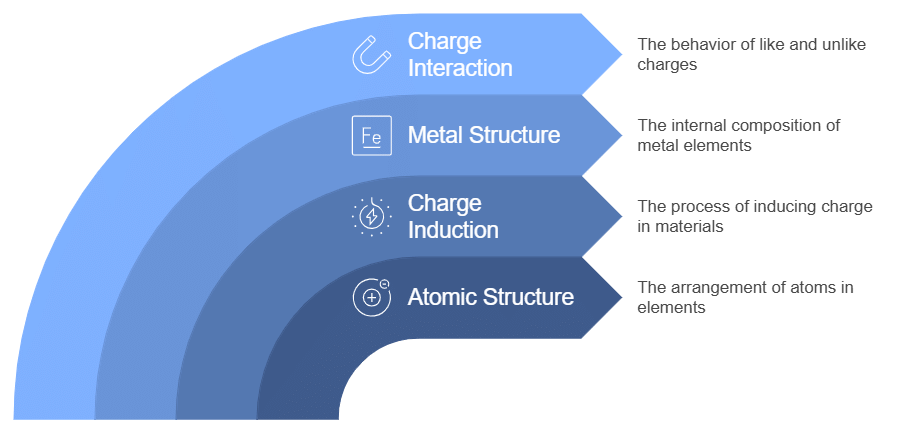 Working of Electroscope
Working of Electroscope
An electroscope is made up of a metal detector knob on top which is connected to a pair of metal leaves hanging from the bottom of the connecting rod. When no charge is present the metals leaves hang loosely downward. But, when an object with a charge is brought near an electroscope, one of the two things can happen.
- When the charge is positive, electrons in the metal of the electroscope are attracted to the charge and move upward out of the leaves. This results in the leaves having a temporary positive charge and because like charges repel, the leaves separate. When the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original positions and the leaves relax.
- When the charge is negative, the electrons in the metal of the electroscope repel and move toward the leaves on the bottom. This causes the leaves to gain a temporary negative charge and because like charges repel, the leaves again separate. Then when the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original position and the leaves relax.
An electroscope responds to the presence of a charge through the movement of electrons either into or away from, the leaves. In both cases, the leaves separate. It is important to note that the electroscope cannot determine if the charged object is positive or negative – it is only responding to the presence of an electrical charge.
Types of electroscope
There are two classical types of electroscopes and they are as follows:
1. Pith-ball electroscope:
Pith-ball electroscope was invented by John Canton in the year 1754. It consists of one or two small light balls that are a lightweight non-conductive substance called pith. In order to find if the object is charged or not, it is brought near an uncharged pith ball. If the ball gets attracted towards the object it means the object is charged.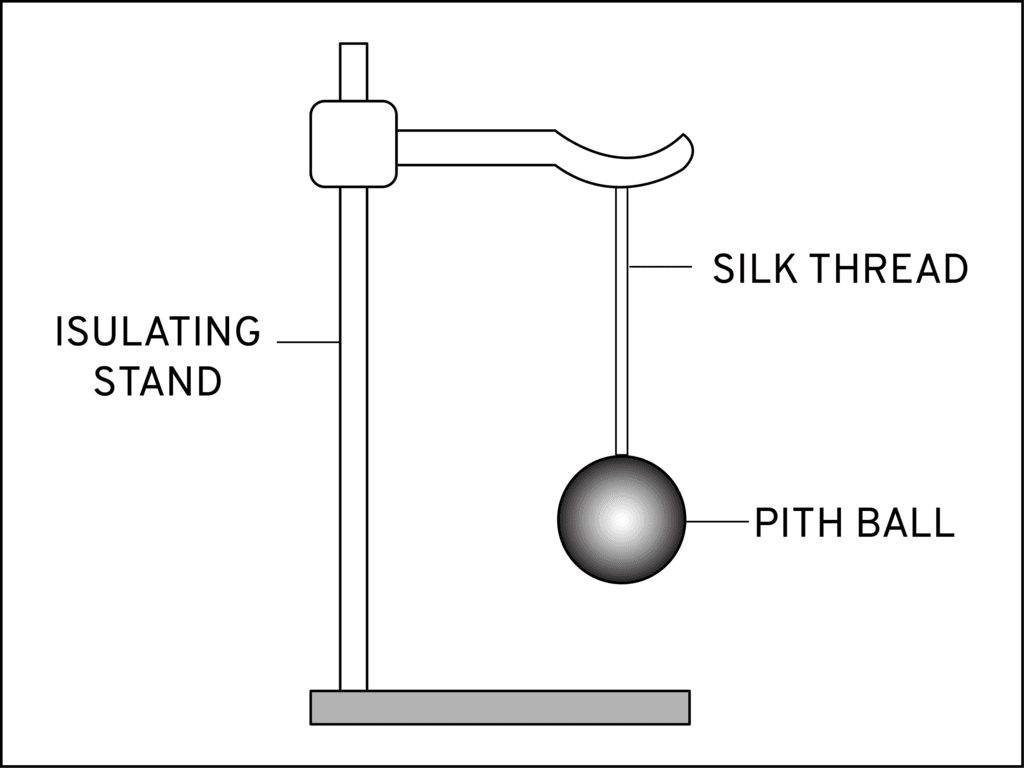
2. Gold-leaf electroscope:
It is an instrument for detecting and measuring static electricity or voltage. A metal disc is connected to a narrow metal plate and a thin piece of gold leaf is fixed to the plate. The whole of this part of the electroscope is insulated from the body of the instrument. A glass front prevents air draughts but allows you to watch the behaviour of the leaf.
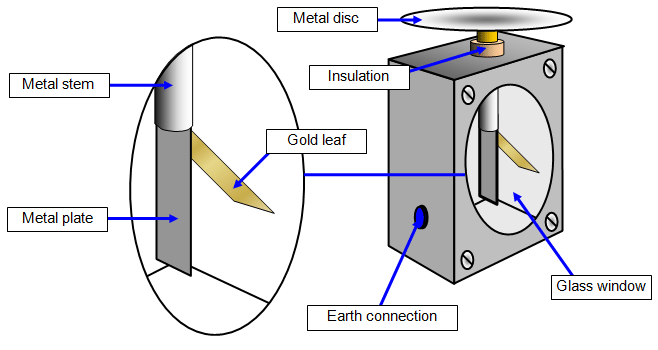 Gold Leaf Electroscope
Gold Leaf Electroscope
When a charge is put on the disc at the top it spreads down to the plate and leaf. This means that both the leaf and plate will have the same charge. Similar charges repel each other and so the leaf rises away from the plate - the bigger the charge the more the leaf rises.
The leaf can be made to fall again by touching the disc - you have earthed the electroscope. An earth terminal prevents the case from becoming live.
Methods of Charging
The electroscope can be charged in two ways:
 Methods of Charging
Methods of Charging
- By contacting: A charged rod is touched on the surface of the disc and some of the charges is transferred to the electroscope. This is not a very effective method of charging the electroscope.
- By induction: A charged rod is brought up to the disc and then the electroscope is earthed, the rod is then removed.
The two methods give the gold leaf opposite charges.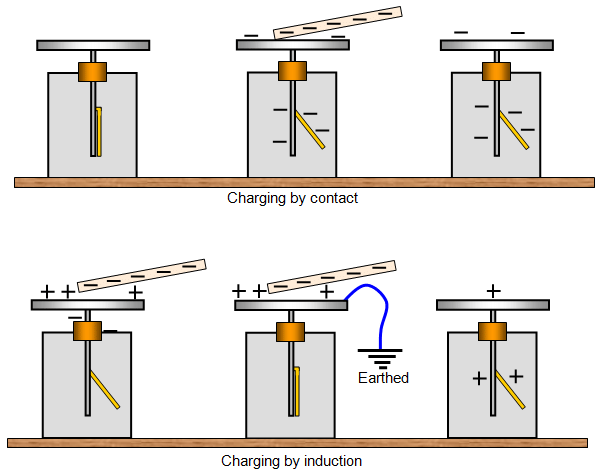
The above diagrams show you how the charges spread over the plate and gold leaf in different conditions.
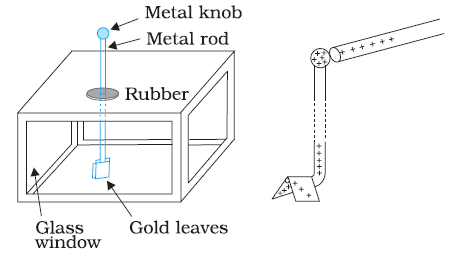
Construction of Gold Leaf Electroscope
It consists of a metal rod that is fitted in an insulating box. The metal rod has a metal knob at its top. Two gold leaves are also attached at the bottom end of the rod.
Working of Gold Leaf Electroscope
- Since electroscope is used to detect the presence of charge. So through it, we can find whether a body is charged or uncharged.
- Therefore the body to be detected is brought close enough to the metal knob. When a charged object touches the knob at the top of the rod, charge flows through the rod onto the leaves.
- Both the gold leaves will have the same charge and hence as a result they will repel and diverge.
- The degree of divergence is an indicator of the amount of charge i.e., the more the charge, the more will be the divergence.
Uses of Electroscope
The various benefits of an electroscope are:
- They are useful to analyze the electrostatic charges and any ionizing radiation present in a body.
- The nature of the electrical charge is measurable using an electroscope.
- Also, with the help of an electroscope, we can easily compare the magnitudes of two different charges.
|
259 videos|253 docs|230 tests
|
FAQs on Gold Leaf Electroscope - Physics for JAMB
| 1. What is an electroscope and how does it function? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of electroscopes? |  |
| 3. How is a Gold Leaf Electroscope constructed? |  |
| 4. What are the practical applications of an electroscope? |  |
| 5. How can you charge an electroscope? |  |
















