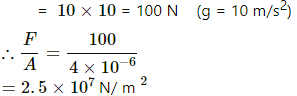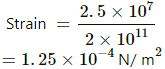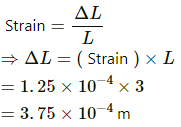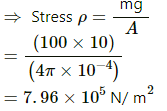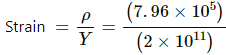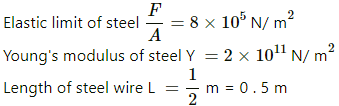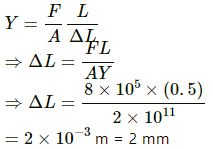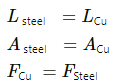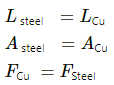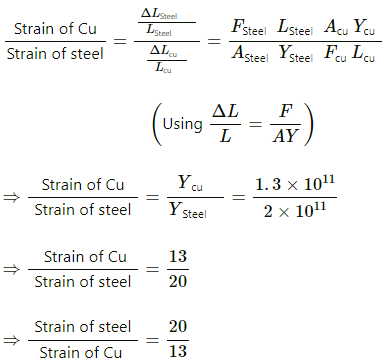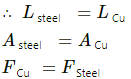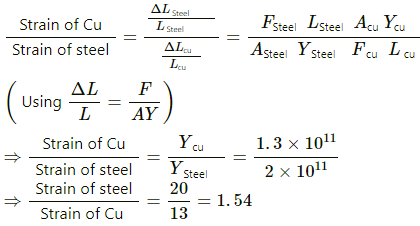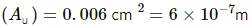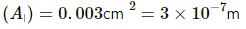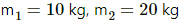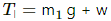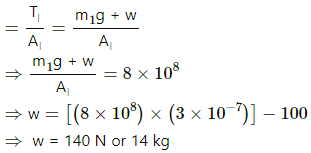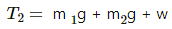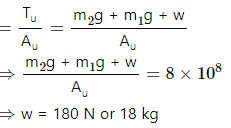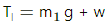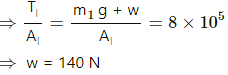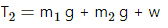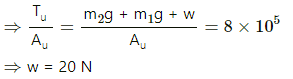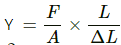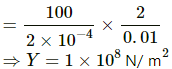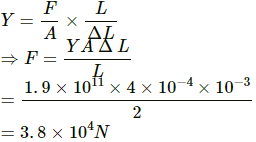HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter- 2 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Exercise
Q.1. A load of 10 kg is suspended by a metal wire 3 m long and having a cross-sectional area 4 mm2. Find (a) the stress (b) the strain and (c) the elongation. Young modulus of the metal is 2.0 × 1011 N m−2.
Given:
Mass of the load (m) = 10 kg
Length of wire (L) = 3 m
Area of cross-section of the wire (A) = 4 mm2 = 4.0 × 10−6 m2
Young's modulus of the metal Y = 2.0 × 1011 N m−2
(a) Stress = F/A
F = mg
(b) Strain = ΔL/L
Or,
Strain = Stress/Y
(c) Let the elongation in the wire be ΔL.
Q.2. A vertical metal cylinder of radius 2 cm and length 2 m is fixed at the lower end and a load of 100 kg is put on it. Find (a) the stress (b) the strain and (c) the compression of the cylinder. Young modulus of the metal = 2 × 1011 N m−2.
Given:
Radius of cylinder (r) = 2 cm = 2 x 10-2m
Length of cylinder (L) = 2 m
Mass of the load = 100 kg
Young's modulus of the metal = 2 x 1011 N/m2
(a) Stress(ρ) is given by : F/A
Here, F is the force given by mg = 100 x 10 = 1000N (Taking g = 10 m/s2)
A is the area of cross-section = πr2 = 4π x 10-4m2
(b) Strain is given by:
= 4 x 10-6
(c) Compression of the cylinder:
ΔL = strain × L
= 4 × 10−6 × 2 = 8 × 10−6 m
Q.3. The elastic limit of steel is 8 × 108 N m−2 and its Young modulus 2 × 1011 N m−2. Find the maximum elongation of a half-metre steel wire that can be given without exceeding the elastic limit.
Given :
The elastic limit of steel indicates the maximum pressure that steel can bear.
Let the maximum elongation of steel wire be ΔL.
Hence, the required elongation of steel wire is 2 mm.
Q.4.1. A steel wire and a copper wire of equal length and equal cross-sectional area are joined end to end and the combination is subjected to a tension. Find the ratio of the stresses developed in the two wires.
Given:
Young's modulus of steel = 2 × 1011 N m−2
Young's modulus of copper = 1.3 × 10 11 N m−2
Both wires are of equal length and equal cross-sectional area. Also, equal tension is applied on them.
As per the question :
Here: Lsteel and LCu denote the lengths of steel and copper wires, respectively.
Asteel and ACu denote the cross-sectional areas of steel and copper wires, respectively.
Fsteel and FCu denote the tension of steel and cooper wires, respectively.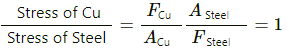
Q.4.2. A steel wire and a copper wire of equal length and equal cross-sectional area are joined end to end and the combination is subjected to a tension. Find the ratio of the strains developed. Y of steel = 2 × 1011N m−2. Y of copper = 1.3 × 10 11 N m−2.
Given:
Young's modulus of steel = 2 × 1011 N m−2
Young's modulus of copper = 1.3 × 10 11 N m−2
Both wires are of equal length and equal cross-sectional area. Also, equal tension is applied on them.
As per the question :
Here: Lsteel and LCu denote the lengths of steel and copper wires, respectively.
Asteel and ACu denote the cross-sectional areas of steel and copper wires, respectively.
Fsteel and FCu denote the tension of steel and cooper wires, respectively.
Hence, the required ratio is 20 : 13.
Q.5. In figure the upper wire is made of steel and the lower of copper. The wires have equal cross section. Find the ratio of the longitudinal strains developed in the two wires.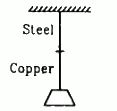
Given that both wires are of equal length and equal cross-sectional area, the block applies equal tension on both of them.
Hence, the required ratio of the longitudinal strains is 20 : 13.
Q.6.1. The two wires shown in figure are made of the same material which has a breaking stress of 8 × 108 N m−2. The area of cross section of the upper wire is 0.006 cm2 and that of the lower wire is 0.003 cm2. The mass m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and the hanger is light. Find the maximum load that can be put on the hanger without breaking a wire. Which wire will break first if the load is increased?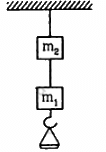
Given:
Breaking stress of wire = 8 x 108 N/m2
Area of cross - section of upper wire
Area of cross - section of lower wire
Tension in lower wire
Here : g is the acceleration due to gravity w is the load
∴ Stress in lower wire
Now, tension in upper wire
∴ Stress in upper wire
For the same breaking stress, the maximum load that can be put is 140 N or 14 kg. The lower wire will break first if the load is increased.
Q.6.2. The two wires shown in figure are made of the same material which has a breaking stress of 8 × 108 N m−2. The area of cross section of the upper wire is 0.006 cm2 and that of the lower wire is 0.003 cm2. The mass m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and the hanger is light. Repeat the above part if m1 = 10 kg and m2 = 36 kg.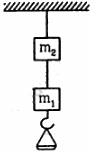
If m1 = 10kg and m2 = 36 kg
Tension in lower wire
Here: g is the acceleration due to gravity w is the load
∴ Stress in lower wire:
Now, tension in upper wire
∴ Stress in upper wire:
For the same breaking stress, the maximum load that can be put is 20 N or 2 kg. The upper wire will break first if the load is increased.
Q.7. Two persons pull a rope towards themselves. Each person exerts a force of 100 N on the rope. Find the Young modulus of the material of the rope if it extends in length by 1 cm. Original length of the rope = 2 m and the area of cross section = 2 cm2.
Given:
Force (F) applied by two persons on the rope = 100 N
Original length of rope L = 2 m
Extension in the rope ∆ L = 0 . 01 m
Area of cross - section of the rope A= = 2 x 10-4
We know that:
Young's modulus
Hence, the required Young's modulus for the rope is 1 x 108N/m2.
Q.8. A steel rod of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 and 2 m shrinks by 0.1 cm as the temperature decreases in night. If the rod is clamped at both ends during the day hours, find the tension developed in it during night hours. Young modulus of steel = 1.9 × 1011 N m−2.
Given:
Cross-sectional area of steel rod A = 4 cm2 = 4 × 10−4 m2
Length of steel rod L = 2 m
Compression during night hours ΔL = 0.1 cm = 10−3 m
Young modulus of steel Y = 1.9 × 1011 N m−2
Let the tension developed at night be F.
∴ Required tension developed in steel rod during night hours = 3.8 × 104 N.
|
134 docs
|