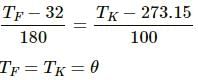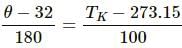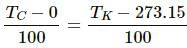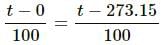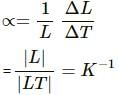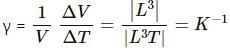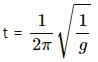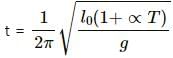Short Answers
Q.1. If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium in one frame, will they be in thermal equilibrium in all frames?
If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium in one frame, they will be in thermal equilibrium in all the frames. In case there is any change in temperature of one body due to change in frame, the same change will be acquired by the other body.
Q.2. Does the temperature of a body depend on the frame from which it is observed?
No, the temperature of a body is not dependent on the frame from which it is observed. This is because atoms /molecules of matter move or vibrate in all possible directions. Increase in velocity at a particular direction of the container/ matter does not increase or decrease the overall velocity of the molecules/atoms because of the random collisions the entities suffer. So, there is no net rise in temperature of the system.
Q.3. It is said that mercury is used in defining the temperature scale because it expands uniformly with temperature. If the temperature scale is not yet defined, is it logical to say that a substance expands uniformly with temperature?
It is not illogical to say that mercury expands uniformly before temperature scale was defined. It's uniform expansion can be studied by comparing the expansion of mercury with expansion of other substances (like alcohol water etc).
Q.4. In defining the ideal gas temperature scale, it is assumed that the pressure of the gas at constant volume is proportional to the temperature T. How can we verify whether this is true or not? Do we have to apply the kinetic theory of gases? Do we have to depend on experimental result that the pressure is proportional to temperature?
The ideal gas thermometer is based on the ideal gas equation, PV=nRT, where P is pressure of the gas at constant volume V with n number of moles at temperature T. Therefore, P = constant × T. According to this relation, if the volume of the gas used is constant, the pressure will be directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. We need not use kinetic theory of gases or any experimental results.
Q.5. Can the bulb of a thermometer be made of an adiabatic wall?
The bulb of a thermometer plays an important role in measuring the temperature of the surrounding body. It is put in contact with the body whose temperature is to be measured. The bulb attains the temperature of the body, which allows calibration of temperature. If the bulb is made of an adiabatic wall, then no heat will be transferred through the wall and the bulb cannot attain thermal equilibrium with the surrounding body. Therefore, the bulb cannot be made of an adiabatic wall.
Q.6. Why do marine animals live deep inside a lake when the surface of the lake freezes?
Water possesses an anomalous behavour. The volume of a given amount of water decreases as it is cooled from room temperature, until its temperature reaches 4 °C. Below 4 °C, the volume increases, and therefore the density decreases.
When the temperature of the surface of lake falls in winter, the water at the surface becomes denser and sinks. As, the temperature reaches below 4 oC , the density of the water at surface becomes less. Thus, it remains at surface and freezes. As, the ice is a bad conductor of heat, it traps the heat present in the lake's water beneath itself. Hence, no further cooling of water takes place once the top layer of the lake is completely covered by ice. Thus the life of the marine animals inside the lake is possible.
Q.7. The length of a brass rod is found to be less on a hot summer day than on a cold winter day as measured by the same aluminium scale. Can we conclude that brass shrinks on heating?
On a hot summer day, metals tend to expand due to the heat. Different metals have different expansion coefficients. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is more than that of brass. Therefore, it'll expand more than brass, leading to an apparent decrease in length of the brass rod, as measured by the aluminium scale. So, we cannot conclude that brass shrinks on heating. Instead, aluminium expands more than brass on heating.
Q.8. If mercury and glass had equal coefficients of volume expansion, could we make a mercury thermometer in a glass tube?
Yes, we can make a mercury thermometer in a glass tube. Mercury and glass have equal coefficients of volume expansion. So, when temperature changes, the increase in the volume of the glass tube as which is equal to the real increase in volume minus the increase in the volume of the container, would be zero. Hence, it will give correct reading at every temperature.
Q.9. The density of water at 4°C is supposed to be 1000 kg m–3. Is it same at sea level and at high altitude?
At sea level, the pressure is around 1 atmosphere and at high altitude, the density of air reduces.
Pressure of liquid,
P = hρg,
where ρ = density of fluid
The above equation shows that pressure depends on density. Therefore at 4oC, the density of water will be less at high altitude, compared to the density at sea level.
Q.10. A tightly closed metal lid of a glass bottle can be opened more easily if it is put in hot water for some time. Explain.
When a bottle with a tightly-closed metal lid is put in hot water for sometime, its lid can be opened easily because metals have greater coefficient of expansion than glass. Therefore, when the metal lid comes in contact with hot water, it'll expand more than the glass container. As a result, it will be easier to open the bottle.
Q.11. If an automobile engine is overheated, it is cooled by pouring water on it. It is advised that the water should be poured slowly with the engine running. Explain the reason.
In a hot engine the hot parts are expanded because of heat, if cold water is poured suddenly then there will be uneven thermal contraction in the parts. This will result in a stress to develop between the various parts of the engine and may let the engine to crack down.
Q.12. Is it possible for two bodies to be in thermal equilibrium if they are not in contact?
Two bodies are said to be in thermal equilibrium if they are at the same temperature. Consider two bodies A and B that are not in contact with each other but in contact with a heat reservoir. Since both the bodies will attain the temperature of the reservoir, they will be at the same temperature and, hence, in thermal equilibrium. Therefore, it is possible to have two bodies in thermal equilibrium even though they are not in contact.
Q.13. A spherical shell is heated. The volume changes according to the equation Vθ = V0 (1 + γθ). Does the volume refer to the volume enclosed by the shell or the volume of the material making up the shell?
When a spherical shell is heated, its volume changes according to the equation, 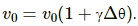 The volume referred to here is the volume of the material used to make up the shell, as its volume expands with the rise of temperature with coefficient of expansion of volume, γ.
The volume referred to here is the volume of the material used to make up the shell, as its volume expands with the rise of temperature with coefficient of expansion of volume, γ.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A system X is neither in thermal equilibrium with Y nor with Z. The systems Y and Z
Explanation
The given data in the question is insufficient to specify the relation between the physical conditions of systems Y and Z. As system X is not in thermal equilibrium with Y and Z, systems Y and Z may be at the same temperature or they may or may not be in thermal equilibrium with each other. So, the only possible option is (c).
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
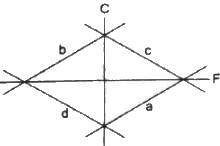
Try yourself:Which of the curves in the following figure represents the relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit temperatures?
Explanation
Celsius and Fahrenheit temperatures are related in the following way:
C = 5/9 F- 160/9
Here, F = temperature in Fahrenheit
C = temperature in Celsius
If this equation is plotted on the graph, then the curve will be represented by curve 'a' lying in the fourth quadrant with slope 5/9.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:Which of the following pairs may give equal numerical values of the temperature of a body?
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:For a constant-volume gas thermometer, one should fill the gas at
Explanation
A constant-volume gas thermometer should be filled with an ideal gas in which particles don't interact with each other and are free to move anywhere, so that the thermometer functions properly. An ideal gas is only a theoretical possibility. Therefore, the gas that is filled in the thermometer should be at high temperature and low pressure, as under these conditions, a gas behaves as an ideal gas.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:Consider the following statements.
(A) The coefficient of linear expansion has dimension K–1.
(B) The coefficient of volume expansion has dimension K–1.
Explanation
The coefficient of linear expansion,
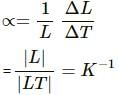
Here, L = initial length
ΔL = change in length
ΔT = change in temperature
On the other hand, the coefficient of volume expansion,
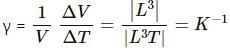
Here, V = initial volume
Δ V = change in volume
ΔT = change in temperature
K = kelvin, the S.I. unit of temperature
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A metal sheet with a circular hole is heated. The hole
Explanation
When a metal sheet is heated, it starts expanding and its surface area will start increasing, which will lead to an increase in the radius of the hole. Hence, the circular hole will become larger.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:Two identical rectangular strips, one of copper and the other of steel, are riveted together to form a bimetallic strip (acopper> asteel). On heating, this strip will
Explanation
We are provided with two metal strips of copper and steel. On heating, both of them will expand. Expansion coefficient of copper is more than that of steel. So, the copper metal strip will expand more, causing the bimetallic strip to bend with copper at the convex side, as it'll have more surface area compared to the steel sheet, which will be on the concave side.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:If the temperature of a uniform rod is slightly increased by ∆t, its moment of inertia I about a perpendicular bisector increases by
Explanation
The change in moment of inertia of uniform rod with change in temperature is given by,
I′ =I (1+2∝Δt)
Here, I = initial moment of inertia
I' = new moment of inertia due to change in temperature
∝= expansion coefficient
Δt = change in temperature
So, I′ - I = 2αIΔt
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:If the temperature of a uniform rod is slightly increased by ∆t, its moment of inertia I about a line parallel to itself will increase by
Explanation
The moment of inertia of a solid body of any shape changes with temperature as
I′ = I (1+2∝Δt)
Here, I = initial moment of inertia
I' = new moment of inertia due to change in temperature
∝ = expansion coefficient
Δt = change in temperature
So, I′ - I = 2∝IΔt
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:The temperature of water at the surface of a deep lake is 2°C. The temperature expected at the bottom is
Explanation
The density of water is maximum at 4ºC, and the water at the bottom of the lake is most dense, compared to the layers of water above. Therefore, the temperature expected at the bottom is 4ºC.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:An aluminium sphere is dipped into water at 10°C. If the temperature is increased, the force of buoyancy
Explanation
When an aluminium sphere is dipped in water and the temperature of water is increased, the aluminium will start expanding leading to increase in its volume. This will lead to increase in the surface area of the shell and it'll exert less pressure on the water such that the volume of the sphere submerged in water will decrease and it'll start float easily on water. Now, the volume of water displaced will be less compared to what was displaced initially. Therefore, the force of buoyancy will decrease, as it is directly proportional to the volume of water displaced.
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A spinning wheel is brought in contact with an identical wheel spinning at identical speed. The wheels slow down under the action of friction. Which of the following energies of the first wheel decreases?
Explanation
The kinetic energy of a body depends on its speed. Since when a spinning wheel is slowed down, its speed decreases leading to reduction in its kinetic energy. The mechanical energy of a body is defined as the sum of its potential and kinetic energies. Since the kinetic energy of the wheel has been decreased, it'll lead to decrease in its mechanical energy. When the wheel slows down due to friction, its mechanical energy gets converted into heat energy, leading to increase in internal energy, which increases with increase in temperature.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A spinning wheel A is brought in contact with another wheel B, initially at rest. Because of the friction at contact, the second wheel also starts spinning. Which of the following energies of the wheel B increases?
Explanation
When the wheel B starts spinning because of the friction at contact, it will gain kinetic energy and, hence, mechanical energy (kinetic + potential energies). Also, internal energy will increase, which increases with rise in temperature. Along with it, the generation of heat energy due to friction will lead to increase in the net sum of all the energies, i.e. total energy.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A body A is placed on a railway platform and an identical body B in a moving train. Which of the following energies of B are greater than those of A, as seen from the ground?
Explanation
As body A is at rest on the ground, it possesses only potential energy, whereas body B, being placed inside a moving train, possesses kinetic energy due to its motion along with the train. Therefore, body B will have greater kinetic, mechanical (energy possessed by the body by virtue of its position and motion = kinetic energy+potential energy) energy and, hence, total (sum of all the energies) energy. No information is given about the temperature of the body so we can not say wheather body B' s internal energy will be or will not be greater than that of body A.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:In which of the following pairs of temperature scales, the size of a degree is identical?
Explanation
Celsius scale and ideal gas scale measure temperature in kelvin (K) and the ideal gas scale is sometimes also called the absolute scale. A mercury scale gives reading in degrees and its size of degree, which depends on length of mercury column, doesn't match any of the above-mentioned scales.
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:A solid object is placed in water contained in an adiabatic container for some time. The temperature of water falls during this period and there is no appreciable change in the shape of the object. The temperature of the solid object
Explanation
The whole system (water + solid object) is enclosed in an adiabatic container from which no heat can escape. After some time, the temperature of water falls, which implies that the heat from the water has been transferred to the object, leading to increase in its temperature.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 23: Heat and Temperature- 1
Try yourself:As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum
Explanation
In general, the time period of a pendulum,t, is given by
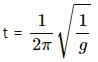
When the temperature (T) is increased, the length of the pendulum (l) is given by,
l =l0(1+∝T),
where l0 = length at 0ºC
∝ = linear coefficient of expansion.
Therefore, the time period of a pendulum will be
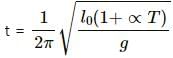
Hence, time period of a pendulum will increase with increase in temperature.
Report a problem
The volume referred to here is the volume of the material used to make up the shell, as its volume expands with the rise of temperature with coefficient of expansion of volume, γ.