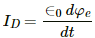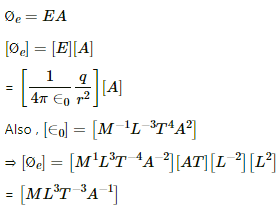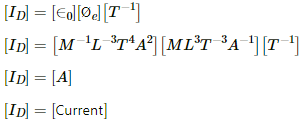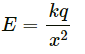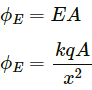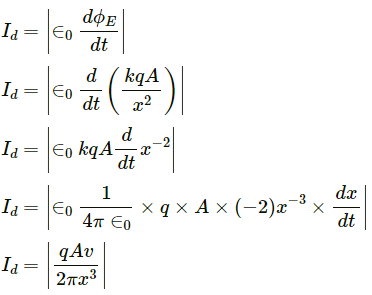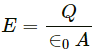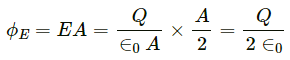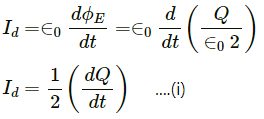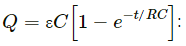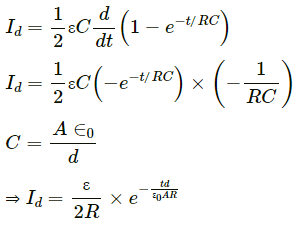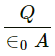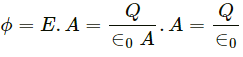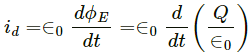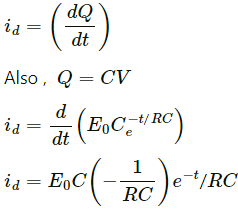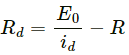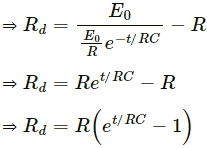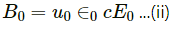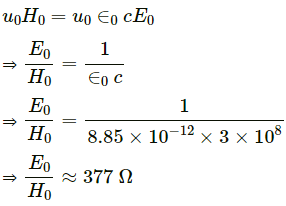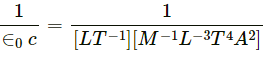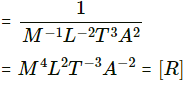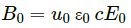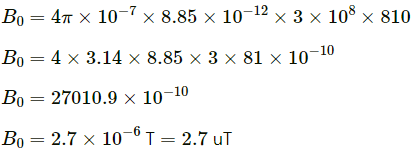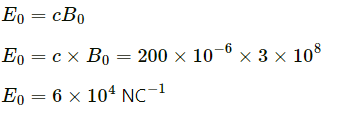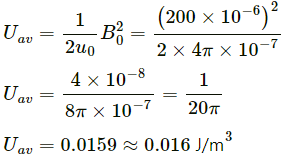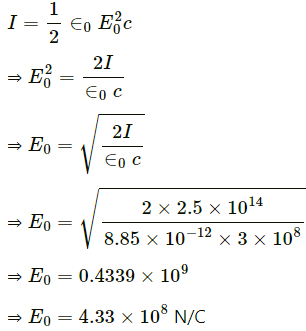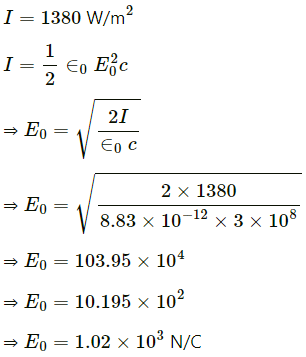HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 40: Electromagnetic Waves- 2 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Exercises
Q.1. Show that the dimensions of the displacement current 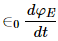 are that of an electric current .
are that of an electric current .
Displacement current,
Electric flux,
Displacement current,
Q.2. A point charge is moving along a straight line with a constant velocity v. Consider a small area A perpendicular to the motion of the charge. Calculate the displacement current through the area when its distance from the charge is x. The value of x is not large, so that the electric field at any instant is essentially given by Coulomb's law.
From Coulomb's law :
Electric field strength,
Electric flux,
Displacement current = Id
Q.3. A parallel-plate capacitor of plate-area A and plate separation d is joined to a battery of emf ε and internal resistance R at t = 0. Consider a plane surface of area A/2, parallel to the plates and situated symmetrically between them. Find the displacement current through this surface as a function of time.
Electric field strength for a parallel plate capacitor,
Electric flux linked with the area,
Displacement current ,
Charge on the capacitor as a function of time during charging,
Putting this in equation (i), we get :
Q.4. Consider the situation of the previous problem. Define displacement resistance Rd = V/id of the space between the plates, where V is the potential difference between the plates and id is the displacement current. Show that Rd varies with time as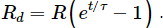
Electric field strength for a parallel plate capacitor = E =
Electric flux,
Displacement current,
Displacement resistance,
Q.5. Using B = µ0 H, find the ratio E0/H0 for a plane electromagnetic wave propagating through vacuum. Show that it has the dimensions of electric resistance. This ratio is a universal constant called the impedance of free space.
Given, B = µ0H
For vacuum we can rewrite this equation as,
B0 = µ0H0 ...(i)
Relation between magnetic field and electric field for vacuum is given as,
From equation (i) by (ii),
Dimension of
Q.6. The sunlight reaching Earth has maximum electric field of 810 Vm−1. What is the maximum magnetic field in this light?
Given :
Electric field amplitude, E0 = 810 V/m
Maximum value of magnetic field = Magnetic field amplitude = B0 = ?
We know :
Speed of a wave = E/B
For electromagnetic waves, speed = speed of light
Putting the values in the above relation , we get :
Q.7. The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by
B = (200 µT) sin [(4.0 × 1015s−1)(t−x/c)].
Find the maximum electric field and the average energy density corresponding to the electric field.
Maximum value of a magnetic field, B0 = 200uT
The speed of an electromagnetic wave is c.
So, maximum value of electric field,
(b) Average energy density of a magnetic field,
For an electromagnetic wave, energy is shared equally between the electric and magnetic fields.
Hence, energy density of the electric field will be equal to the energy density of the magnetic field.
Q.8. A laser beam has intensity 2.5 × 1014 W m−2. Find amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields in the beam.
Given:
Intensity, I = 2.5 × 1014 W/m2
We know :
Maximum value of magnetic field,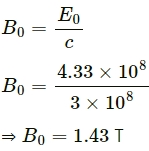
Q.9. The intensity of the sunlight reaching Earth is 1380 W m−2. Assume this light to be a plane, monochromatic wave. Find the amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields in this wave.
Given :
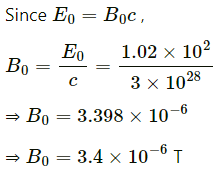
|
134 docs
|