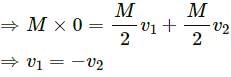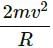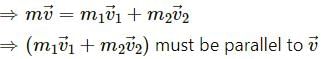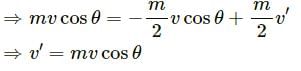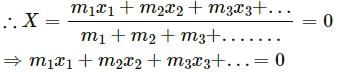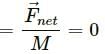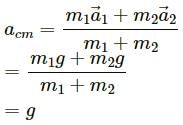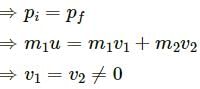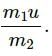HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision- 1 | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Short Answers
Q.1. Can the centre of mass of a body be at a point outside the body?
Yes, the centre of mass can be at a point outside the body.
For example, the centre of mass of a ring lies at its centre, which is not a part of the ring.
Q.2. If all the particles of a system lie in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in X-Y plane?
Yes, if all the particles of a system lie in the X–Y plane, then it's necessary that its centre of mass lies in the X–Y plane.
As all the particles lie in the X–Y plane, their z-coordinates are zero.
Therefore, for the whole system, zcm = 0; i.e., its centre of mass lies in the X–Y plane.
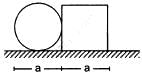
Q.3. If all the particle of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in the cube?
Yes. As a cube is a 3-dimensional body, all the particles of a system lying in a cube lie in the x,y and z plane.
Let the ith element of mass ∆mi is located at the point (xi,yi,zi).
The co-ordinates of the centre of mass are given as:
X, Y and Z lie inside the cube because it is a weighted mean.
Q.4. The centre of mass is defined as 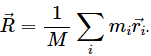 Suppose we define "centre of charge" as
Suppose we define "centre of charge" as 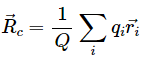 where qi represents the ith charge placed at
where qi represents the ith charge placed at  and Q is the total charge of the system.
and Q is the total charge of the system.
(a) Can the centre of charge of a two-charge system be outside the line segment joining the charges?
(b) If all the charges of a system are in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in X-Y plane?
(c) If all the charges of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in the cube?
(a) Yes
Consider a charge distributed in X-Y plane.
(b) Yes. Because the z-coordinates of all the charges are zero, the centre of charge lies in X-Y plane.
(c) No, it is not necessary that the centre of charge lies in the cube because charge can be either negative or positive.
Q.5. The weight Mg of an extended body is generally shown in a diagram to act through the centre of mass. Does it mean that the earth does not attract other particles?
In order to simplify the situation, we consider that the weight Mg of an extended body acts through its centre of mass.
Although the earth attracts all the particles, the net effect can be assumed to be at the centre of mass.
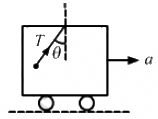
Q.6. A bob suspended from the ceiling of a car which is accelerating on a horizontal road. The bob stays at rest with respect to the car with the string making an angle θ with the vertical. The linear momentum of the bob as seen from the road is increasing with time. Is it a violation of conservation of linear momentum? If not, where is the external force changes the linear momentum?
There is no violation of conservation of momentum because in the earth's frame the component of tension is acting in the horizontal direction.
Q.7. You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
The trunk does not recoil as the girl jumps off on the platform because the force exerted by the girl is less than the limiting friction between the platform and the iron trunk.
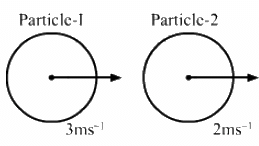
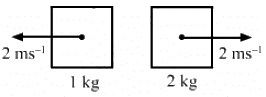
Q.8. In a head-on collision between two particles, is it necessary that the particles will acquire a common velocity at least for one instant?
Yes.
For example, consider particle-1 at a velocity of 4 ms-1 and particle-2 at a velocity of 2 ms-1 undergo a head-on collision.
The velocity of particle-1 decreases but particle-2 increases. Therefore, at an instant, their velocities will be equal.
Q.9. A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the non-inertial character of the frame?
No. As the collision experiment is being done on a horizontal table in the elevator that is accelerating up or down in vertical direction, no extra force is experienced in the horizontal direction. Hence, the objects in the horizontal direction remain unaffected.
Q.10. Two bodies make an elastic head-on collision on a smooth horizontal table kept in a car. Do you expect a change in the result if the car is accelerated in a horizontal road because of the non inertial character of the frame? Does the equation "Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach" remain valid in an accelerating car? Does the equation "final momentum = initial momentum" remain valid in the accelerating car?
No, due to the non-inertial character of the frame and the presence of a pseudo force, both the equations, i.e., Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach and Final momentum = Initial momentum, do not remain valid in the accelerating car.
Q.11. If the total mechanical energy of a particle is zero, is its linear momentum necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
No. As the potential energy can have a negative value, the total energy of the system may sum up to zero.
For example:
Two masses A and B having masses 2 kg and 4 kg respectively move with a velocity of 4 ms-1 in opposite directions.
Kinetic energy of system (A and B)
If the gravitational potential energy of the system is −48 J, the total energy of the system will be zero. However, the linear momentum will be non-zero.
Q.12. If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Yes, the kinetic energy of the particle can be determined if the value of linear momentum is known. The kinetic energy is calculated using the formula:
where, p is the linear momemtum having value mv.
But linear momentum cannot be determined even if the kinetic energy is known because linear momentum is a vector quantity, whereas kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. Thus, the direction of the linear momentum remains unknown, however its magnitude can be calculated.
Q.13. What can be said about the centre of mass of a uniform hemisphere without making any calculation? Will its distance from the centre be more than r/2 or less than r/2?
The distance of centre of mass of a uniform hemisphere from its centre will be less than r/2 because the portion of the hemisphere lying below r/2 from the diameter is heavier than the portion lying above r/2.
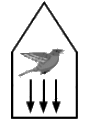
Q.14. You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
More effort is needed when the cage is closed, while less effort is required when the cage has rods to let the air pass. When a bird flies from its position, it pushes the air downwards. Thus, when the bird is in a cage, the net downward force will be equal to the weight of the cage plus the downward force due to air (the weight of the bird).
However, if the cage has rods to let air pass, the downward force exerted by air become less. Therefore, less effort will be required to hold the cage.
Q.15. A fat person is standing on a light plank floating on a calm lake. The person walks from one end to the other on the plank. His friend sitting on the shore watches him and finds that the person hardly moves any distance because the plank moves backward about the same distance as the person moves on the plank. Explain.
According to the question, the weight of plank is very less as compared to the fat person. Therefore, the centre of mass of the whole system effectively lies on the person. As the net external force on the system is zero, the centre of mass of the system does not move.
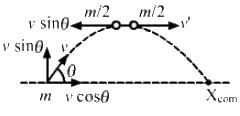
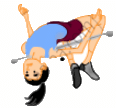
Q.16. A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
From the figure, it can be seen that when a high-jumper successfully clears the bar, it is possible that her centre of mass crosses the bar from below it because the legs as well as the arms of the high-jumper are below the bar.
Hence, the point shown in the figure can be her Centre of mass.
Q.17. Which of the two persons shown in figure is more likely to fall down? Which external force is responsible for his falling down?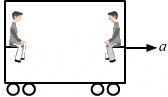
The person shown on the right hand side of the figure is more likely to fall down because in the given cart frame the pseudo force will be in backward direction.
Q.18. Suppose we define a quantity 'Linear momentum' as linear momentum = mass × speed.
The linear momentum of a system of particles is the sum of linear momenta of the individual particles. Can we state principle of conservation of linear momentum as "linear momentum of a system remains constant if no external force acts on it"?
It is not necessary that the linear momentum of a system remains constant even if no external force acts on it because during collision, the sum of magnitudes of momenta does not remain constant.
Q.19. Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
Yes, if the external force applied on the particle is zero, its speed does not change and hence, the momentum remains constant.
Q.20. To accelerate a car we ignite petrol in the engine of the car. Since only an external force can accelerate the centre of mass, is it proper to say that "the force generated by the engine accelerates the car"?
Yes, it's proper to say that the force generated by the engine accelerates the car. When petrol burns inside the engine, the piston moves, which in turn rotates the wheel. As the wheel rotates, the frictional forces from the road moves the car.
Q.21. A ball is moved on a horizontal table with some velocity. The ball stops after moving some distance. Which external force is responsible for the change in the momentum of the ball?
The frictional force acting between the surface of the table and the ball is responsible for the change in momentum of the ball. As the force opposes the motion of the ball, it stops after moving some distan.
Q.22. Consider the situation of the previous problem. Take "the table plus the ball" as the system. friction between the table and the ball is then an internal force. As the ball slows down, the momentum of the system decreases. Which external force is responsible for this change in the momentum?
Considering the table plus the ball as a system, it can be said that the frictional force is responsible for the change in the momentum. As the force acts between the surface of the table and ground, it opposes the motion of the table plus the ball. Hence, the ball slows down and the momentum of the system decreases.
Q.23. When a nucleus at rest emits a beta particle, it is found that the velocities of the recoiling nucleus and the beta particle are not along the same straight line. How can this be possible in view of the principle of conservation of momentum?
In view of the principle of conservation of momentum, the given situation is possible because as a beta particle is ejected, another particle called an antineutrino is also ejected.
Q.24. A van is standing on a frictionless portion of a horizontal road. To start the engine, the vehicle must be set in motion in the forward direction. How can be persons sitting inside the van do it without coming out and pushing from behind?
According to the question, the van is standing on a frictionless surface. When throwing something in backward direction, the persons sitting inside the van sets the van in motion in the forward direction according to the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
Q.25. In one-dimensional elastic collision of equal masses, the velocities are interchanged. Can velocities in a one-dimensional collision be interchanged if the masses are not equal?
No. If the masses are different, the velocities in a one-dimensional collision cannot be interchanged because that would be violation of the principle of conservation of momentum.
Multiple Choice Questions
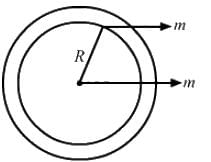
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision- 1Try yourself:All the particles of a body are situated at a distance R from the origin. The distance of the centre of mass of the body from the origin is
View Solution
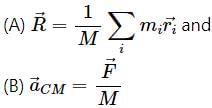
In a noninertial frame
(A) Linear momentum of the system remains constant.
(B) Centre of mass of the system remains at rest.
(A) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero.
(B) Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.
(A) The linear momentum of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
(B) The kinetic energy of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
 emits an α-particle. Let the velocities of the α-particle and the remaining nucleus be v1 and v2 and their masses be m1 and m2.
emits an α-particle. Let the velocities of the α-particle and the remaining nucleus be v1 and v2 and their masses be m1 and m2.
|
134 docs
|
FAQs on HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision- 1 - HC Verma Solutions - JEE
| 1. What is the concept of centre of mass? |  |
| 2. How is linear momentum defined and calculated? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of centre of mass in real-life scenarios? |  |
| 4. How does the concept of collision relate to the study of linear momentum? |  |
| 5. How can the centre of mass of an irregularly shaped object be determined? |  |


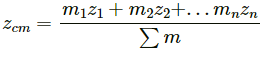
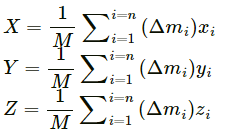
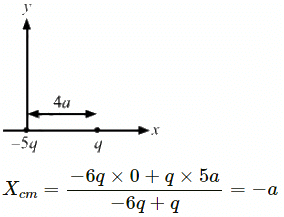
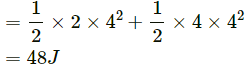
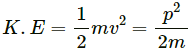
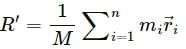
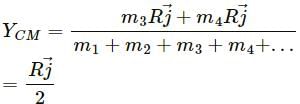
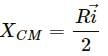
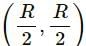
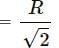
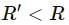
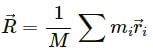
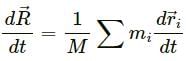
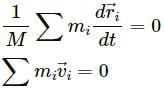
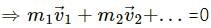
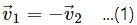
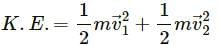
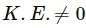
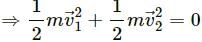
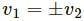
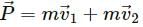
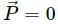
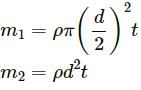
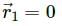
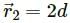
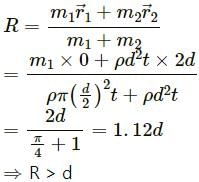
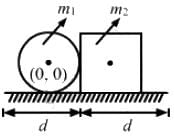
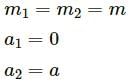
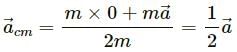
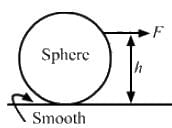
 , which is independent of height h.
, which is independent of height h.