HOTS Questions: Maps and Locations | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1: Calculate the area of rectangle if one square represents an area of 1 cm2. A) 2cm2
A) 2cm2
B) 9cm2
C) 50cm2
D) 24cm2
Ans: (d)
Sol: There are 6 ×4 = 24 squares and each square has an area of = 1cm2. So, the area of rectangle
= 6 × 4 × 1 = 24cm2.
Q2: What is the area of rectangle if Length = 2m, Breadth = 5m
A) 12m2
B) 14m2
C) 10m2
D) 18m2
Ans: (c)
Sol: The area of rectangle is given by length × breadth. So the area is 2 × 5 = 10m2.
Q3: Each side of square is of 10m. What will be the area of the square?
A) 100m2
B) 90m2
C) 34m2
D) 115m2
Ans: (a)
Sol: Area of square = side × side =10 × 10= 100m2.
Q4: The third side of the triangle if the perimeter of a triangle is 20m and two of its sides are 5m and 4m, is
A) 11 m
B) 10m
C) 12m
D) 5m
Ans: (a)
Sol: Perimeter of a triangle =1st side + 2nd side + 3rd side So, 20 = 5 + 4 + 3rd side 3rd side
= 20 − 9
= 11m.
Q5: Find the missing side in the figure given below if the perimeter of the figure is 28m.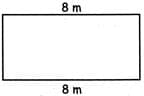 A) 12m
A) 12m
B) 3m
C) 9m
D) 6m
Ans: (c)
Sol: Given figure is a rectangle. Also, given I = length = 8m Let b be the breadth of the rectangle. Perimeter of rectangle = 2(1 + b) = 28
⇒ l + b = 28 / 2
⇒ l + b = 14 ⇒ b = 14 ? 8 = 6m.
Q6: Find the area of shaded region. (Each square = 1m2)
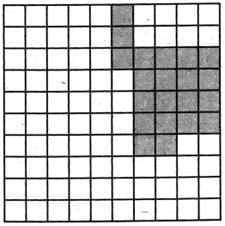 A) 21m2
A) 21m2
B) 35m2
C) 34m2
D) 13m2
Ans: (a)
Sol: Calculate no. of shaded boxes. It comes out to be 21. And each box has area of 1m2. So the area of shaded region becomes 21m2.
Q7:The length and breadth of a rectangle are (3a + 2) and (2a - 1). Which of the following represents its perimeter?
A) 2(5a - 1)
B) (5a + 1)
C) (5a - 1)
D) 2(5a + 1)
Ans: (d)
Sol: Perimeter = 2[3a + 2 + 2a - 1] = 2[5a + 1]
Q8: The difference between the length and the breadth of a rectangle is 8 cm and the perimeter is 64 cm. Which of the following can be the length and breadth of this rectangle?
A) L = 12 cm, B = 4 cm
B) L = 20 cm, B = 8 cm
C) L = 20 cm, B = 12 cm
D) L = 12 cm, B = 8 cm
Ans: (c)
Sol: Length of rectangle = x cm Breadth of rectangle = (x - 8) cm
Perimeter of rectangle = 2(x + x - 8)
= 2(2x - 8) Given 2(2x - 8)
= 64
⇒ 2x = 40
⇒ x = 20 L = 20,
B = 20 - 8 = 12
Q9: The area of a triangle whose base is 12 cm and the Height twice the base, is
A) 144sq.cm
B) 288 sq. cm
C) 289 sq. cm
D) Cannot be determined
Ans: (a)
Sol: Base of Δ = 12 cm
Height of Δ = 2 × 12 = 24cm
Area of Δ = 12 × 12 × 24
= 144sq.cm.
Q10: The area of a square is 100 sq. cm. If the sides this square are increased by 10% then what will be the area of new square?
A) 121 sq. cm
B) 101 sq. cm
C) 81 sq. cm
D) 169 sq. cm
Ans: (a)
Sol: Given area of square = 100 side × side = 100 = 10 × 10
⇒Side = 10 cm
Increased in side of square = 10% of 10 = 1
∴ New side = 10 + 1 = 11
∴ Area of new square =(11)2
=121sq.cm.
Q11: The breadth of a rectangle is increased by 2 units. Its perimeter is now increased by?
A) 2 units
B) 4 units
C) 8 units
D) 16 units
Ans: (b)
The initial perimeter (P1) of the rectangle is given by:
P1 = 2L + 2B
Now, the breadth is increased by 2 units, so the new breadth is B + 2.
The new perimeter (P2) of the rectangle with the increased breadth is given by:
P2 = 2L + 2(B + 2) = 2L + 2B + 4
The increase in perimeter (ΔP) is the difference between the new perimeter and the initial perimeter:
ΔP = P2 - P1 = (2L + 2B + 4) - (2L + 2B) = 4
So, the perimeter is increased by 4 units when the breadth of the rectangle is increased by 2 units.
The correct answer is (B) 4 units.
Q12: The area of a square is equal to the area of a rectangle of I = 8 cm and b = 2 cm. What is the side of the square?
A) 6 cm
B) 4 cm
C) 3 cm
D) 8 cm
Ans: (b)
Q13: How many small cubes of side 2 cm can be put in a cubical box of side 6 cm?
A) 9
B) 12
C) 27
D) 6
Ans: (c)
Sol: Volume of the cubical box = (side length)3 = (6 cm)3 = 216 cubic cm.
Volume of one small cube = (side length)3 = (2 cm)3 = 8 cubic cm.
Now, divide the volume of the box by the volume of one small cube:
Number of small cubes that can fit = (Volume of box) / (Volume of one small cube) = 216 cubic cm / 8 cubic cm = 27.
So, you can fit 27 small cubes with a side length of 2 cm inside a cubical box with a side length of 6 cm.
The correct answer is (C) 27.
Q14: A cuboid measures 24m × 12m × 10m.how many cubes of side 3m can fit in the box?
A) 9
B) 16
C) 15
D) 24
Ans: (a)
Sol: 9 m
Q15: Area of a square is:
A) product of all sides
B) sum of all sides
C) side × side
D) 2 × side
Ans: (c)
Q16: Calculate the area of rectangle given below if each square has an area of 4m2.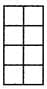 A) 80m2
A) 80m2
B) 64m2
C) 40m2
D) 15m2
Ans: (c)
Sol: There are 2 x 5 = 10 squares and each square has an area of 4m2 So, the area of rectangle
= 2 × 5 × 4 = 40m2.
Q17: Which of these figures represents the area of 24m2 if given that each block  = 2m2
= 2m2
(a) 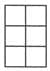
(b) 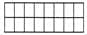
(c) 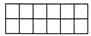
(d) 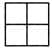
Ans: (c)
Sol: Given each block is of 2m2,so there should be 12 blocks in a figure to get an area of 24m2. In option (c), there are 2 × 6 = 12 blocks in figure.
Q18: Area of rectangle is 32m2. If the length is 8m then breadth = ________
A) 20m
B) 4m
C) 10m
D) 12m
Ans: (b)
Sol: Given, area = length × breadth
⇒ breadth = area ÷ length
So, the breadth = 32/8
= 4m.
Q19: Consider the following two statements.
Statement A: Perimeter is defined as the length of boundary line of a close geometrical figure.
Statement B: Holding capacity of a container is called volume.
Which one of the following option is correct about the above statements?
A) Only A is correct.
B) Only B is correct
C) Both A and B are correct.
D) Neither A nor B are correct.
Ans: (c)
- Statement A accurately defines what perimeter is, which is the length of the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
- Statement B accurately defines what volume is, which is the holding capacity of a container or the amount of space enclosed by a three-dimensional object.
- Both statements are correct in their respective definitions.
Q20: Consider the following two statements.
Statement A: If edge of a cube measures 25 m and I = 20 m, b = 20m, h = 30 m are the measures of a cuboid then cuboid has the larger volume.
Statement B: Dilip breaks a rod of 90 cm into four equal pieces. Taking three parts he makes a triangle by joining end to end. Perimeter of the triangle is 67.5 cm.
Which one of the following option is correct about the above statements?
A) Statement A is false and B is correct.
B) Statement A is true and B is false.
C) Both statements are true.
D) Both statements are false.
Ans: (a)
Statement A is false. In statement A cube has the larger volume.
Statement B: Each part = 90 / 4 = 2.25cm.
∴ Perimeter of triangle = 3 × (22.5)cm = 67.5cm.
|
35 videos|276 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on HOTS Questions: Maps and Locations - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key elements of a map that help in understanding locations? |  |
| 2. How do maps differ from globes in representing locations? |  |
| 3. Why is understanding map scales important in geography? |  |
| 4. How can symbols on a map enhance the understanding of locations? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of maps, and what purposes do they serve? |  |















