EmSAT Achieve Exam > EmSAT Achieve Notes > Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve > Half Life
Half Life | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Introduction
- Half-Life, also referred to as the Half-Life Period, is a frequently used term in physics to characterize the radioactive decay of a specific sample or element over a defined time interval. Students studying nuclear physics encounter this term frequently during their studies.
- Nevertheless, the concept of half-life is not limited to radioactive decay alone. It is also employed to describe different types of decay processes, including exponential and non-exponential decay. In addition to its usage in physics, the term finds application in medical sciences to denote the biological half-life of certain chemicals within the human body or in pharmaceutical drugs.
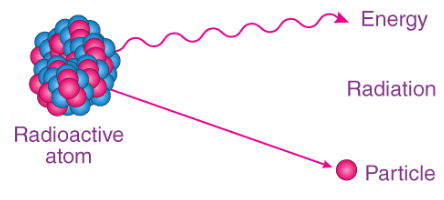
Definition of Half-Life
- The term "half-life" is commonly defined as the time required for a radioactive substance (or half of its atoms) to undergo disintegration or transform into a different substance. This principle was first discovered by Ernest Rutherford in 1907 and is typically denoted by the symbol Ug or t1/2.
- To illustrate this concept, let's consider a radioactive element with a half-life of one hour. In this case, half of the atoms would decay within the first hour, and the remaining half would decay within the subsequent hour. This prompts the question: why doesn't the remaining material decay within the initial hour?
- The reason lies in the assumption that when a radioactive element has undergone decay for half of its half-life, the remaining atoms possess a relatively long average lifespan. This suggests that the half-life divided by 2, represented by the natural logarithm, approximates the average lifespan. Alternatively, half-life is often defined in terms of probability.
Understanding the Concept through an Experiment
- To grasp the process of radioactive decay, let's conduct an experiment using a large group of individuals, ensuring that statistical observations yield clear results.
- Imagine a scenario where around 1000 people are gathered in a hall, with each person given a coin representing their capacity to decay, akin to atoms with radioactivity. Each individual is instructed to flip their coin once per minute. If the result is heads, the person must leave the hall (representing atom decay), while a tails result prompts them to wait for another minute before flipping again.
- Through the aforementioned example, one can appreciate the enthusiasm surrounding this topic among students, given its significance. It is no wonder that the subject of radioactivity continues to be extensively researched in the future.
Half-Life Formulas
Students will find below the formulas for half-life that are used to describe the decay in substances.
- N(t) = No (½) t / t ½
- N(t) = No e-t / r
- N(t) = Noe– λt
Here we consider the following,
- N0 = the initial quantity of the substance
- N(t) = the quantity that is left over
- t1⁄2 = half-life
- τ = mean lifetime of the decaying quantity
- λ = decay constant
The document Half Life | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve is a part of the EmSAT Achieve Course Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve.
All you need of EmSAT Achieve at this link: EmSAT Achieve
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
Related Searches




















