Year 6 Exam > Year 6 Notes > Year 6 Computing > How do digital images work?
How do digital images work? | Year 6 Computing PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are pixels? |

|
| What are bitmap images? |

|
| What are vector images? |

|
| Working with Objects |

|
What are pixels?
- A digital image is a picture stored on a computer, created by assembling numerous tiny squares known as pixels (short for picture element).
- When an image is digitized to be stored on a computer, it's transformed into a set of pixels.

How do pixels make up an image?
- Imagine an avatar with a square grid overlaid on it. Each square in the grid represents a pixel.
- The computer assigns a number to represent the color of each pixel to store the image, akin to a digital color-by-numbers activity.

How Pixels Make Up a Display?
- When you observe a computer screen closely, you'll notice it comprises millions of small squares, known as pixels.
- Each of these squares represents a pixel.
- To showcase an image, the computer instructs the screen to display a specific color for each pixel.

How Pixel Images are Stored?
- Images composed of pixels can be saved as files utilizing various formats.
- Different file types employ pixels in different ways to store the image.
Some common formats include:- JPEG
- TIFF
- PNG
- GIF
- BMP (short for bitmap)

What are bitmap images?
- A bitmap image is a type of image format that stores graphics using a grid of individual pixels. The term "bitmap" comes from the fact that it is essentially a map of where each bit of information is located. Each pixel's color information is represented as a sequence of numbers.
- In a simple black and white bitmap image, only two colors are used - black and white. Each pixel is represented by a single bit, where '1' typically signifies black and '0' signifies white. This binary representation simplifies the storage of such images.
- For color images, more complex bit patterns are used to represent a wider range of colors. Typically, 24 bits are used to represent the color of each pixel. With 24 bits, it is possible to represent up to 16.8 million different colors in an image, providing a rich and detailed color palette.
Question for How do digital images work?Try yourself: What is the term used for a type of image format that stores graphics using a grid of individual pixels?View Solution
What are vector images?
- Definition of Vector Images: Vector images differ from traditional images as they are constructed using lines, curves, and shapes instead of pixels.
- Components of Vector Graphics:
- Lines, Curves, and Shapes: Instead of being composed of pixels, vector graphics are built using these elements.
- Objects: Each element within a vector graphic is referred to as an object, which is easily editable and modifiable.
- Advantages of Vector Graphics:
- Editable Nature: Objects in vector graphics can be easily modified without compromising image quality.
- Smooth Lines: Algorithms used to store objects ensure smooth lines, making vector graphics ideal for diagrams and graphics.
- Comparison with Raster Graphics:
- Raster Images vs. Vector Images: Raster graphics, composed of pixels, can lose quality when resized, unlike vector graphics.
- Photographs as Raster Images: Photographs are typically raster images due to their pixel-based composition.
Working with Objects
Vector graphic applications offer numerous methods for manipulating objects.
- Resizing Objects
- Vector graphic applications offer various methods to resize objects, allowing you to make them larger or smaller as needed.
- For instance, in design software like Adobe Illustrator, you can easily adjust the size of shapes, text, or images by dragging the corners of the object.
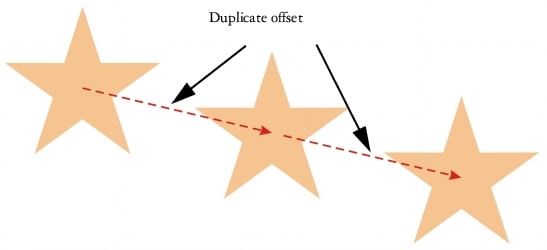
Duplicating Objects
- You can quickly create copies of objects within vector graphics applications.
- For example, in programs like CorelDRAW, duplicating an object is as simple as selecting it and then using a keyboard shortcut to create a copy.
Alignment
- Objects can be aligned next to each other in a straight line to create a visually appealing composition.
- Tools like Adobe InDesign allow users to align objects precisely using grids and guides for professional layouts.
Layers
- Objects in vector graphic design can be organized in layers, allowing you to place them in front of or behind other elements.
- Software like Sketch enables designers to work with layers, making it easier to manage complex designs by separating elements into different levels.

The document How do digital images work? | Year 6 Computing is a part of the Year 6 Course Year 6 Computing.
All you need of Year 6 at this link: Year 6
|
19 videos|26 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on How do digital images work? - Year 6 Computing
| 1. How do digital images work? |  |
Ans. Digital images work by converting light into electronic signals that are then translated into digital data. This data is captured by a digital camera, processed by a computer or electronic device, and displayed on a screen as an image.
| 2. What is the difference between a digital image and a printed image? |  |
Ans. A digital image is stored as electronic data on a computer or device, while a printed image is a physical copy of that data on paper or another medium. Digital images can be easily edited and shared electronically, while printed images are static and require physical reproduction.
| 3. What are pixels and how do they affect digital images? |  |
Ans. Pixels are the smallest controllable element of a digital image. They are tiny dots that make up the image and determine its resolution and clarity. The more pixels there are in an image, the higher the resolution and quality will be.
| 4. How is color represented in digital images? |  |
Ans. Color in digital images is represented using a combination of red, green, and blue light, known as RGB. Each pixel in a digital image is made up of these three colors in varying intensities, which combine to create the full spectrum of colors visible to the human eye.
| 5. How can digital images be compressed for storage or transmission? |  |
Ans. Digital images can be compressed using algorithms that reduce the file size by removing redundant or unnecessary data. This compression allows for easier storage, sharing, and transmission of images without significantly affecting the quality of the image.
Related Searches



















