Human Diseases | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Transmission of Diseases
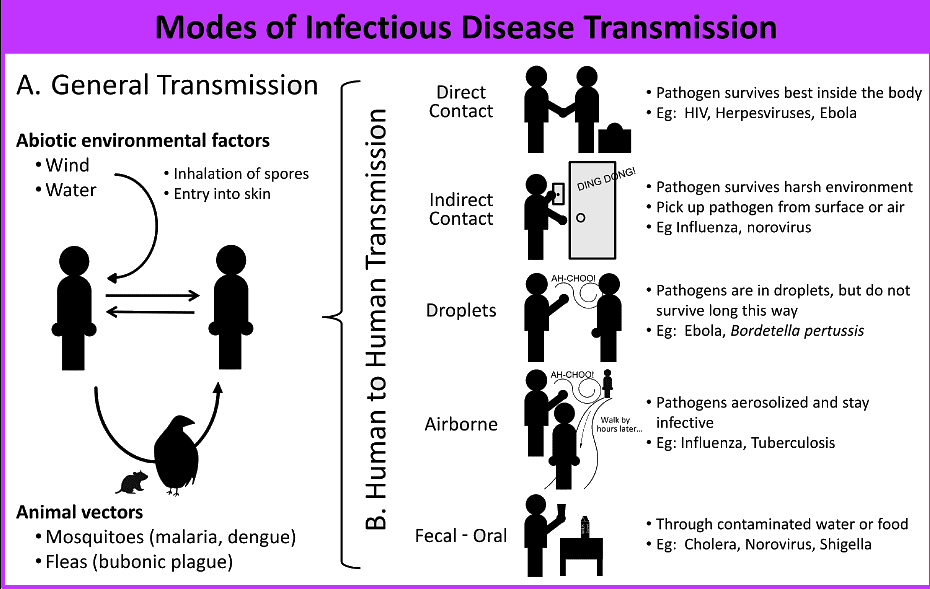
Diseases can be transmitted from one host to another through four primary routes: airborne, contact, vehicle, and vector-borne transmission.
Airborne Transmission Pathogens remain suspended in the air and are transmitted through droplet nuclei, which can linger for hours or days. These pathogens cannot grow in the air but can be carried to individuals. Examples of airborne diseases include chickenpox, flu, measles, mumps, viral pneumonia, diphtheria, pneumonia, tuberculosis, and meningitis.
Contact Transmission Pathogens spread through direct contact with the host and the pathogen reservoir. This includes person-to-person contact via touching, kissing, or sexual activity. Diseases transmitted through contact include herpes, boils (through oral secretions or body lesions), staphylococcal infections (by nursing mothers), and AIDS and syphilis (through placenta or blood-to-blood contact).
Vehicle Transmission Vehicles refer to inanimate objects such as utensils, towels, bedding, surgical materials, needles, food, and water. Bacteria that spread through food and cause food poisoning include Staphylococcus, Bacillus cereus, E. coli, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella typhi, and Clostridium difficile.
Vector-Borne Transmission A vector is a living organism that transmits a pathogen, such as vertebrates (e.g., dogs, cats, bats, goats, sheep) or arthropods (e.g., fleas, mites, insects, ticks). For example, flies can carry Shigella from feces to food materials. When a pathogen does not undergo changes within the vector, it is called harborage transmission.
Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, are long-lasting and result from a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental, and behavioral factors. The main types of NCDs are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma), and diabetes.
Classification of Diseases
Human diseases can be classified into several categories:
Caused by Microbes
- Protozoan Diseases
- Viral Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
Diseases of Sex Chromosomes
Diseases of Different Organ Systems
- Genetic Diseases:
- Nervous System Diseases
- Heart Diseases
- Blood Diseases
- Respiratory Diseases
- Skeletal Diseases
- Kidney Diseases
Diseases Caused by Microbes
Protozoan Diseases
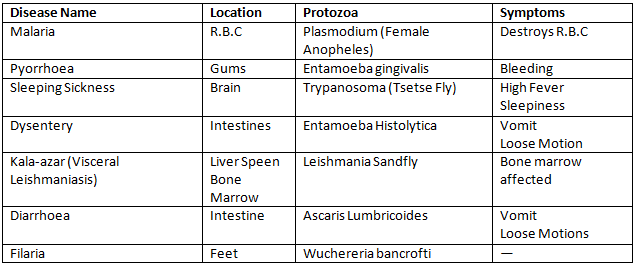
Viral Diseases
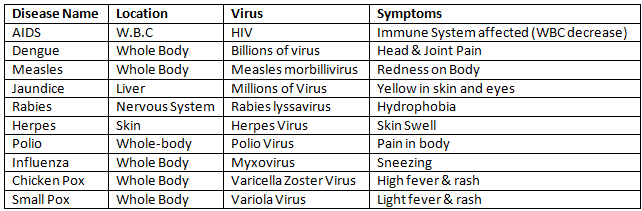
Fungal Diseases
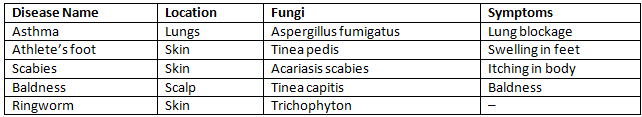
Bacterial Diseases
Diseases of Sex Chromosomes
Turner Syndrome
- A disorder caused by abnormalities in sex chromosomes, specifically when an individual has a single X chromosome (45, X).
- Only one X chromosome is functional, resulting in underdeveloped reproductive organs and infertility in affected women.
Klinefelter Syndrome
- This disorder occurs in males who have an extra X or Y chromosome (e.g., XXY or XYY), leading to a total of 47 chromosomes.
- Affected males are typically underdeveloped and infertile, with a mix of masculine and feminine traits.
Down Syndrome
- Caused by chromosomal abnormalities, specifically trisomy 21, where individuals have an extra 21st chromosome, resulting in a total of 47 chromosomes.
- Characteristics include mental retardation, stunted growth, and distinctive physical features such as a short flat nose, crooked fingers, wide neck, and sparse hair.
Patau Syndrome
- A disorder characterized by an additional chromosome in the 13th pair, causing mental retardation and physical defects like a cleft lip.
- It also leads to rapid destruction of erythrocytes, causing anemia.
Color Blindness
- A genetic disorder where individuals cannot distinguish between red and green colors.
- The gene responsible is located on the X chromosome, making the condition more common in males.
Hemophilia
- A hereditary disorder where blood does not clot properly, causing excessive internal and external bleeding.
- Symptoms include large bruises, joint pain and swelling, unexplained bleeding, and blood in urine or stool.
- Treatment involves injections of clotting factors or plasma.
Diseases of Different Organ Systems
Genetic Diseases
- Inherited medical conditions caused by abnormalities in the genome DNA.
- Classified into chromosomal disorders (absence or excess of chromosomes) and Mendelian disorders (alterations in a single gene).
Nervous System Diseases
- Neurological disorders affecting the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Can result from structural, biochemical, or electrical abnormalities, causing a wide range of symptoms.
Heart Diseases
- Conditions affecting the heart, including diseased vessels, structural problems, and blood clots.
- Lifestyle changes have contributed to the prevalence of these disorders.
Blood Diseases
- Disorders such as anemia, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, lymphoma, and hemophilia.
- These can be fatal and may arise from genetic, hereditary, or lifestyle factors.
Respiratory Diseases
- Ranging from mild conditions like the common cold to severe diseases like lung cancer.
- Common disorders include asthma, COPD, bronchitis, emphysema, pneumonia, and pleural effusion.
Skeletal Diseases
- Disorders of bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
- Common conditions include osteoporosis, osteopetrosis, bursitis, fibromyalgia, tendinitis, and spinal stenosis.
Kidney Diseases
- The kidneys filter and eliminate waste from the body; dysfunction can lead to waste buildup and other diseases.
- Common kidney disorders include renal hypertension, hydronephrosis, kidney stones, and polycystic kidney disease.
Cancer
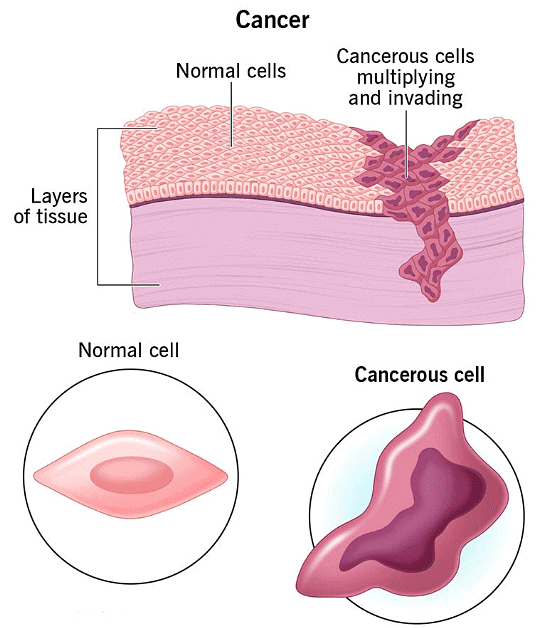
Types of Cancer
- Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
- Benign tumors do not spread, while malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
Causes and Treatment
- Tobacco use can cause oral and lung cancer; alcohol consumption can lead to liver cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals increases the risk of lung and skin cancer.
- Treatments include surgery, gene therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and radiotherapy (e.g., using Cobalt-60).
Specific Cancers
- Leukemia: A group of cancers starting in the bone marrow, resulting in high numbers of abnormal white blood cells.
- Sarcoma: Cancer of connective tissue.
- Oncology: The study of cancer.
|
528 videos|2108 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on Human Diseases - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are some common examples of non-communicable diseases (NCDs)? |  |
| 2. How are diseases caused by microbes different from non-communicable diseases? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of diseases of sex chromosomes? |  |
| 4. Can you provide some examples of diseases that affect different organ systems in the body? |  |
| 5. How can cancer be classified in terms of its origin and behavior? |  |
















