ICAI Notes 7.2: Consignment Accounting - 1 - CA Foundation PDF Download
CONSIGNMENT ACCOUNTING
Introduction – a diagramatic representation:
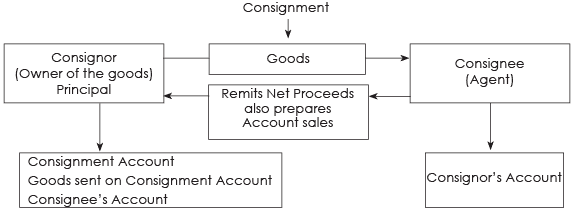
Nature of a Consignment
- If the owner of the goods does not have retail outlets, he can consign the goods to an agent.
- The agent will sell the goods for him and receive a commission in return.
Main Terms of Consignment Trade Consignor – He is the person who sends goods to agents e.g. a manufacturer or wholesaler.
Consignee – He is the agent to whom goods are sent for selling.
Ordinary Commission – This is a fee payable by consignor to consignee for sale of goods when the consignee does not guarantee the collection of money from ultimate customer. The % of such commission is generally lower.
Del Credere Commission – This is additional commission payable to the consignee for taking over additional responsibility of collecting money from customers. In case, the customers do not pay of the consignee takes over the loss of bad debts in his books. Although it’s paid for taking over risk of bad debts that arise out of credit sales only, this commission is calculated on total sales and not on credit sales.

Account Sales – This is a periodical statement prepared by consignee to be sent to the consignor giving details of all sales (cash and credit), expenses incurred and commission due for sales, destroyed-in-transit, or in godown and deducting the amount of advance remitted by him.
Operating Cycle of Consignment Arrangement
(i) Goods are sent by consignor to the consignee
(ii) Consignee may pay some advance or accept a bill of exchange
(iii) Consignee will incur expenses for selling the goods
(iv) Consignee maintains records of all cash and credit sale.
(v) Consignee prepares a summary of results called as Account sales
(vi) Consignor pays commission to the consignee
Sometimes, the consignor may send the goods at a price higher than cost so that the consignee gets no knowledge of the real cost of goods which is confidential for the consignor.
Accounting for Consignment Business
The consignor and consignee keep their own books of accounts. The consignor may send goods to many consignees. Also, a consignee may act as agent for many consignors. It is appropriate that both of them would want to know profit or loss made on each consignment. There are certain new accounts that are to be opened in addition to regular accounts as cash or bank. Let us see the entries in the books of consignor as well as consignee.
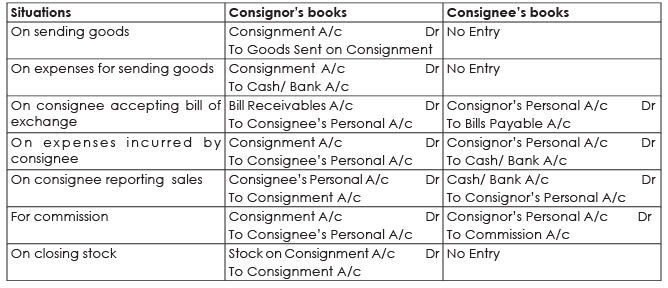
Credit Sales Accounting in books of Consignor
In case consignee sales goods on cash and credit both, the responsibility of collection from customers may be either with consignee or consignor. The risk of non-collection is usually borne by the consignor. If consignor want this to be shouldered by the consignee, additional commission in the form of ‘Del Credere’ commission is payable. It may be noted that in case of credit sales, the personal accounts of debtors are to be maintained by the consignor and not the consignee. The entry for credit sales will be:
Consignment Debtors A/c Dr
To Consignment A/c
Del Credere Commission and Bad Debts
Sometimes the consignor allows an extra commission to the consignee in order to cover the risk of collection from customer. On account of credit sales which is known as Del Credere Commission. Naturally, if debt is found to be irrecoverable the same must be form borne by the consignee. There will be no effect in the books of consignor. In short, credit sales will be treated as cash sales to consignor. If no Del credere commission is given by the consignor to the consignee, the amount of Bad debts must be borne by the consignor.
Entries in the Books of Consignor
(a) When Del Credere Commission is given

(b) When Del Credere Commission is not given

Entries in the Books of Consignee
(a) When Del Credere Commission is given

(b) When Del Credere Commission is not given – There will be no entry against a bad debts entry in the books of consignee.
Valuation of Stock
- If there are unsold goods on consignment at the end of the accounting period, the value of the unsold stock will be carried down to the following period.
- Unsold stock on consignment should properly value; otherwise final accounts cannot be prepared.
- Usually, unsold stock on consignment is value at (Consignor’s Cost +Consignee’s Expenses)
- Alternatively, total cost of goods plus total expenses incurred by the consignor plus total non recurring expenses of the consignee are to be added and stock should valued on the basis of proportionate unsold goods.
The entry will be: Stock on Consignment A/c To, Consignment A/c (Unsold stock on consignment will appear in the asset side of Balance Sheet.) | Dr. |
Illustration 14.
Sree Traders of Gujrat purchased 10,000 sarees @  100 per saree. Out of these 6,000 sarees were sent on consignment to Nirmala Traders of Kolkata at the selling price of
100 per saree. Out of these 6,000 sarees were sent on consignment to Nirmala Traders of Kolkata at the selling price of  120 per saree. The consignors paid
120 per saree. The consignors paid  3,000 for packing and freight.
3,000 for packing and freight.
Nirmala Traders sold 5,000 sarees @  125 per saree and incurred
125 per saree and incurred  1,000 for selling expenses and remitted
1,000 for selling expenses and remitted  5,00,000 to Gujrat on account. They are entitled to a commission of 5% on total sales plus a further of 25% commission on any surplus price realized over
5,00,000 to Gujrat on account. They are entitled to a commission of 5% on total sales plus a further of 25% commission on any surplus price realized over  120 per saree. 3,000 sarees were sold at Gujrat @
120 per saree. 3,000 sarees were sold at Gujrat @ 110 per saree.
110 per saree.
Owing to fall in market price, the value of stock of saree in hand is to be reduced by 5%. Your are required to prepare
(i) Consignment Account, and
(ii) Nirmala Traders Account.
Solution:

Note:
3,000 sarees which were sold at Gujrat @  110 per saree are not to be taken into consideration since it is not a consignment transaction and hence the same is extended from Consignment Account.
110 per saree are not to be taken into consideration since it is not a consignment transaction and hence the same is extended from Consignment Account.
Although the consignor purchased 10,000 sarees, only 6,000 sarees are related to consignment transaction, balance is not to be taken into Consignment Account at all.
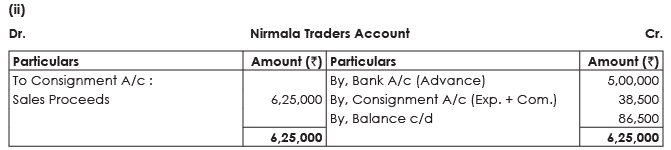

2. Valuation of Unsold Stock:
Since market price has fallen by 5%, valuation of unsold stock on consignment will be calculated as under:

Losses on Consignment
There are two types of losses which may arise in case of a consignment transaction, viz.
(a) Normal Loss, and
(b) Abnormal Loss
(a) Normal Loss – Normal Losses arise as a result of natural causes, e.g. evaporation, leakage, breakage etc., and they are inherent in nature. Since normal loss is a charge against gross profit no additional adjustment is required for this purpose. Moreover, as the same is a part of cost of goods, when valuation of unsold stock is made in case of consignment account the quantity of such loss (not the amount) should be deducted from the total quantity of the goods received by the consignee in good condition. Thus,



(b) Abnormal Losses - Abnormal Losses arises as a result of negligence/ accident etc., e.g., theft, fire etc. Before ascertaining the result of the consignment, value of abnormal loss should be adjusted. The method of calculation is similar to the method of calculating unsold stock. Sometimes insurance company admits the claim in part or in full. The same should also be adjusted against such abnormal loss.
Treatment of Abnormal Loss
(i) For abnormal Loss – Abnormal Loss A/ c To Consignment A/c | Dr |
(ii) If goods are insured and admitted or covered by Insurance Company. Insurance Co./Ba nk A/c To Abnormal Loss A/c | Dr |
(iii) If goods are not insured: Profit & Loss A/c To Abnormal Loss A/c | Dr |
(iv) For the balance (i.e. which is not covered/ admitted by Insurance Co.): Profit & Loss A/c To Abnormal Loss A/c | Dr |
Illustration 16.
5,000 shirts were consigned by Raizada & Co. of Delhi to Zing of Tokyo at cost of  375 each. Raizada & Co. paid freight
375 each. Raizada & Co. paid freight  50,000 and Insurance
50,000 and Insurance  7,500.
7,500.
During the transit 500 shirts were totally damaged by fire. Zing took delivery of the remaining shirts and paid  72,000 on custom duty.
72,000 on custom duty.
Zing had sent a bank draft to Raizada & Co. for  2,50,000 as advance payment. 4,000 shirts were sold by him at
2,50,000 as advance payment. 4,000 shirts were sold by him at  500 each. Expenses incurred by Zing on godown rent and advertisement etc. amounted to
500 each. Expenses incurred by Zing on godown rent and advertisement etc. amounted to  10,000. He is entitled to a commission of 5% One of the customer to whom the goods were sold on credit could not pay the cost of 25 shirts.
10,000. He is entitled to a commission of 5% One of the customer to whom the goods were sold on credit could not pay the cost of 25 shirts.
Prepare the Consignment Account and the Account of Zing in the books of Raizada & Co. Zing settled his account immediately. Nothing was recovered from the insurer for the damaged goods.

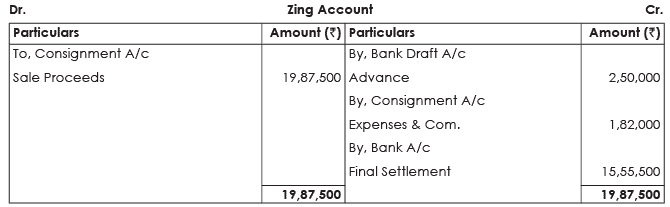


Note: Since Del Credere Commission is not given by the consignor to the consignee, amount of bad debt is to be charged against Consignment Account.
FAQs on ICAI Notes 7.2: Consignment Accounting - 1 - CA Foundation
| 1. What is consignment accounting? |  |
| 2. How are consignment sales recorded in the books of the consignor? |  |
| 3. How is the consignee's commission calculated in consignment accounting? |  |
| 4. How is the unsold stock handled in consignment accounting? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of consignment accounting for both the consignor and consignee? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|


















