ICAI Notes- Finance, Stock & Commodity Market Terminology | Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation PDF Download
Agent
- A brokerage firm is said to be an agent when it acts on behalf of the client in buying or purchasing of shares. At no point of time in the entire transaction the agent will own the shares.
Amortize
- To amortize is to charge a regular portion of an expenditure over a fixed period of time. For example: If something cost ₹ 1,00,000 and is to be amortized over ten years, the financial reports will show an expense of ₹ 10,000 per year for ten years.
Annuity Due
- An annuity whose payments occur at the beginning of each period.
Annuity
- A series of payments of an equal amount at fixed intervals for a specified number of periods.
Appreciation
- Appreciation is an increase in value. If a machine cost ₹ 5 lakh last year and is now worth ₹ 7 lakh, it has appreciated in value by ₹ 2 lakh
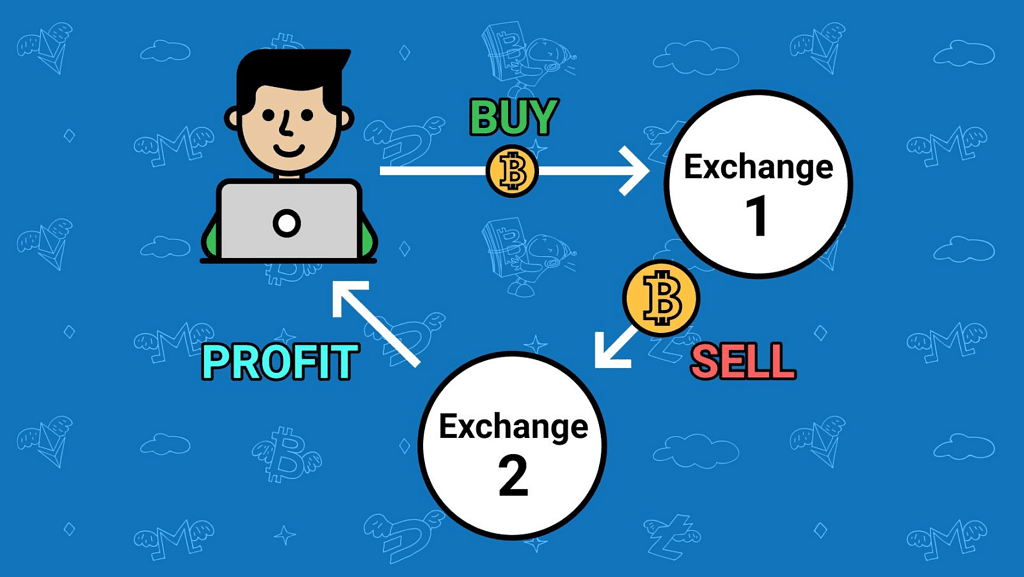
Arbitrage
- Arbitrage is the simultaneous purchase and sale of two identical commodities or instruments. This simultaneous sale and purchase is done in order to take advantage of the price variations in two different markets. For example: Purchase of gold in one nation and the simultaneous sale in another.

Asset
Asset means an economic resource that is expected to be of benefit in the future.
Probable future economic benefits obtained as a result of past transactions or events. Anything of value to which the firm has a legal claim. Any owned tangible or intangible object having economic value useful to the owner. In other words, an asset may be a physical property such as a building, or an object such as a stock certificate, or it may be a right, such as the right to use a patented process. These can be:
- Current Assets: Current Assets are those assets that can be expected to turn into cash within a year or less. For example: Cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and inventory.
- Fixed Assets: Fixed Assets cannot be quickly turned into cash without interfering with business operations. These are valuable items that last more than one year. For example: Land, buildings, machinery, vehicle, equipment, furniture, and long term investments.
- Intangible Assets: Intangible Assets are items such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, and other kinds
of rights or things of value to a company, which are not physical objects. Often, they do not appear on
financial reports.
Ask/Offer
- The lowest price at which an owner is willing to sell his securities.
Audit
- Audit is a careful review of financial records of an organisation to verify their accuracy.
Bad debts
Bad debts are amounts owed to a company that are not going to be paid. An account receivable becomes a bad debt when it is recognized that it won’t be paid. Sometimes, bad debts are written off when recognized.
Balance sheet
- Balance Sheet is a statement of the financial position of a company at a single specific time (often at the close of business on the last day of the month, quarter, or year.) The balance sheet normally lists all assets on the left side or top while liabilities and capital are listed on the right side or bottom.

Bond
- Bond is a type of long-term Promissory Note. Bonds can either be registered in the owner’s name or are issued as bearer instruments. It is a written record of a debt payable in the future. The bond shows amount of the debt, due date, and interest rate.
Book Value
- Book value means total assets minus total liabilities. Book value also means the value of an asset as recorded on the company’s books or financial reports. Book value is often different than true value. It may be more or less.
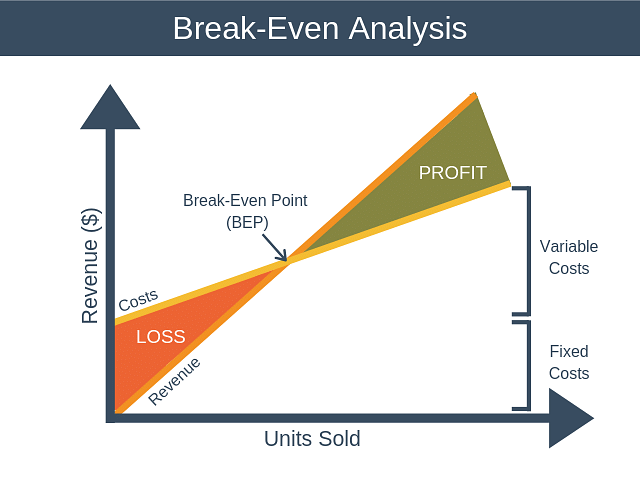
Breakeven point
- It is the amount of revenue from sales which exactly equals the amount of expense. Breakeven point is often expressed as the number of units that must be sold to produce revenues exactly equal to expenses. Sales above the breakeven point produce a profit and below produces loss.

Budget
- Budget is a detailed plan for the future, usually expressed in formal quantitative terms. It is also a detailed plan for the acquisition and use of financial and other resources over a specified time period.
Bears
- These stock-market players are pessimists, they expect share prices or any other type of investment to fall. In a ‘bear market’ the general sentiment is that prices are going to go lower and majority of dealers will sell as quickly as possible for fear of holding shares which diminish in value.

Base Price
- This is the price of a security at the beginning of the trading day which is used to determine the Day Minimum/Maximum and the Operational ranges for that day.
Basket Trading
- Basket trading is a facility by which investors are in a position to buy/sell all 30 scrips of Sensex in the proportion of current weights in the Sensex, in one go.
Bear Market
- A market in which stock prices are falling consistently.
Badla
- Carrying forward of transaction form one settlement period to the next without effecting delivery or payment. Badla involves carrying forward of a transaction from one settlement period to the next. The carry-forward is done at the making up price, which is usually the closing price of the last day of settlement. A badla transaction attracts the following payments / charges:
a. ‘margin money’ specified by the stock exchange board; and
b. contango or badla charges (interest charges) determined on the basis of demand and supply forces.
Blue Chips
- Blue Chips are shares of large, well established and financially sound companies with an impressive record of earnings and dividends. Generally, Blue Chip shares provide low to moderate current yield and moderate to high capital gains yield. The price volatility of such shares is moderate.
Beta
- It is a measurement of relationship between stock price of any particular stock and the movement of whole market.
Bid
- It is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a stock. It is opposite of ask/offer.
Bonds
- It is promissory note issued by companies or government to its buyers. It speaks about the specified amount held for a specified time period by the buyer.
Broker/Brokerage Firm
- A registered securities firm are called broker/brokerage firm. Broker’s acts as an advisor for purchase and sell of listed stocks, they do not own the securities at any point of the time. But they charge a commission for their service.
Bull Market
- A market in which the stock price is increasing consistently.
Business Day
- Days on which stock markets are open. Monday to Friday, excluding public holidays.
Call
- The demand by a company or any other issuer of shares for payment. It may be the demand for full payment on the due date, such as, for example, with a rights issue. It may, alternatively, be the demand for a further payment when the total amount is payable by instalments. A call by a company should not be confused with a call option.
Bid and Offer
- Bid is the price at which the market maker buys from the investor and offer is the price at which he offers to sell the stock to the investor. The offer is higher than the bid.
Bonus
- A free allotment of shares made in proportion to existing shares out of accumulated reserves. A bonus share does not constitute additional wealth to shareholders. It merely signifies recapitalization of reserves into equity capital. However, the expectation of bonus shares has a bullish impact on market sentiment and causes share prices to go up.
Book Closure
- Dates between which a company keeps its register of members closed for updating prior to payment of dividends or issue of new shares or debentures.
Brokerage
- Brokerage is the commission charged by the broker. The maximum brokerage chargeable is determined by SEBI.
Bull
- A bull is one who expects a rise in price so that he can later sell at a higher price.

Business Risk
- The riskiness inherent in the firm’s operations if it uses no debt.
Buyer
- The trading member who has placed the order for the purchase of the securities.
Call Option
- An option that is given to investor the right but not obligation to buy a particular stock at a specified price within a specified time period.
Close Price
- The final price at which the stock is traded on a given particular trading day.
Capital Budgeting
- The process of planning expenditure on assets whose cash flows are expected to extend beyond one year.
Capital Gains Yield
- The capital gain during a given year divided by the beginning price.
Capital Markets
- The financial markets for stocks and for intermediate or long-term debt.
Cash Budget
- A table showing cash flows (receipts, disbursements, and cash balances) for a firm over a specified period.
Credit Period
- The length of time for which credit is granted.
Closing Price
- The trade price of a security at the end of a trading day. Based on the closing price of the security, the base price at the beginning of the next trading day is calculated.
Commercial Paper
- Unsecured, short-term promissory notes of large firms, usually issued in denominations of ₹ 100,000 or more and having an interest rate somewhat below the prime of lending rate of commercial bank.
Commodities
- Product used for commerce that are traded on a separate, authorized commodities platform. Commodities include agricultural products and natural resources.
Convertible Securities
- A security (bonds, debentures, preferred stocks) by an issuer that can be converted into other securities of that issuer are known as convertible securities. The conversion usually occurs at the option of the holder, but it may occur at the option of the issuer.
Consolidation
- Business combination of two or more entities that occurs when the entities transfer all of their net assets to a new entity created for that purpose.
Creditors
- These are people/organisations you owe money to at any particular time – the value of the creditors is included in the published accounts.
Debentures
- A type of debt instrument that is not secured by physical assets or collateral. Debentures are backed only by the general creditworthiness and reputation of the issuer. A debenture is an unsecured form of investment.
Debtors
- Although debtors are considered an asset, if you are owed a vast amount, this might indicate problems collecting monies owed and possible cash flow difficulties. A debtor is a company or individual who owes money.
Defensive Stock
- A stock that provides a constant dividends and stable earnings even in the periods of economic downturn i.e. even in the extreme critical situations of the stock market these companies continue to pay the dividends at a constant rate.
Depreciation
- Depreciation is a way of spreading the cost of an asset over its expected useful economic life. It is an expense allowance made for wear and tear on an asset over its estimated useful life. It is an expense that is supposed to reflect the loss in value of a fixed asset.
- For example: If a machine will completely wear out after ten year’s use, the cost of the machine is charged as an expense over the ten year life rather than all at once, when the machine is purchased. Straight line depreciation charges the same amount to expense each year. Accelerated depreciation charges more to expense in early years, less in later years. Depreciation is an accounting expense.
Derivatives
- A security whose price is derived from one or more underlying assets. The most common underlying assets include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates and market indexes.
Diversification
- Reducing the investment risk by purchasing shares of different companies operating in different sectors.
Dividend
- A portion of the company’s earnings decided to pay to its shareholders in return to their investments. It is usually declared as a percentage of current share price or some specified rupee value, usually decided by the board of directors of the company.
Equity (Net Worth)
- The capital supplied by common stock holders common stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and, occasionally, certain reserves. Total equity is common equity plus preferred stock.
Exchange Rate
- The number of units of given currency that can be purchased for one unit of another currency.
Face Value
- It is the cash denomination or the amount of money the holder of the individual security going to earn from the issuer of the security at the time of maturity. It is also known as par value.
Financial Instrument
- A financial instrument is anything that ranges from cash, deed, negotiable instrument, or for that matter any written and authenticated evidence that shows the existence of a transaction or agreement.
Financial Intermediary
- A financial intermediary is basically a party or person who acts as a link between a provider who provides securities and the user, who purchases the securities. Share brokers, and almost all the banks, are the best examples of financial intermediaries.
Government Bonds
- A government bond, which is also known as a government security, is basically any security that is held with the government and has the highest possible rate of interest.
Hedge
- Hedge is a strategy that is used to minimize the risk of a particular investment and maximize the returns of an investment.
- A ‘hedge’ strategy is, most of the times, implemented with the help of a hedge fund. This term has been written from the banker’s point of view and may be interpreted differently in the field of financial and commodity market.
Holding Period
- The holding period is the time duration during which a capital asset is held/owned by an individual or corporation. The holding period is taken into consideration, while pledging the asset as collateral.
Income Stock
- A security which has a solid record of dividend payments and offers the dividend higher than the common stocks.
Index
- A statistical measurement of change in the economy or security market. Such indices have their own calculation methodology and are usually measured as a percentage change in the base value over the time.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
- A company’s first issue of shares to general public. IPOs are issued by smaller, younger companies seeking funds for expansion and growth, but large companies also practice this to become publicly traded companies.
Internet Trading
- Internet Trading is a platform with Internet as a medium. Internet trading execution takes place through order routing system, which will rout traders order to exchange trading system.
- Thus, traders sitting in any part of the world can be able to trade using their brokers Internet Trading System. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) approved Internet Trading in January 2000.
Limit Order
- An order to buy or sell a share at a specified price. The order will be executed only at the specified limit price or even better.
- A limit order sets a minimum price the seller is willing to accept and maximum price the buyer is willing to pay for it.
Liquidation
- A liquidation occurs when the assets of a division are sold off piecemeal, rather than as an operating entity.
Listed Stocks
- The shares of a company that are traded on the stock exchange. The company has to pay fees to be listed in the stock exchange and abide by the regulations of the stock exchange to maintain listing privilege.
Market Capitalization
- The total value in rupee of all of a company’s outstanding shares. It is calculated by multiplying all the outstanding shares with the current market price of one share. It determines the company’s size in terms of its wealth.
Mutual Fund
- A pool of money managed by experts by investing in stocks, bonds and other securities with the objective of improving their savings. These experts will create a diversified portfolio from these funds.
One-sided Market
- A market that has only potential sellers or only potential buyers but not both.
Out-of-The-Money (OTM)
- For call options, this means the stock price is below the strike price. For put options, this means the stock price is above the strike price. The price of out-of-the-money options consists entirely of “time value.”
Portfolio
- Holding of any individual or institution. A portfolio may include various type of securities of different companies operating in different sectors.
Pre-opening Session
- The pre-open session is for duration of 15 minutes i.e. from 9:00 AM to 9:15 AM. In pre-open session order entry, modification and cancellation takes place.
Price Earnings (P/E) Ratio
- The market price of a share of stock divided by the earnings (profit) per share. P/E ratios can vary from sky high to dismally low, but may not reflect the true value of a company.
Put Option
- An option that gives an investor the right to sell a particular stock at a stated price within a specified time period. Put option is purchased by those who believe that particular stock price is going to fall down than the stated price.
Return On Investment (ROI)
- ROI is a measure of the effectiveness and efficiency with which managers use the resources available to them, expressed as a percentage.
- Return on equity is usually net profit after taxes divided by the shareholders’ equity. Return on invested capital is usually net profit after taxes plus interest paid on long term debt divided by the equity plus the long term debt.
- Return on assets used is usually the operating profit divided by the assets used to produce the profit. Typically used to evaluate divisions or subsidiaries. Different companies and different industries have different ROIs.
Risk
- A probable chances of investments actual returns will be reduced then as calculated. Risk is usually measured by calculating the standard deviation of the historical price returns. Standard deviation is directly proportional to the degree of risk associated.
Securities
- A transferable certificate of ownership of investment in products such as stocks, bonds, future contracts and options which an individual holds.
Strike Price
- The price at which the holder of an option can buy (in case of call option) or sell (in case of put option) the securities they hold when the option is executed.
Stock
- A certificate (or electronic or other record) that indicates ownership of a portion of a corporation; a share of stock. Preferred stock promises its owner a dividend that is usually fixed in amount or percent.
- Preferred shareholders get paid first out of any profits. They have preference. Common stock has no preference and no fixed rate of return. Stock also means the stock of goods, the stock on hand, the inventory of a company.
Stock Split
- An attempt to increase the number of outstanding shares of a company by splitting the existing shares. It is usually done to increase the availability of shares in the market. The usual split ratio is 2:1 or 3:1,i.e. one share is split into two or three.
Thin Market
- A market in which there are comparatively low number of bids to buy and offers to sell. Since the number of transactions is low, the prices are very volatile.
Trading Session
- The period of time stock market is open for trading for both sellers and buyers, within this time frame all the orders of the day must be placed. [9:15 AM to 3:30 PM] Here all the orders placed in preopening sessions are matched and executed.
Yield
- It is the measure of return on investments in terms of percentage. Stock yield is calculated by dividing the current price of the share by the annual dividend paid by the company for that share. For example, if the current price of the share is ₹ 100 and the dividend paid is INR 5 per share annually, then the stock yield is 5%.
Yield to Call (YTC)
- The rate of return earned on a bond if it is called before its maturity date.
Zero Coupon Bond
- A bond that pays no annual interest but is sold at a discount below par, thus providing compensation to investors in the form of capital appreciation.
|
21 videos|90 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on ICAI Notes- Finance, Stock & Commodity Market Terminology - Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation
| 1. What is the meaning of finance in the context of the stock and commodity market? |  |
| 2. What is the role of stock and commodity markets in finance? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between stocks and commodities in the finance market? |  |
| 4. What are some commonly used terms in the stock and commodity market? |  |
| 5. How do stock and commodity markets impact the overall economy? |  |
|
21 videos|90 docs|24 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|