UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Important Crops
Important Crops | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cropping Seasons |

|
| Major Food Crops |

|
| Major Cash Crops |

|
| Plantation Crops |

|
| Fibre Crops |

|
| Changing Cropping Patterns of India |

|
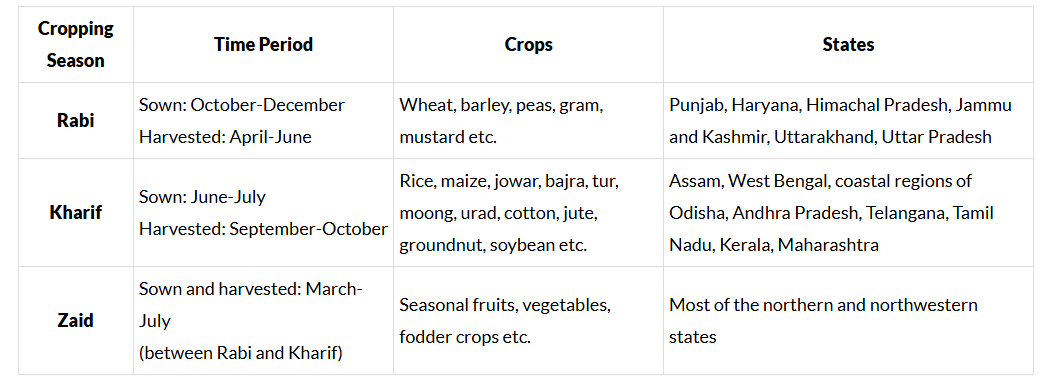
Two-thirds of India's population is involved in agriculture. Agriculture is the main work, producing food grains and raw materials for industries. India is a large country with different food and non-food crops grown in three main seasons - rabi, kharif, and zaid. Food crops include Rice, Wheat, Millets, Maize, and Pulses. Cash crops consist of Sugarcane, Oilseeds, Horticulture crops, Tea, Coffee, Rubber, Cotton, and Jute.
Cropping Seasons
Major Food Crops
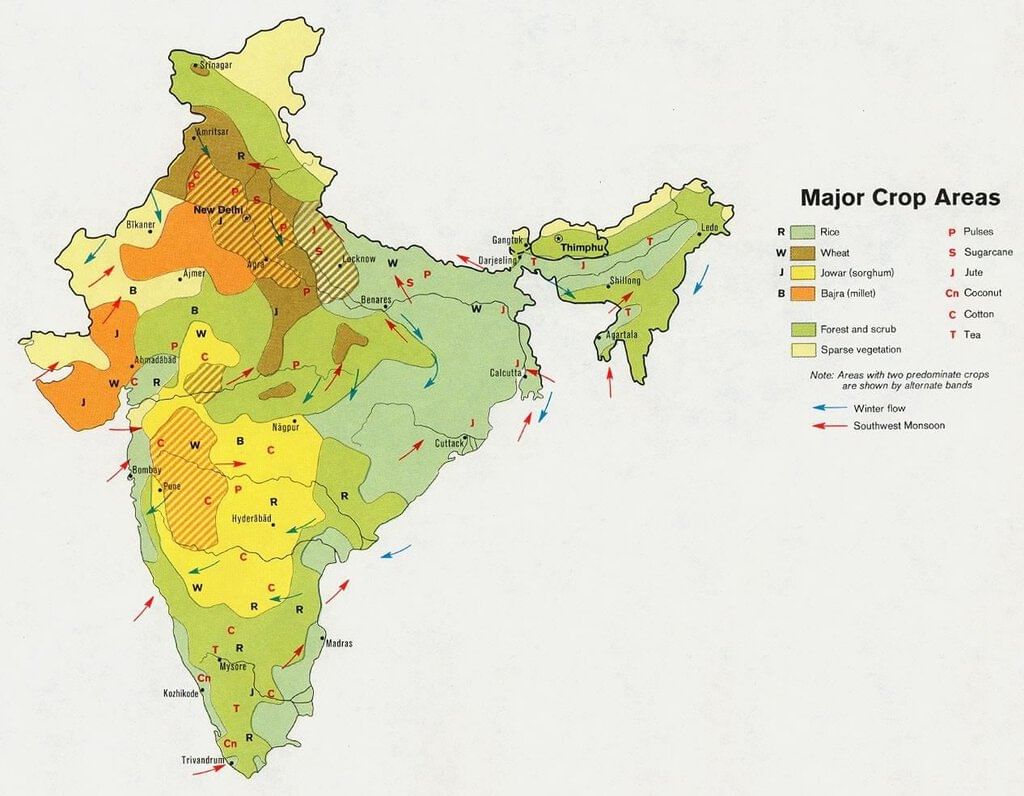
Rice
- Temperature: Between 22-32°C with high humidity.
- Rainfall: Around 150-300 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep clayey and loamy soil.
- Top Rice Producing States: West Bengal >Punjab >Uttar Pradesh >Andhra Pradesh >Bihar.
- It is the main food crop for most Indian people.
- India is the second largest rice producer globally, following China.
- In regions like Assam, West Bengal, and Odisha, three types of rice are cultivated yearly: Aus, Aman, and Boro.
- Government programs like National Food Security Mission, Hybrid Rice Seed Production, and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana aid rice farming.
Wheat
- Temperature: Between 10-15°C (Time for planting seeds) and 21-26°C (Time for the wheat to be ready for harvesting) with plenty of sunlight.
- Rainfall: Approximately 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Fertile soil that drains well, including loamy soil and clayey loamy soil found in specific regions.
- Top Wheat Producing States: Uttar Pradesh is the leading producer, followed by Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, and Rajasthan.
- India is the second largest wheat producer globally, just behind China.
- Wheat is the second most crucial cereal crop and the primary food crop in northern and northwestern parts of India.
- The success of the Green Revolution significantly boosted the cultivation of Rabi crops, particularly wheat.
- Various government programs like Macro Management Mode of Agriculture, National Food Security Mission, and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana have been introduced to support wheat farming.
Millets (Nutri-Cereals)
- Temperature: Between 27-32°C
- Rainfall: Around 50-100 cm
- Soil Type: Suitable for inferior alluvial or loamy soil due to lower sensitivity to soil deficiencies.
- Jowar: Grown in moist areas with minimal or no irrigation.
- Bajra: Thrives in sandy soils and shallow black soil.
- Ragi: Flourishes in red, black, sandy, loamy, and shallow black soils, particularly in dry regions.
- Top Millets Producing States:
- Rajasthan
- Karnataka
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Jowar:
- Maharashtra
- Karnataka
- Madhya Pradesh
- Tamil Nadu
- Andhra Pradesh
- Bajra:
- Rajasthan
- Uttar Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Madhya Pradesh
- Haryana
- Coarse grains: Have high nutritional value, with Ragi being particularly rich in iron, calcium, and other essential nutrients.
- Jowar: Ranked as the third most significant food crop in terms of cultivation area and production.
- Government Initiatives: National Agricultural Insurance Scheme and Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion aim to bolster millet production.
Maize
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C
- Rainfall: High rainfall.
- Soil Type: Old alluvial soil.
- Top Maize Producing States:
- Karnataka
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- India is the seventh largest producer worldwide.
- It is used both as food and fodder.
- Use of modern inputs such as High-Yielding Variety seeds, fertilisers, and irrigation have contributed to the increasing production of maize.
- Technology Mission on Maize is one of the government's initiatives for maize.
Pulses
- Temperature: Between 20-27°C
- Rainfall: Around 25-60 cm.
- Soil Type: Sandy-loamy soil.
- Top Pulses Producing States: Madhya Pradesh > Rajasthan > Maharashtra > Uttar Pradesh > Karnataka.
- India is the largest producer as well as the consumer of pulses in the world.
- These are the major source of protein in a vegetarian diet.
- Major pulses grown in India are tur (arhar), urad, moong, masur, peas and gram.
- Being leguminous crops, all these crops except arhar help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air. Therefore, these are mostly grown in rotation with other crops.
- National Food Security Mission for Pulses, Pulses Development Scheme and Technological Mission on Pulses are few of the government's plans to support pulses production.
Major Cash Crops
Sugarcane- Temperature: Ranges from 21 to 27 degrees Celsius in a hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Approximately 75 to 100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep, nutrient-rich loamy soil.
- Top States for Sugarcane Production: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Bihar.
- India is the second largest sugarcane producer globally, following Brazil.
- Sugarcane can be cultivated in various soils, including sandy loam and clay loam, provided they are well-drained.
- Requires manual labor from planting to harvesting.
- Primary uses include sugar, gur (jaggery), khandsari, and molasses.
- Government initiatives like SEFASU and National Policy on Biofuels support sugarcane farming and the sugar industry.
Oil Seeds
- Temperature: Between 15-30°C
- Rainfall: Around 30-75 cm
- Soil Type: Loam to clayey loam and well drained sandy loams
- Top Oilseeds Producing States:
- Madhya Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- Main oil-seeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard, coconut, sesamum (til), soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed, and sunflower. These are used for cooking and in products like soap, cosmetics, and ointments.
- Yellow Revolution and Integrated Scheme on Oilseeds, Pulses, Oil Palm, and Maize (ISOPOM) are government programs supporting oilseed production.
- Groundnut is a major kharif crop in India, contributing to half of the country's oilseeds production.
- Linseed and mustard are rabi crops.
- Sesamum is a kharif crop in the north and a rabi crop in the south of India.
- Castor seed is cultivated as both a rabi and kharif crop.
Horticulture Crops
- Horticulture is the branch of agriculture concerned with cultivation, production and sale of fruits, vegetables, flowers, herbs, ornamental or exotic plants.
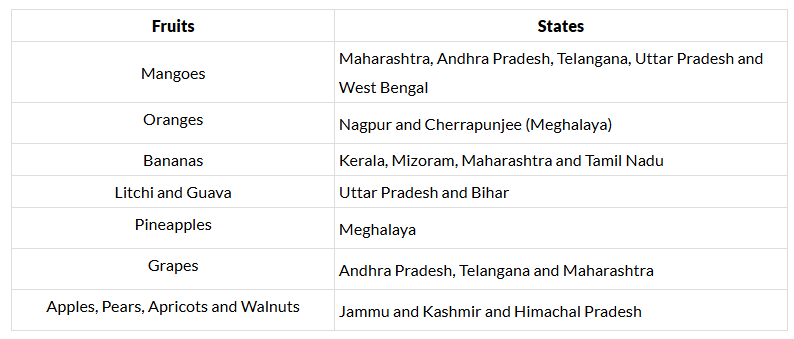
- India stands as the second largest cultivator of fruits and vegetables globally, spanning both tropical and temperate varieties.
- Constituting approximately 13% of the world's vegetable output, India plays a significant role in the cultivation of peas, cauliflower, onions, cabbage, tomatoes, brinjal, and potatoes.
- Government endeavors such as the Golden Revolution, Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), and Coordinated Horticulture Assessment and Management using geo-informatics (Project CHAMAN) aim to bolster the horticulture sector.
Plantation Crops
Tea- Temperature: Between 20-30°C
- Rainfall: Around 150-300 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
- Top Tea Producing States: Assam >West Bengal >Tamil Nadu
- India is the second largest producer of tea.
- It was introduced in the eastern hill slopes of India by the British.
- Slopes of eastern hills have humid climate and evenly distributed rainfall without water logging which are optimal conditions for terrace farming of tea.
- Tea is a labour intensive industry. It requires abundant, cheap and skilled labour. Tea is processed within the tea garden to retain its freshness.
- Tea Development and Promotion Scheme, Wage Compensation Scheme and Tea Boutiques are few of the government schemes for tea.
Coffee
- Temperature: Between 15-28°C
- Rainfall: Around 150-250 cm.
- Soil Type: Well drained, deep friable loamy soil.
- Top Coffee Producing States: Karnataka > Kerala > Tamil Nadu.
- India is the seventh largest producer.
- Coffee was first brought from Yemen and introduced on the Baba Budan Hills.
- Hills with well-defined shade canopy, including evergreen leguminous trees, offer optimal conditions for coffee cultivation, which is mainly concentrated in hilly regions.
- Indian type of coffee 'Arabica' is globally renowned.
- Various Government-supported projects and schemes have been initiated to enhance coffee production.
Rubber
- Temperature: Above 25°C with a warm and wet climate.
- Rainfall: More than 200 cm.
- Soil Type: Fertile well-drained soil found near rivers.
- Top States for Rubber Production: Kerala followed by Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- Rubber is a crucial material for industries.
- Rubber is mainly grown in equatorial regions, but with certain conditions, it can also thrive in tropical and sub-tropical zones.
- Government initiatives like the Rubber Plantation Development Scheme and Rubber Group Planting Scheme support rubber cultivation.
Fibre Crops
Cotton- Temperature: Between 21-30°C
- Rainfall: Around 50-100cm
- Soil Type: Well drained black cotton soil of Deccan Plateau
- Top Cotton Producing States: Gujarat >Maharashtra >Telangana >Andhra Pradesh >Rajasthan
- India is thought to be the original birthplace of the cotton plant. Cotton is a major material for cotton textile industry.
- Cotton requires 210 frost-free days and bright sunlight for its growth.
- It is a kharif crop and takes 6 to 8 months to mature.
- Silver Fibre Revolution and Technology Mission on Cotton are government efforts to enhance cotton production in India.
- Cotton has been genetically modified into BT Cotton to combat environmental stress and pest attacks.
Jute
- Temperature: Between 25-35°C
- Rainfall: Around 150-250 cm
- Soil Type: Well drained alluvial soil
- Top Jute Producing States: West Bengal > Bihar > Assam > Andhra Pradesh > Odisha
- Region: Jute production is mainly concentrated in eastern India due to the fertile alluvial soil of the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta
- India's Role: India is the largest producer of jute, known as the golden fibre, utilized in the creation of gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets, and various other products
- Market Challenge: Jute faces market competition from synthetic fibers and packing materials like nylon due to its higher cost
- Government Initiatives: The Golden Fibre Revolution and the Technology Mission on Jute and Mesta are governmental efforts aimed at enhancing jute production in India
Changing Cropping Patterns of India
- Cropping pattern is a dynamic concept that changes across space and time. It refers to the mix of crops grown in a particular area at a specific time.
- In India, the cropping pattern is influenced by factors like rainfall, climate, temperature, soil type, technology, and the socio-economic status of farmers.
- Changes in cropping patterns in India have been driven largely by fluctuations in crop prices.
- The Green Revolution also played a significant role in altering cropping patterns, introducing crops like rice to regions such as Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- The adoption of new agricultural technologies has made the cultivation of food crops more profitable and efficient.
- Farmers are increasingly shifting towards cultivating cash crops such as oilseeds, fruits, vegetables, and spices, moving away from traditional non-commercial crops like cereals and pulses.
- Farmers are adjusting their crop choices to capitalize on economic opportunities and advancements.
- Cropping patterns in India are being impacted by climate change, which has also affected the monsoon patterns.
- Population growth and urbanization have led to land use changes, promoting intensive farming practices and influencing cropping patterns.
- In the early 21st century, around 83% of India's cultivable land was used for food crops, while 17% was allocated for non-food crops. This distribution shifted by 1944-45, with food crop area decreasing to 80% and non-food crop area increasing slightly to 20%.
- Wheat cultivation has shown a substantial increase in area since 1950-51, with a remarkable 132% growth by 1987-88. However, rice and pulses have seen more modest area expansions of only 23%, and coarse cereals have experienced a marginal 11% increase by 1987-88.
The document Important Crops | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Important Crops - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major food crops grown during cropping seasons? |  |
Ans. Major food crops grown during cropping seasons include rice, wheat, maize, and pulses like lentils and chickpeas.
| 2. Which crops are considered major cash crops during cropping seasons? |  |
Ans. Major cash crops grown during cropping seasons include cotton, sugarcane, tobacco, and coffee.
| 3. What are some important crops that are grown during cropping seasons? |  |
Ans. Some important crops grown during cropping seasons are soybeans, potatoes, barley, and sunflowers.
| 4. When do cropping seasons typically occur for different crops? |  |
Ans. Cropping seasons vary depending on the region and the specific crop being grown. Generally, they can be categorized as rabi (winter) and kharif (summer) seasons.
| 5. How do farmers prepare for different cropping seasons? |  |
Ans. Farmers prepare for different cropping seasons by selecting appropriate crops based on weather conditions, soil fertility, and market demand. They also engage in practices like soil preparation, seed selection, and irrigation planning.
Related Searches
















