Important Diagrams: Atoms and Molecules | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Q1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
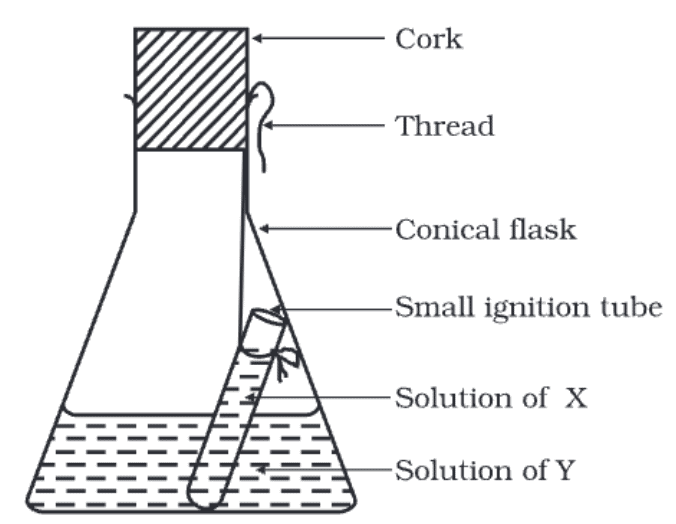
(i) What is the purpose of conducting this experiment with solutions X and Y?
Ans: This experiment aims to demonstrate the law of conservation of mass during a chemical reaction.
(ii) What is the role of the ignition tube in this experiment?
Ans: The ignition tube containing solution X is used to showcase the mass of the substances involved before the chemical reaction takes place.
(iii) Why is it important to weigh the flask's contents before and after tilting and swirling?
Ans: Weighing the flask before and after mixing the solutions helps us observe any changes in mass, demonstrating the law of conservation of mass.
(iv) Why is a cork placed on the flask during the experiment?
Ans: Placing a cork on the flask prevents the escape of any gases produced during the chemical reaction, ensuring that the mass remains within the system as per the law of conservation of mass.
(v) Does the total mass of the flask and its contents change during the experiment?
Ans: No, the total mass of the flask and its contents remains the same before and after the chemical reaction, by the law of conservation of mass.
Q2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
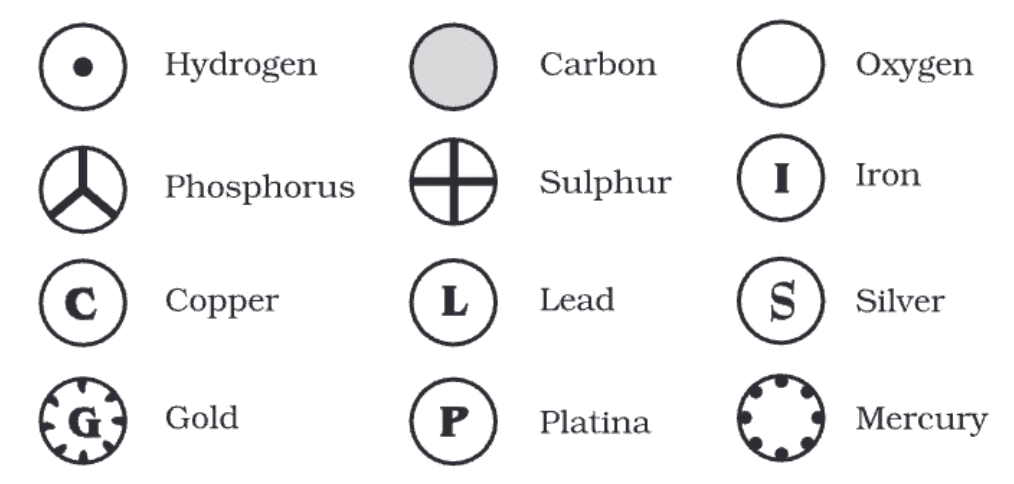
(i) Who was the first scientist to utilize symbols to represent elements and their composition?
Ans: John Dalton was the first scientist to use symbols to quickly represent components, where the sign for an element denoted both the element and one atom of that element.
(ii) What did Dalton's symbols for elements signify?
Ans: Dalton's symbols signified:
- The element itself
- One atom of that element
(iii) How were the original names of elements derived historically?
Ans: The original names of elements were often derived from the places where they were first discovered or from specific colours associated with them.
(iv) Can you provide an example of an element named after a location?
Ans: Certainly, copper is an example of an element named after a place, specifically Cyprus.
(v) Which organization is responsible for approving names, symbols, and units of elements in the present day?
Ans: The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is the organization responsible for approving names, symbols, and units of elements in the contemporary scientific context.
Q3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
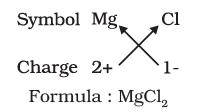
(i) What are binary compounds, and how are they formed?
Ans: Binary compounds are the simplest compounds made up of two different elements. They are formed by combining two elements in a specific ratio.
(ii) How are chemical formulae for compounds written?
Ans: Chemical formulae for compounds are written by indicating the symbols of the constituent elements and their valencies. The valencies are used to determine the ratio in which the elements combine, and the charges of the ions are criss-crossed to obtain the correct formula.
(iii) Explain the procedure to write the formula for magnesium chloride.
Ans: To write the formula for magnesium chloride, the symbol of the cation (Mg²⁺) is written first, followed by the symbol of the anion (Cl⁻). The charges of the ions (2+ for Mg and 1- for Cl) are criss-crossed to obtain the formula MgCl₂.
(iv) How is the ratio of chloride ions to magnesium ions balanced in magnesium chloride?
Ans: The ratio of chloride ions to magnesium ions is:
- There are two chloride ions (Cl−) for every magnesium ion (Mg2+).
- This ratio balances the positive and negative charges, ensuring the compound is neutral overall.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Atoms and Molecules - Science Class 9
| 1. What are atoms and how do they relate to molecules? |  |
| 2. What is the structure of an atom? |  |
| 3. How do atoms bond to form molecules? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an element and a compound? |  |
| 5. Why are atoms considered the fundamental units of matter? |  |
















