Important Diagrams: The Fundamental Unit of Life | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Q1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: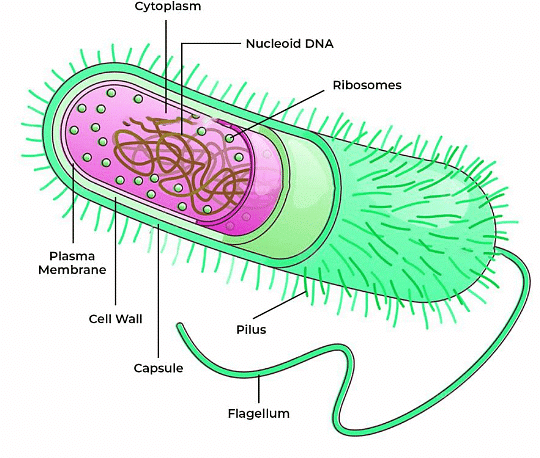
(i) What is the main characteristic feature of a prokaryotic cell?
Ans: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
(ii) Which part of the prokaryotic cell contains the genetic material?
Ans: The genetic material in a prokaryotic cell is found in the nucleoid region.
(iii) What surrounds the prokaryotic cell and provides structure and protection?
Ans: The prokaryotic cell is surrounded by a cell wall.
(iv) What is responsible for the movement of a prokaryotic cell?
Ans: The flagellum is responsible for the movement of a prokaryotic cell.
(v) Where in the prokaryotic cell does protein synthesis occur?
Ans: Protein synthesis in a prokaryotic cell occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Q2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
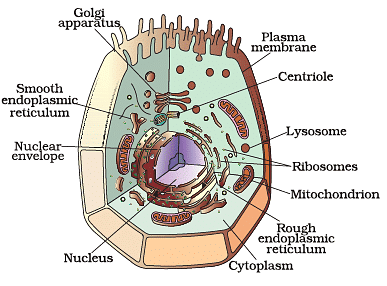
(i) What is the main function of the nucleus in an animal cell?
Ans: The nucleus controls all the activities of the cell and contains genetic information (DNA) that determines the cell's characteristics and functions.
(ii) Name two organelles found in animal cells that are responsible for energy production. What is the primary difference between them?
Ans: The two organelles responsible for energy production are mitochondria and ribosomes. The primary difference is that mitochondria produce ATP (energy) through cellular respiration, while ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis.
(iii) How do lysosomes contribute to the functioning of animal cells?
Ans: Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris. They help in cleaning up the cell and are often referred to as the cell's "garbage disposal" or "recycling center."
(iv) Compare and contrast animal cells with plant cells. What is the main structural difference between the two?
Ans: Animal cells and plant cells are both eukaryotic and share many similarities, but a key structural difference is that animal cells lack a cell wall, while plant cells have a rigid cell wall outside the cell membrane. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, which animal cells do not.
(v) In an animal cell, what organelle is responsible for protein synthesis, and what is the primary function of the proteins it produces?
Ans: Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in animal cells. The proteins they produce are essential for various cellular functions, including building cellular structures, enzymes for chemical reactions, and signaling molecules for communication within and between cells.
Q3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: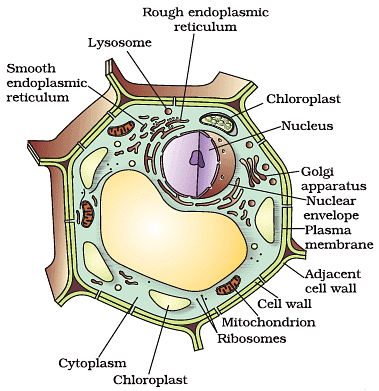
(i) Name the key organelle responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy in a plant cell. What is the process by which this organelle performs this function?
Ans: The key organelle responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy in a plant cell is the chloroplast. This process is called photosynthesis, where chlorophyll, a green pigment in the chloroplasts, absorbs light energy and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
(ii) What is the main structural difference between a plant cell and an animal cell as seen in the image?
Ans: The main structural difference between plant cells and animal cells, as seen in the image, is the presence of a rigid cell wall in plant cells. Animal cells lack a cell wall and have a flexible cell membrane instead.
(iii) Identify the organelle in the plant cell responsible for storing water, nutrients, and waste products. What is the function of this organelle?
Ans: The organelle responsible for storing water, nutrients, and waste products in a plant cell is the central vacuole. Its main function is to maintain turgor pressure, store nutrients, and contain waste products.
(iv) In the provided plant cell image, identify an organelle that is responsible for the synthesis of proteins. What is the name of this organelle, and how does it carry out its function?
Ans: The organelle responsible for the synthesis of proteins in a plant cell is the ribosome. It can be found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes read the instructions from the cell's DNA and build proteins by linking amino acids together.
(v) Point out an organelle in the plant cell that is involved in cellular respiration. What is the function of this organelle, and what does it produce during the process of cellular respiration?
Ans: The organelle involved in cellular respiration in a plant cell is the mitochondrion. Its function is to generate energy (ATP) by breaking down glucose and other organic molecules using oxygen. During cellular respiration, mitochondria produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP as products.
Q4: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: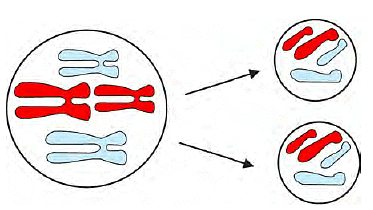
(i) What are the two main types of cell division?
Ans: The two main types of cell division mentioned are mitosis and meiosis.
(ii) What is the purpose of mitosis in cell division?
Ans: Mitosis helps in growth and repair of tissues in organisms.
(iii) Describe the outcome of mitosis in terms of daughter cells.
Ans: In mitosis, a mother cell divides to form two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell.
(iv) How does mitosis contribute to the growth of an organism?
Ans: Mitosis contributes to growth by producing new cells that are identical to the original cell, allowing the organism to increase in size.
(v) Provide one difference between mitosis and meiosis based on the information.
Ans: Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Q5: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: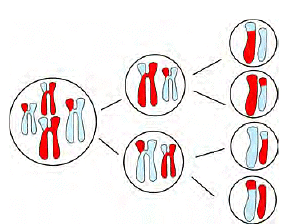
(i) Why do cells divide by meiosis to produce gametes?
Ans: Cells divide by meiosis to form gametes because it ensures that each gamete has half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, which is essential for maintaining the correct chromosome number in the offspring.
(ii) How does meiosis differ from mitosis in terms of cell division?
Ans: Meiosis involves two consecutive divisions, resulting in four new cells with half the chromosome number of the parent cell. Mitosis, on the other hand, is a single division process that produces two identical daughter cells with the same chromosome number as the parent cell.
(iii) What is the significance of having half the chromosome number in gametes?
Ans: Having half the chromosome number in gametes ensures that when fertilization occurs, the resulting zygote has the correct number of chromosomes for the species. This maintains genetic stability and diversity in the offspring.
(iv) How many divisions occur during meiosis, and what is the result of these divisions?
Ans: Meiosis involves two divisions. The first division separates homologous chromosomes, resulting in two daughter cells with half the chromosome number. The second division separates sister chromatids, yielding a total of four daughter cells, each with half the original chromosome number.
(v) Explain one major difference between meiosis and mitosis.
Ans: A major difference between meiosis and mitosis is that meiosis results in the formation of four daughter cells with half the chromosome number, while mitosis produces two identical daughter cells with the same chromosome number as the parent cell.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: The Fundamental Unit of Life - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the fundamental unit of life? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of cells found in living organisms? |  |
| 3. What are organelles and their functions in a cell? |  |
| 4. How are cells involved in the growth and repair of organisms? |  |
| 5. How do cells communicate with each other? |  |






















