Important Diagrams: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: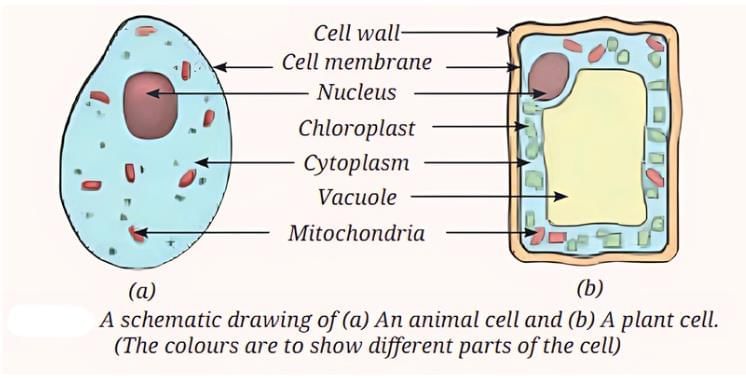
(i) What are the main components labeled in the diagram for both animal and plant cells?
Ans: The diagram labels the cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm as common components in both animal and plant cells. The plant cell additionally has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large vacuole, while the animal cell has small vacuoles and mitochondria.
(ii) Define the role of the cell wall based on the diagram’s context.
Ans: The cell wall, shown in the plant cell diagram, is a rigid outer layer that provides strength and support, maintaining the compact arrangement and firm structure of plant cells.
(iii) How does the diagram illustrate the differences between plant and animal cells?
Ans: The diagram shows plant cells with a cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large vacuole for storage and shape maintenance, while animal cells lack a cell wall and chloroplasts and have smaller vacuoles.
(iv) Which of the following components is present only in the plant cell, as shown in the diagram?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Chloroplast
(d) Cell membrane
Answer: (c)
The diagram shows chloroplasts in the plant cell, which contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis, but they are absent in the animal cell.
(v) What is the significance of the cell structures shown in the diagram for the survival of organisms?
Ans: The structures, such as the nucleus (regulates cell activities), cell membrane (controls material entry/exit), and chloroplasts (enable photosynthesis in plants), ensure cells perform essential functions like growth, energy production, and survival, supporting the organism’s life.
Question 2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: Root Nodules of Cowpea plant which contain Rhizobium
Root Nodules of Cowpea plant which contain Rhizobium
(i) What is the role of the structures shown in the diagram on the roots of the cowpea plant?
Ans: The diagram shows root nodules containing Rhizobium bacteria, which fix atmospheric nitrogen into compounds that the cowpea plant can use for growth, enhancing soil fertility.
(ii) Define nitrogen fixation based on the diagram’s context.
Ans: Nitrogen fixation, as depicted in the diagram, is the process by which Rhizobium bacteria in root nodules convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds, such as ammonia, for plants.
(iii) How does the diagram illustrate the relationship between the cowpea plant and Rhizobium bacteria?
Ans: The diagram shows root nodules on the cowpea plant’s roots, indicating a symbiotic relationship where Rhizobium bacteria fix nitrogen for the plant in exchange for shelter and nutrients.
(iv) Which of the following microorganisms is shown in the diagram as residing in the root nodules?
(a) Lactobacillus
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Yeast
(d) Amoeba
Answer: (b)
The diagram illustrates Rhizobium bacteria in the root nodules of the cowpea plant, responsible for nitrogen fixation.
(v) What is the significance of the process shown in the diagram for agriculture?
Ans: The nitrogen fixation process shown in the diagram enriches soil with nitrogen compounds, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting healthy crop growth, and supporting sustainable farming practices.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the microscopic world and why is it important in understanding life? |  |
| 2. How do scientists study organisms that are invisible to the naked eye? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of microorganisms and their roles in the environment? |  |
| 4. Why is it essential to study the invisible living world in relation to human health? |  |
| 5. How has the understanding of microorganisms evolved over time? |  |
















