Important Formulas: Angles as Turns | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Turns |

|
| Types of Angles |

|
| Measuring Angles with Turns |

|
| Directions of Turns |

|
| Everyday Examples |

|
Turns
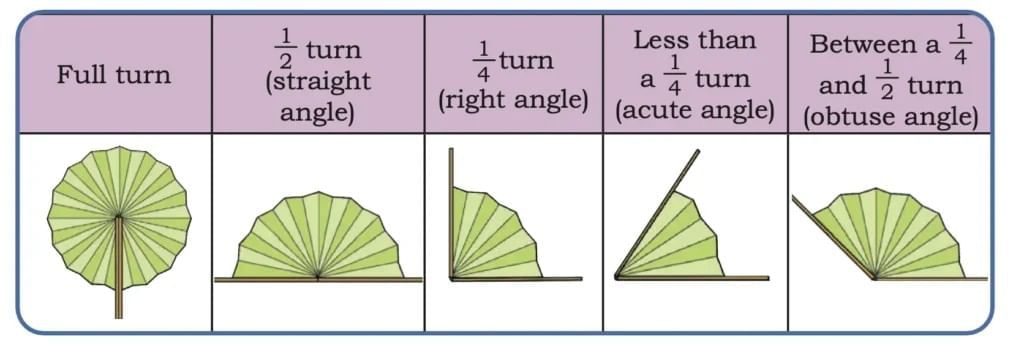
Full Turn: Turning completely around and coming back to the starting position.
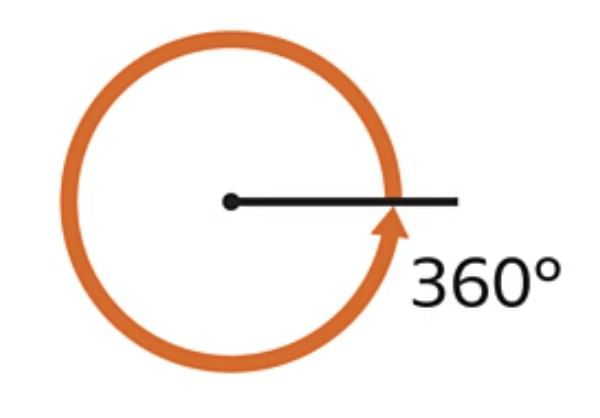
Half Turn: Turning halfway and facing the opposite direction.
Quarter Turn: Turning one-fourth of a full turn, facing sideways.
Rule:
2 Half Turns = 1 Full Turn
4 Quarter Turns = 1 Full Turn
2 Quarter Turns = 1 Half Turn
Types of Angles
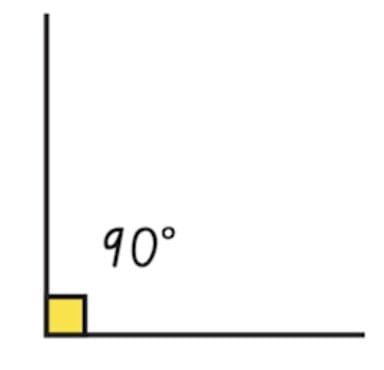
Right Angle: 1/4 of a full turn. Looks like the corner of a book.
Acute Angle: Less than a right angle. Sharp and small.
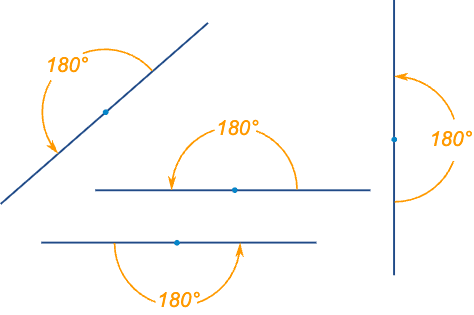
Obtuse Angle: Bigger than a right angle but smaller than a straight angle.
Straight Angle: 1/2 of a full turn. Forms a straight line.
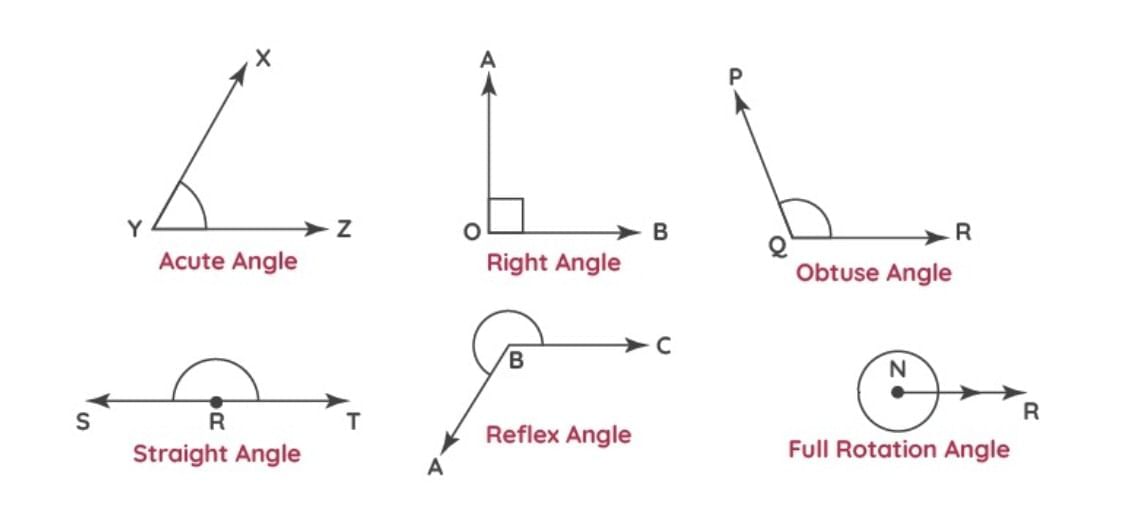
Measuring Angles with Turns
Angles can be measured as fractions of a full turn.
Examples:
1/8 turn = Small angle
2/8 turn = Right angle
4/8 turn = Straight angle
8/8 turn = Full turn
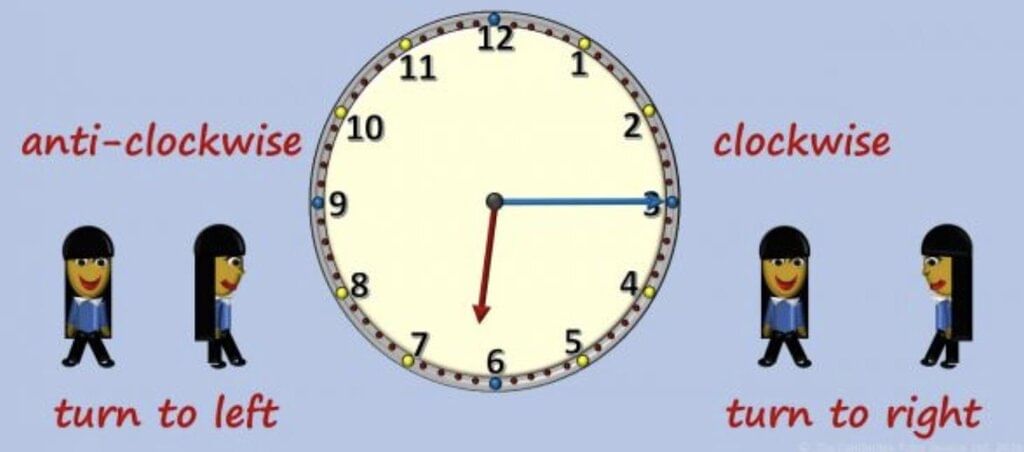
Directions of Turns
Clockwise (CW): Same direction as a clock’s hands.
Anti-clockwise (ACW): Opposite direction of clock’s hands.
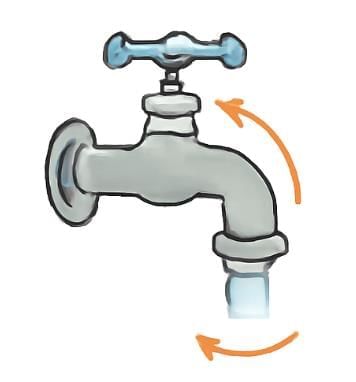
Everyday Examples
Taps → Quarter or half turn.
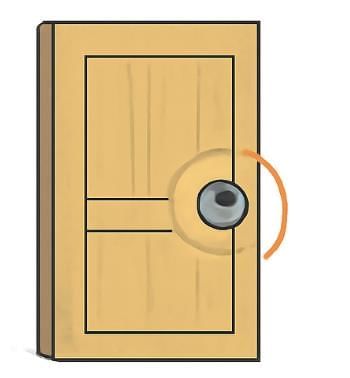
Doors → Quarter or half turn.
Scissors → Small turns.

Giant Wheel → Full turns.
|
35 videos|318 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Angles as Turns - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is a turn in the context of measuring angles? |  |
| 2. How do you measure angles using turns? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of angles based on turns? |  |
| 4. What are the common directions of turns that can be used to describe angles? |  |
| 5. Can you give everyday examples of angles as turns? |  |




















