Important Formulas: Coconut Farm | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Multiplication Basics
Multiplication = repeated addition (same number added many times).
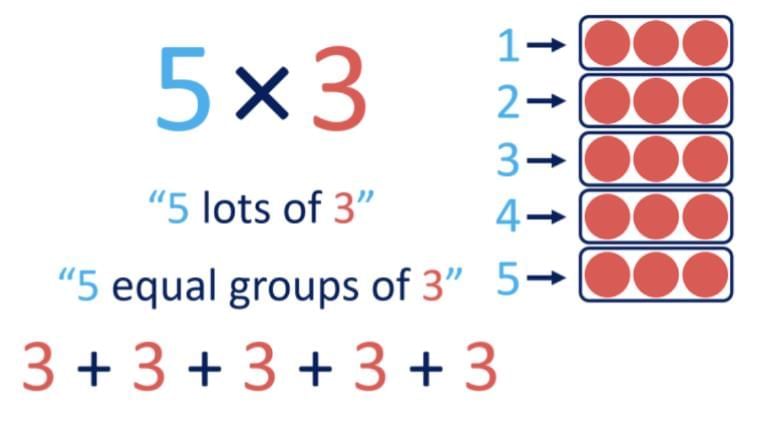
Notation:
×(times).Numbers multiplied = factors.
Result = product.
Example: 2 × 4 = 8
→ factors = 2, 4
→ product = 8.
Daily Life Uses: Counting baskets of apples, chairs in rows, or boxes in stacks.
Division Basics
Division = sharing equally OR grouping equally.
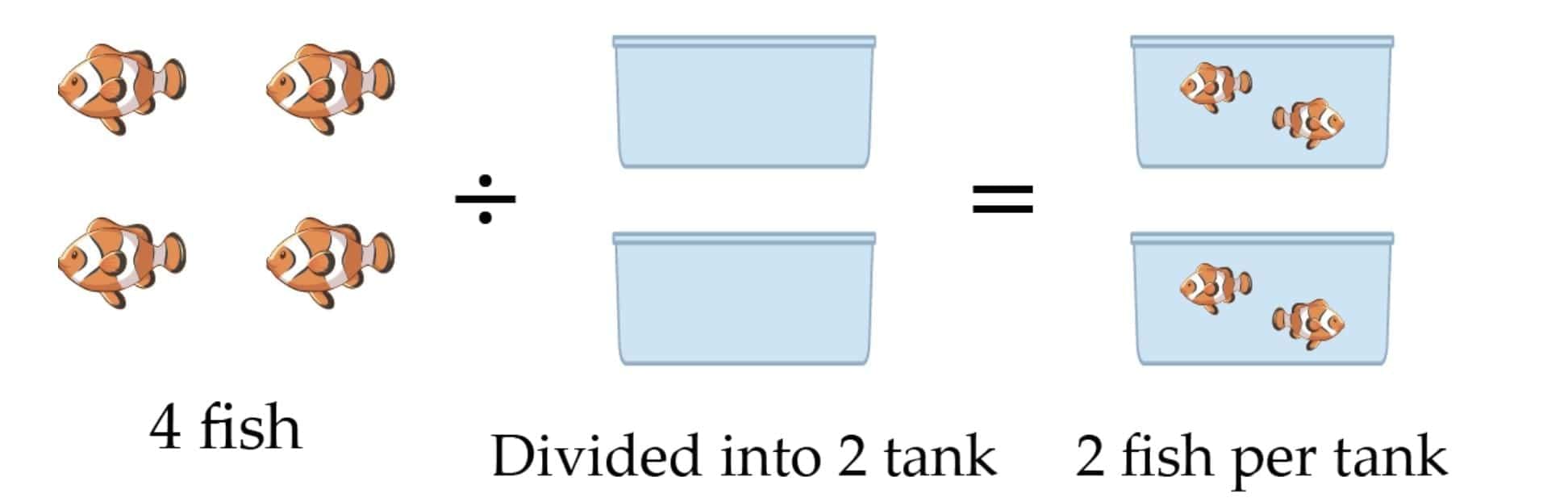
Notation:
÷or/.Parts of division:
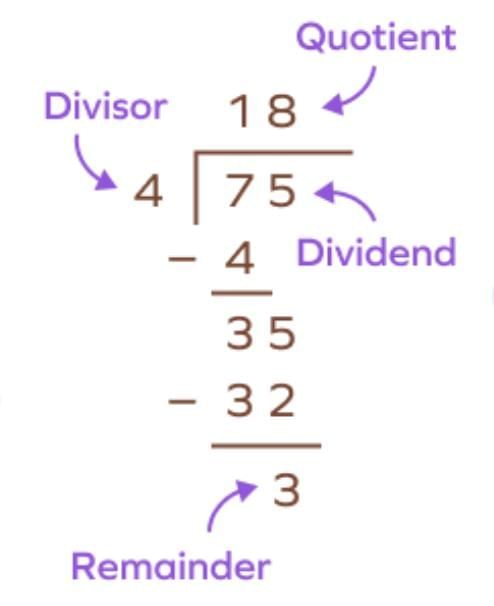
Dividend = number being divided.
Divisor = number of groups / how many in each group.
Quotient = result of division.
Remainder = what is left.
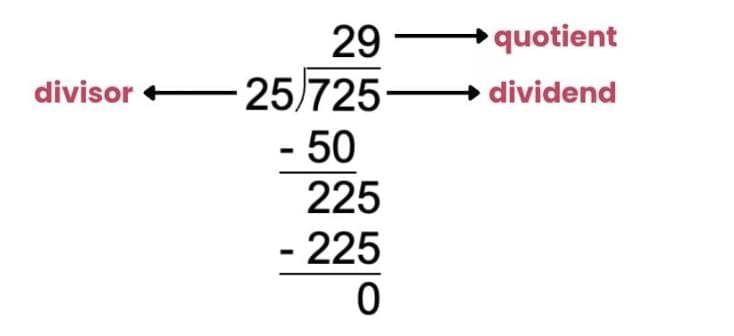
Formula: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
Example: 122 ÷ 5 = 24 remainder 2.
Daily Life Uses: Sharing chocolates, splitting money, forming equal teams.
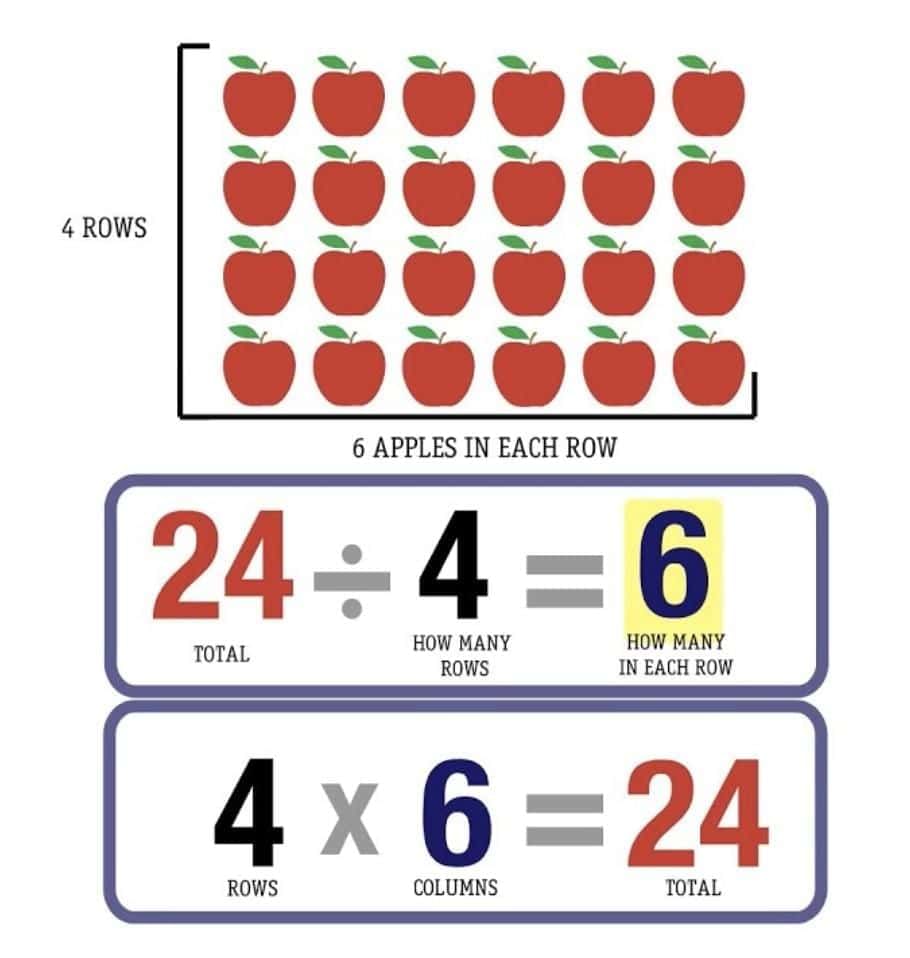
Arrays – Link Between Multiplication & Division
Arrays = arrangement of objects in rows × columns.
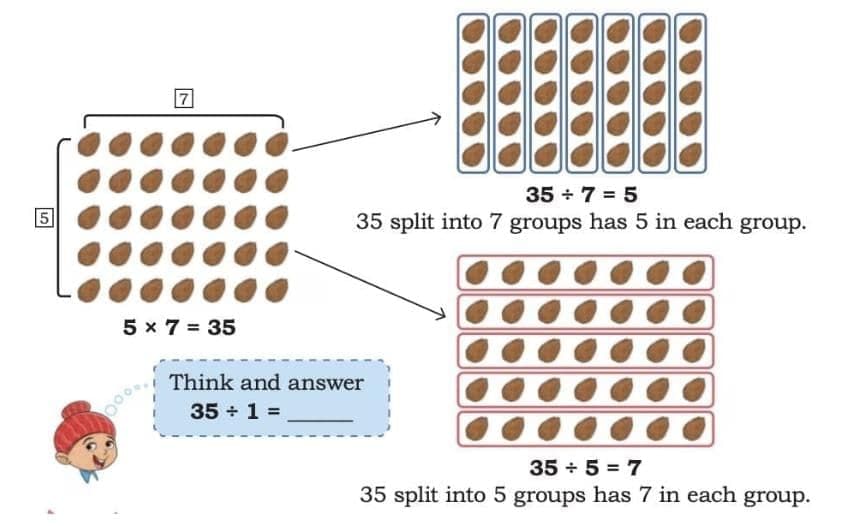
From one multiplication fact, we can write two division facts.
Example: 5 × 7 = 35 →
35 ÷ 7 = 5
35 ÷ 5 = 7
Relation Between Multiplication & Division
Multiplication: factors → product.
Division: product ÷ one factor → gives the other factor.
Patterns in Division
Dividing by 10, 100, 1000 → number becomes smaller by 10, 100, 1000.
Place value rule:
÷10 → digits move 1 place right.
÷100 → digits move 2 places right.
÷1000 → digits move 3 places right.
Example:
1000 ÷ 10 = 100
3300 ÷ 300 = 11
Division Strategies
Mental Division
Break into parts (64 ÷ 4 → 60 ÷ 4 + 4 ÷ 4 = 15 + 1 = 16).
Halving: ÷4 → halve twice; ÷8 → halve thrice.
Use multiplication tables to check.
Estimate first, then calculate.
Partial Quotients Method
Subtract big groups of divisor repeatedly.
Faster if large multiples are used.
Example: 582 ÷ 6 → quotient = 97.
Remainders Rule
Always smaller than divisor.
If remainder = 0 → exact division.
If remainder ≠ 0 → leftover exists.
Formula check: N = (D × Q) + R.
Example: 902 ÷ 16 → Q = 56, R = 6 → 902 = (16 × 56) + 6.
Division Using Place Value
Write the problem:
Dividend = 100, Divisor = 7 → 100 ÷ 7
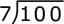
- Look at the first digit (1):
1 ÷ 7 is not possible. So, we look at the first two digits together (10).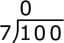
- Divide 10 by 7:
7 goes into 10 only 1 time.
Write 1 on top.
Multiply 7 × 1 = 7.
Subtract 10 – 7 = 3.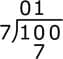
- Bring down the next digit (0):
Now we have 30.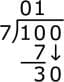
- Divide 30 by 7:
7 goes into 30 - 4 times (because 7 × 4 = 28).
Write 4 on top.
Subtract 30 – 28 = 2.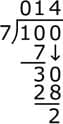
- Final Answer:
Quotient = 14
Remainder = 2
So, 100 ÷ 7 = 14 remainder 2.
Applications of Division
Distance & time: Find per day/hour values.
Capacity & packing: Bags, boxes, bottles.
Sharing equally: Money, food, resources.
Data handling: Complete tables by dividing totals by units.
Special Tricks & Observations
Multiplication & division are inverse operations.
Patterns with 10, 100, 1000 → digit shifts.
Large number division = easier with estimation + partial quotients.
Remainder concept important in practical life (e.g., leftover items).
|
35 videos|318 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Coconut Farm - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the basic principles of multiplication and division? |  |
| 2. How are arrays used to connect multiplication and division? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between multiplication and division? |  |
| 4. What are some effective strategies for division? |  |
| 5. How do remainders work in division, and what is the Remainders Rule? |  |




















