Important Functions Formulas Formulas for JEE and NEET
Introduction
A Function is a relation between two sets of values in which one set is the input value and the other set is the output value and each input value gives a particular output value.
We represent a function in maths as, y = f(x) where x is the input value and for each x we get an output value as y.
If to every value of x belonging to some set there corresponds one or several values of the variable y, then y is called a multiple-valued function of x.
Conventionally the word "FUNCTION” is used only as the meaning of a single valued function, if not otherwise stated.
 is called the image of x & x is the pre-image of y under f.
is called the image of x & x is the pre-image of y under f.
Every function from A → B satisfies the following conditions.
(i) f ⊂ A x B
(ii) ∀ a ∈ A ⇒ (a, f(a)) ∈ f and
(iii) (a, b) ∈ f & (a, c) ∈ f ⇒ b = c
Domain, Co-Domain, and Range of a Function
Let f: A → B, then the set A is known as the domain of f & the set B is known as the co-domain of f. The set of all f images of elements of A is known as the range of f. Thus,Domain of f = {a | a ∈ A, (a, f(a)) ∈ f}
Range of f = {f(a) | a ∈ A, f(a) ∈ B}
It should be noted that range is a subset of the co−domain. If only the rule of function is given then the domain of the function is the set of those real numbers, where function is defined. For a continuous function, the interval from minimum to maximum value of a function gives the range.
Important types of function
(i) Polynomial Function
If a function f is defined by f (x) = a0 xn + a1 xn−1 + a2 xn−2 + ... + an−1 x + an, where n is a non-negative integer and a0, a1, a2, ..., an are real numbers and a0 ≠ 0, then f is called a polynomial function of degree n
NOTE : (a) A polynomial of degree one with no constant term is called an odd linear function.
i.e. f(x) = ax, a ≠ 0
(b) There are two polynomial functions, satisfying the relation; f(x).f(1/x) = f(x) + f(1/x).
They are : (i) f(x) = xn + 1 & (ii) f(x) = 1 − xn, where n is a positive integer.
(ii) Algebraic Function
'y' is an algebraic function of 'x', if it is a function that satisfies an algebraic equation of the form
P0 (x) yn + P1 (x) yn−1 + ....... + Pn−1 (x) y + Pn (x) = 0
Where n is a positive integer and P0 (x), P1 (x) ........... are Polynomials in x.
e.g. y = |x| is an algebraic function, since it satisfies the equation y² − x² = 0.
Note that all polynomial functions are Algebraic but not the converse. A function that is not algebraic is called a Transcendental Function.
(iii) Fractional Rational Function
A rational function is a function of the form
y = f (x) =  where g (x) & h (x) are polynomials & h (x) ≠ 0.
where g (x) & h (x) are polynomials & h (x) ≠ 0.
(iv) Absolute Value Function
A function y = f (x) = |x| is called the absolute value function or Modulus function. It is defined as : 
(v) Exponential Function
A function f(x) = ax = ex/n a (a > 0, a ≠ 1, x ∈ R) is called an exponential function. The inverse of the exponential function is called the logarithmic function. i.e. g(x) = loga x.
Note that f(x) & g(x) are inverse of each other & their graphs are as shown.


(vi) Signum Function
A function y= f (x) = Sgn (x) is defined as follows :


It is also written as Sgn x = |x|/ x ; x ≠ 0 ; f (0) = 0
(vii) Greatest Integer or Step Up Function
The function y = f (x) = [x] is called the greatest integer function where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x.
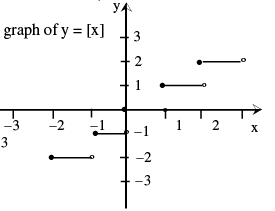
Note that for y=[x],
−1 ≤ x < 0 ; [x] = −1
0 ≤ x < 1 ; [x] = 0
1 ≤ x < 2 ; [x] = 1
2 ≤ x < 3 ; [x] = 2 and so on.
Properties of greatest integer function :
(a) [x] ≤ x < [x] + 1 and x − 1 < [x] ≤ x , 0 ≤ x − [x] < 1
(b) [x + m] = [x] + m if m is an integer .
(c) [x] + [y] ≤ [x + y] ≤ [x] + [y] + 1
(d) [x] + [− x] = 0 if x is an integer = − 1 otherwise.
(viii) Fractional Part Function
It is defined as : g (x) = {x} = x − [x] .
e.g. the fractional part of the no. 2.1 is 2.1− 2 = 0.1 and the fractional part of − 3.7 is 0.3. The period of this function is 1 and the graph of this function is as shown.

Domain and Range of Some Common Functions







Equal or Identical Functions
Two functions f & g are said to be equal if :
(i) The domain of f = the domain of g.
(ii) The range of f = the range of g and
(iii) f(x) = g(x), for every x belonging to their common domain.
eg.  are identical functions.
are identical functions.
Classification of Functions
One-One Function (Injective mapping) :
A function f: A → B is said to be a one−one function or injective mapping if different elements of A have different f images in B.
Thus for x1, x2 ∈ A & f(x1), f(x2) ∈ B,
f(x1) = f(x2) ⇔ x1 = x2 or x1 ≠ x2 ⇔ f(x1) ≠ f(x2).

Note :
(i) Any function which is entirely increasing or decreasing in the whole domain, then f(x) is one−one.
(ii) If any line parallel to the x−axis cuts the graph of the function at most at one point, then the function is one−one.
Many–one function :
A function f: A → B is said to be a many one function if two or more elements of A have the same f image in B. Thus f : A → B is many one if for ; x1, x2 ∈ A, f(x1) = f(x2) but x1 ≠ x2

Note :
(i) Any continuous function which has at least one local maximum or local minimum, then f(x) is many−one. In other words, if a line parallel to x−axis cuts the graph of the function at least at two points, then f is many−one .
(ii) If a function is one−one, it cannot be many−one and vice versa.
Onto function (Surjective mapping):
If the function f: A → B is such that each element in B (co−domain) is the f image of at least one element in A, then we say that f is a function of A 'onto' B. Thus f: A → B is surjective if ∀ b ∈ B, ∃ some a ∈ A such that f (a) = b.

Note that: if range = co−domain, then f(x) is onto. Into function: If f: A → B is such that there exists at least one element in the co−domain which is not the image of any element in the domain, then f(x) is into.

Note: If a function is onto, it cannot be into and vice versa. A polynomial of degree even will always be into function. Thus a function can be one of these four types :
(a) one−one onto (injective & surjective) 
(b) one−one into (injective but not surjective) 
(c) many−one onto (surjective but not injective) 
(d) many−one into (neither surjective nor injective) 
Note : (i) If f is both injective & surjective, then it is called a Bijective mapping.
The bijective functions are also named as invertible, non-singular, or bi-uni form functions.
(ii) If a set A contains n distinct elements then the number of different functions defined from A → A is nn & out of it n ! are one-one.
Identity function:
The function f: A → A defined by f(x) = x ∀ x ∈ A is called the identity of A and is denoted by IA. It is easy to observe that the identity function is a bijection.
Constant function :
A function f: A → B is said to be a constant function if every element of A has the same f image in B. Thus f: A → B; f(x) = c, ∀ x ∈ A, c ∈ B is a constant function. Note that the range of a constant function is a singleton and a constant function may be one-one or many-one, onto or into.
Algebraic Operations on Functions
If f & g are real-valued functions of x with domain set A, B respectively, then both f & g are defined in
A ∩ B.
Now we define f + g, f − g, (f . g) & (f/g) as follows :
 domain in each case is A ∩ B
domain in each case is A ∩ B
 domain is {x | x ∈ A ∩ B s. t g(x) ≠ 0} .
domain is {x | x ∈ A ∩ B s. t g(x) ≠ 0} .
Composite of Uniformly and Non-Uniformly Defined Functions
Let f : A → B & g : B → C be two functions.
Then the function g of : A → C defined by (g of) (x) = g (f(x)) ∀ x ∈ A is called the composite of the two functions f & g .
Diagrammatically, 
Thus the image of every x ∈ A under the function g of is the g−image of the f−image of x.
Note that g of is defined only if ∀ x ∈ A, f(x) is an element of the domain of g so that we can take its g-image. Hence for the product g of of two functions f & g, the range of f must be a subset of the domain of g.
Properties of Composite Functions :
(i) The composite of functions is not commutative i.e. gof ≠ fog .
(ii) The composite of functions is associative i.e. if f, g, h are three functions such that fo (goh) & (fog) oh are defined, then fo (goh) = (fog) oh.
(iii) The composite of two bijections is a bijection i.e. if f & g are two bijections such that gof is defined, then gof is also a bijection.
Homogeneous Functions :
A function is said to be homogeneous with respect to any set of variables when each of its terms is of the same degree with respect to those variables.
For example 5x2 + 3y2 − xy is homogeneous in x & y .
Symbolically if, f (tx , ty) = tn . f (x , y) then f (x , y) is homogeneous function of degree n.
Bounded Function:
A function is said to be bounded if |f(x)| ≤ M, where M is a finite quantity.
Implicit and Explicit Function:
A function defined by an equation not solved for the dependent variable is called an implicit function. For eg. the equation x3 + y3 = 1 defines y as an implicit function. If y has been expressed in terms of x alone then it is called an explicit function.
Inverse of a function: Let f : A → B be a one−one & onto function, then there exists a unique
function g: B → A such that f(x) = y ⇔ g(y) = x, ∀ x ∈ A & y ∈ B. Then g is said to be inverse of f.
Thus g = f−1 : B → A = {(f(x), x) | (x, f(x)) ∈ f} .
Properties of Inverse Function:
(i) The inverse of a bijection is unique.
(ii) If f : A → B is a bijection & g : B → A is the inverse of f, then fog = IB and gof = IA, where IA & IB are identity functions on the sets A & B respectively.
Note that the graphs of f & g are the mirror images of each other in the line y = x. As shown in the figure given below a point (x ',y ' ) corresponding to y = x2 (x > 0) changes to (y ',x ') corresponding to
y = +√x, the changed form of x = √y.



(iii) The inverse of a bijection is also a bijection.
(iv) If f & g two bijections f : A → B , g : B → C then the inverse of gof exists and (gof)−1 = f−1o g−1
Odd and Even Functions:
If f (−x) = f (x) for all x in the domain of ‘f’ then f is said to be an even function.
e.g. f (x) = cos x ; g (x) = x² + 3 . If f (−x) = −f (x) for all x in the domain of ‘f’ then f is said to be an odd function. e.g. f (x) = sin x ; g (x) = x3 + x .
NOTE :
(a) f (x) − f (−x) = 0 => f (x) is even & f (x) + f (−x) = 0 => f (x) is odd.
(b) A function may neither be odd nor even.
(c) The inverse of an even function is not defined.
(d) Every even function is symmetric about the y−axis & every odd function is symmetric about the origin.
(e) Every function can be expressed as the sum of an even & an odd function.

(f) The only function which is defined on the entire number line & is even and odd at the same time is f(x)= 0.
(g) If f and g both are even or both are odd then the function f.g will be even but if any one of them is odd then f.g will be odd.
Periodic Function:
(a) A function f(x) is called periodic if there exists a positive number T (T > 0) called the period of the function such that f (x + T) = f(x), for all values of x within the domain of x.
e.g. The function sin x & cos x both are periodic over 2π & tan x is periodic over π
NOTE : (a) f (T) = f (0) = f (−T) , where ‘T’ is the period.
(b) Inverse of a periodic function does not exist.
(c) Every constant function is always periodic, with no fundamental period.
(d) If f (x) has a period T & g (x) also has a period T then it does not mean that f (x) + g (x) must have a period T.
e.g. f(x) = |sinx| + |cosx|.
(e) If f(x) has a period p, then  also has a period p.
also has a period p.
(f) if f(x) has a period T then f(ax + b) has a period T/a (a > 0).
GENERAL: If x, y are independent variables, then:
(i) f(xy) = f(x) + f(y) ⇒ f(x) = k ln x or f(x) = 0.
(ii) f(xy) = f(x) . f(y) ⇒ f(x) = xn, n ∈ R
(iii) f(x + y) = f(x) . f(y) ⇒ f(x) = akx.
(iv) f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) ⇒ f(x) = kx, where k is a constant.
|
204 videos|290 docs|139 tests
|
FAQs on Important Functions Formulas Formulas for JEE and NEET
| 1. What are some common types of functions in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you determine if a function is even or odd? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a function and a relation in mathematics? |  |
| 4. How do you find the domain and range of a function? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the vertical line test in relation to functions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|



















