Important Formulas: Lines and Angles | Mathematics for Class 6 PDF Download
1. Point: A point is a precise location with no size—no length, width, or height. It is represented by a small dot. Points are labeled with capital letters, like A, B, or C.
2. Line Segment: A line segment has two distinct endpoints and is the shortest distance between these points.
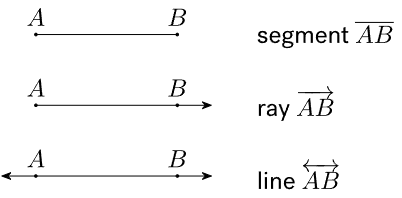
3. Line: A line extends infinitely in both directions and has no endpoints.
4. Ray: A ray starts at one specific point and extends infinitely in one direction.
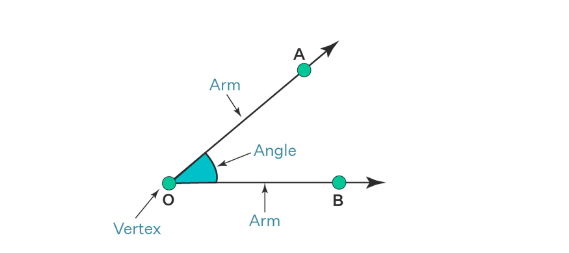
5. Angle: An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common starting point, known as the vertex. The rays are called the arms of the angle. Angles are named using points on each arm and the vertex, like ∠AOB, with the vertex in the middle.
6. Comparing Angles:
- Superimposition: Overlaying one angle on top of another to compare their sizes.
- Alternative Method: Using a transparent circle to compare angles without superimposition.
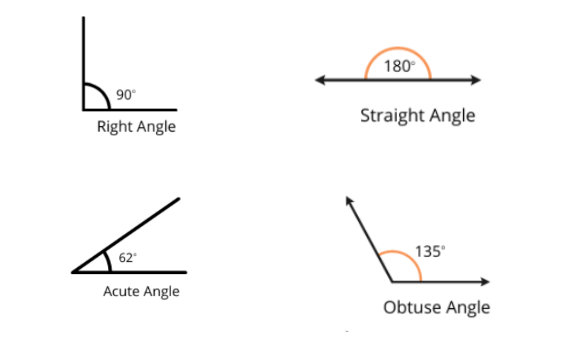
7. Types of Angles:
- Right Angle: Exactly 90°, like the corner of a piece of paper.
- Straight Angle: Exactly 180°, forming a straight line.
- Acute Angle: Less than 90°, like a barely open book.
- Obtuse Angle: More than 90° but less than 180°, like a door opened wider than a right angle.
8. Measuring Angles:
- Degrees: A full circle has 360°, a straight angle is 180°, and a right angle is 90°.
- Protractor: Tool for measuring angles, with units marked in degrees.
- Labeled Protractor: Displays numbers for easy measurement.
- Unlabeled Protractor: Requires counting marks.
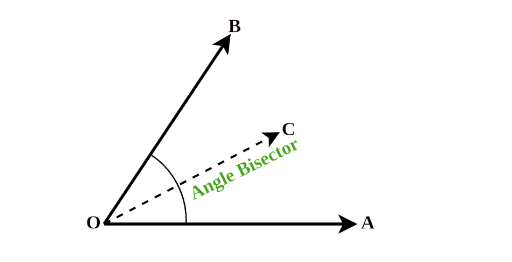
9. Angle Bisector: A line that divides an angle into two equal parts.
10. Common Mistakes with Protractors:
- Incorrect Placement: Ensure the center is on the vertex.
- Misalignment: Align one arm of the angle with the 0° line.
- Wrong Scale: Use the correct scale based on the protractor’s alignment.
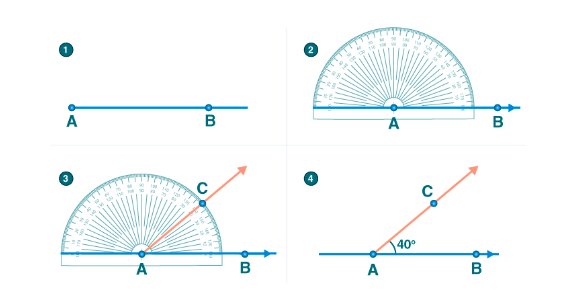
11. Drawing Angles:
Example: To draw a 40° angle, use a protractor to measure and mark the angle, then draw the second arm.
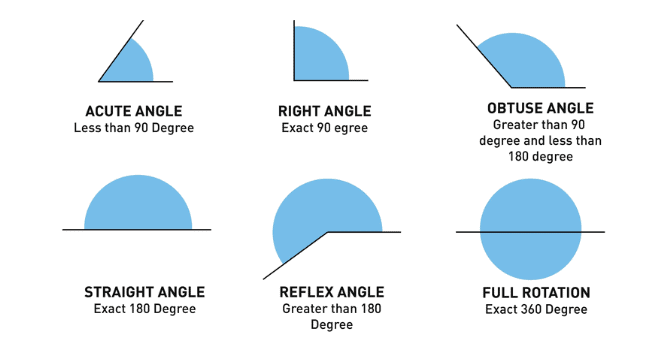
12. Types of Angles and Their Measures:
- Straight Angle: 180°
- Right Angle: 90°
- Acute Angle: More than 0° and less than 90°
- Obtuse Angle: More than 90° and less than 180°
- Reflex Angle: More than 180° and less than 360°
|
48 videos|334 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Lines and Angles - Mathematics for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of angles formed when a transversal crosses two parallel lines? |  |
| 2. How can we identify if two lines are perpendicular to each other? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle? |  |
| 5. How can we determine if two lines are parallel by looking at their slopes? |  |

















