Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 > Important Formulas: Surface Areas & Volumes
Important Formulas: Surface Areas & Volumes | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
Definitions
- Surface area is like the total paper to cover a 3D object.
- Volume is the space it occupies.
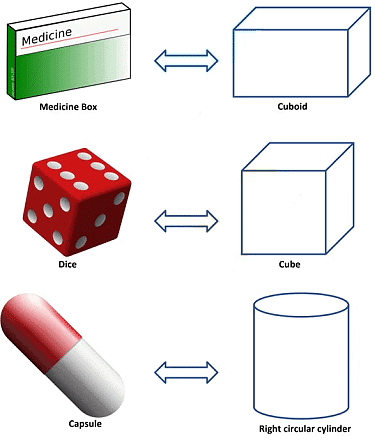
- Cuboid: A 3D box-shaped object with 6 rectangular faces (e.g., bricks, books). Has different lengths, breadths, and heights.
- Cube: A special cuboid where all edges are equal in length. All 6 faces are equal squares (e.g., dice, Rubik’s cube).
- Cylinder: A solid with two parallel circular bases and one curved surface (e.g., cans, pipes).
- Hollow Cylinder: A cylindrical pipe with an empty interior. It has both an inner radius and an outer radius. Example: water pipes or straws.
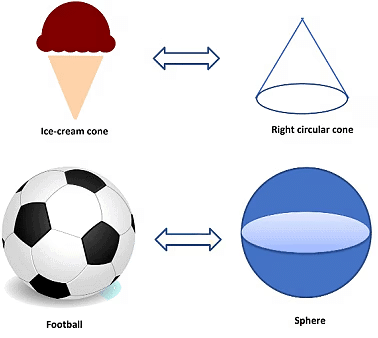
- Right Circular Cones: These cones are three-dimensional shapes with a circular base that narrows down to a single point known as the apex or vertex. For example, an ice cream cone.
- Total Surface Area of a Cone: The total surface area of a cone is the total of its curved surface area (CSA) and the area of its base.
- Spheres: These are completely round three-dimensional shapes, similar to balls or globes. Every point on a sphere's surface is the same distance from its centre.
- Hemispheres: A hemisphere is half of a sphere ('hemi' means half).
- Hollow Sphere (Spherical Shell): A 3D shell with both an outer and inner radius. It’s like a ball with a hollow inside (e.g., a cricket ball or a basketball).
Formulas
- Total surface area of a cuboid = 2[ℓb + bh + ℓh]
- Total surface area of a cube = 6(side)2
- Lateral surface area of a cuboid = Area of walls of a room = 2(ℓ + b) x h
- Lateral surface area of a cube = 4a2
- Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrh
- Total surface area of a cylinder = 2πr(r + h)
- Curved surface area of a cone = πrℓ
- Total surface area of a cone = πr(r + ℓ)
- Surface area of a sphere = 4πr2
- Curved surface area of a hemisphere = 2πr2
- Total surface area of a hemisphere = 3πr2
- Volume of a cuboid = ℓ x b x h
- Volume of a cube = (side)3
- Volume of a cylinder = πr2h
- Volume of a cone =
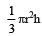
- Volume of a hemisphere =
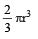 .
. - Volume of a sphere =
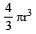
- 1000 cm3 = 1 litre
Now, here is the table for all the formulas in a summarised manner-
The document Important Formulas: Surface Areas & Volumes | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Mathematics (Maths) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
40 videos|560 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Surface Areas & Volumes - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What are the basic formulas for calculating the surface area of common geometric shapes? |  |
Ans. The basic formulas for calculating the surface area of common geometric shapes are as follows:
- Cube: \(6a^2\), where \(a\) is the length of a side.
- Rectangular Prism: \(2(lw + lh + wh)\), where \(l\), \(w\), and \(h\) are the length, width, and height, respectively.
- Sphere: \(4\pi r^2\), where \(r\) is the radius.
- Cylinder: \(2\pi r(h + r)\), where \(r\) is the radius and \(h\) is the height.
- Cone: \(\pi r(r + l)\), where \(r\) is the radius and \(l\) is the slant height.
| 2. How can I calculate the volume of a cylinder? |  |
Ans. The volume of a cylinder can be calculated using the formula \(V = \pi r^2 h\), where \(r\) is the radius of the base and \(h\) is the height of the cylinder.
| 3. What is the formula for the volume of a sphere, and how is it derived? |  |
Ans. The formula for the volume of a sphere is \(V = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3\), where \(r\) is the radius. It is derived using calculus by integrating the area of circular cross-sections of the sphere.
| 4. How do I find the surface area of a cone? |  |
Ans. The surface area of a cone can be calculated using the formula \(S = \pi r(l + r)\), where \(r\) is the radius of the base and \(l\) is the slant height. The formula includes the area of the base (\(\pi r^2\)) and the lateral area (\(\pi rl\)).
| 5. What is the difference between surface area and volume? |  |
Ans. Surface area refers to the total area that the surface of a three-dimensional object occupies, measured in square units, while volume measures the amount of space an object occupies, measured in cubic units. Surface area is concerned with the exterior of the shape, whereas volume deals with the capacity within the shape.
Related Searches






















