Important Formulas: The Dairy Farm | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
1. What is Multiplication?
Multiplication = making equal groups.
Example: 6 × 2 = 6 groups of 2 = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
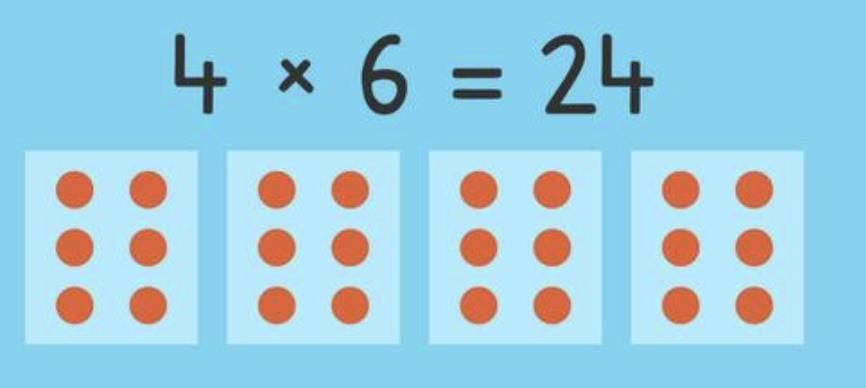
It is faster than repeated addition.
2. Key Properties of Multiplication
1. Commutative Property
a × b = b × a
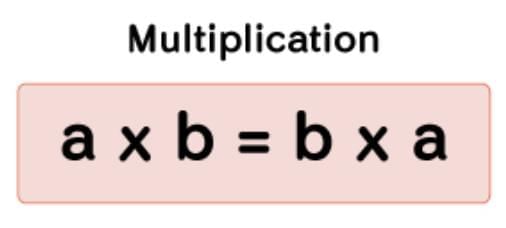
Example: 7 × 6 = 42 and 6 × 7 = 42
2. Multiplicative Identity
a × 1 = a

Example: 13 × 1 = 13
3. Multiplication by Zero
a × 0 = 0
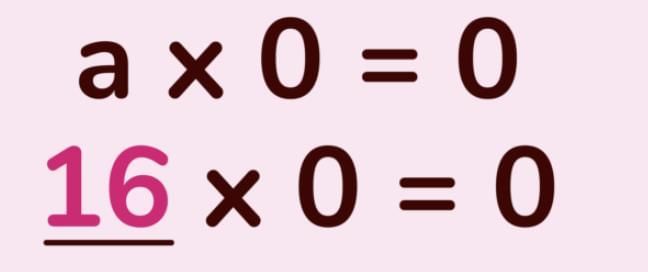
Example: 9 × 0 = 0
4. Distributive Property
a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
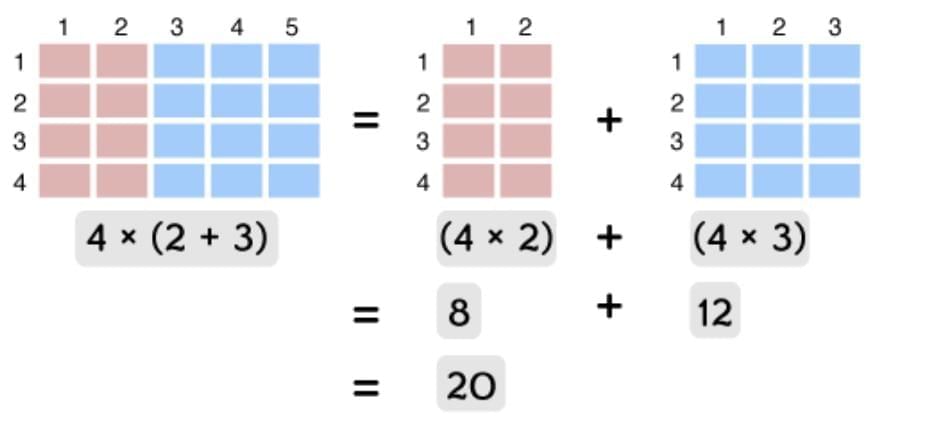
Example: 12 × (10 + 2) = (12 × 10) + (12 × 2) = 120 + 24 = 144
3. Multiplying by 10, 100, 1000…
When we multiply by 10, shift digits one place left, add 1 zero.
When we multiply by 100, shift digits two places left, add 2 zeros.
When we multiply by 1000, shift digits three places left, add 3 zeros.
Examples:
7 × 10 = 70
23 × 10 = 230
56 × 100 = 5600
8 × 1000 = 8000
4. Strategies to Multiply
Breaking into Parts (Distributive Law)
35 × 12 = (30 + 5) × (10 + 2)
= (30 × 10) + (30 × 2) + (5 × 10) + (5 × 2)
= 420
Nearest Multiple Method
19 × 4 = (20 × 4) – (1 × 4) = 80 – 4 = 76
Doubling & Halving
22 × 5 = (11 × 10) = 110
Splitting Numbers
18 × 5 = (10 × 5) + (8 × 5) = 50 + 40 = 90
Repeated Multiplication (Powers)
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 2⁴ = 16
5. Long Multiplication & Place Value
Always align digits by ones, tens, hundreds.
Put 0 when multiplying by tens, 00 for hundreds.
Carries belong to the next place value (not to small numbers).
Example:
268 × 4 = 1,072
453 × 13 = 5,889
6. Patterns in Multiplication
Numbers ending in 5:
(a5)² = a × (a+1) followed by 25
Example: 45² = (4×5)25 = 2025
All 1s squared:
11 × 11 = 121
111 × 111 = 12321
Multiplying by 11:
11 × ab = a (a+b) b (with carry if needed)
Example: 11 × 82 = 902
Pattern with 9s:
1 × 9 + 1 = 10
12 × 9 + 2 = 110
123 × 9 + 3 = 1110
7. Growth with Repeated Multiplication (King’s Reward Story)
Repeated multiplication grows numbers very fast.
Example: Minister 3 (×5 daily) → 78,125 coins after 7 days, biggest reward.
|
35 videos|276 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: The Dairy Farm - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is multiplication and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are the key properties of multiplication? |  |
| 3. How does multiplying by 10, 100, and 1000 affect a number? |  |
| 4. What are some effective strategies for multiplying numbers? |  |
| 5. What is long multiplication and how does place value play a role in it? |  |





















