Force and Pressure Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 8
What is a Force?
When a push or pull is applied to an object it is called force.
- A force can change the state of an object from rest to motion or vice versa.
- To let a force come into play, two or more objects must interact with each other.
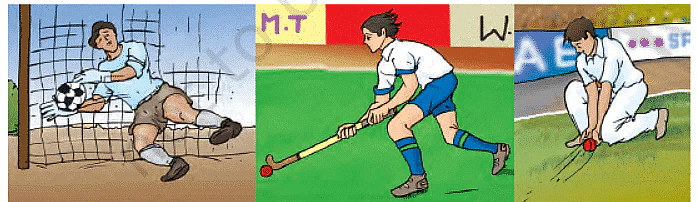 Examples of Force
Examples of Force
Characteristics of forces
We know that a magnet can attract a piece of iron. Hence, we can say that the magnet pulls the iron piece towards itself due to its magnetic force. Similarly, when opposite poles of a magnet repel each other, we can say that they are pushing each other away.
- When two forces act in the same direction, the net resultant force on an object is the sum of these two forces.
- When two forces act in opposite directions, the net resultant force is the difference between these two forces. The force has a magnitude that describes its strength.
- The force always has a direction in which it is applied and a measure of its strength or magnitude.
- The effects of a force may alter when the direction of the magnitude of the force is changed.
- The effect of more than one force being applied on an object is calculated by evaluating the net force acting on that object.
- If two forces are acting upon each other having equal magnitudes (strength) and in opposite directions, then the net force acting on the object will be zero.
- Force can bring different effects on an object’s position, size and shape.
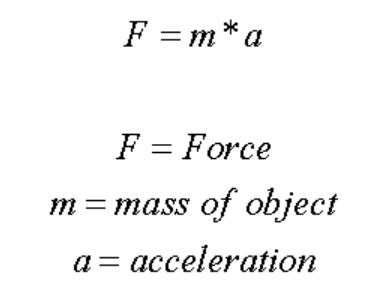
- The SI unit of force is Newton (N).
Force can change the state of motion of an object
- An object is said to be in motion if it is moving at a certain speed in a particular direction.
- If the object is at rest, it means that it is not changing its position with respect to an observing point. Hence it has zero speed.
- When the object starts moving it means that its position is being changed with respect to an observation point.
In order to move an object from one place to another, a force is required to bring that object in motion.
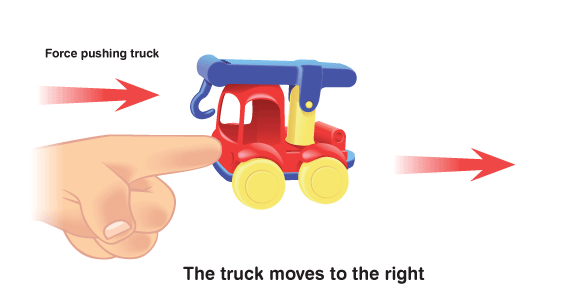
- Not only this, a force applied on to an object can change its speed, bring it to rest, or even change the direction of its motion.
- It may bring a combination of these effects as well, such as a change in the direction of motion and a change in the speed of the motion altogether.
- Hence, we can say that force can change an object's state of motion.
- Any object cannot move by itself or change its state of motion on its own without the application of a force.
- However, it is not a case that this change of state of motion will take place every time with every kind of object. For instance, if a person tries to push a very heavy object, such as a wall, it would not at all.
Force can change the shape of an object
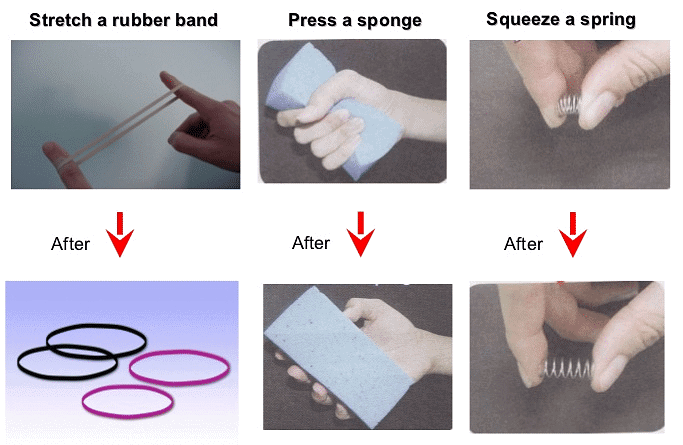 Force can change the shape of an object
Force can change the shape of an object
- The shape of an object can be altered if some force is applied on to it.
- Depending upon the magnitude of the force that is being applied and the rigidity of the object, the effect on its shape and size can be observed.
Types of Forces
On the basis of the nature of the interaction between two or more objects, forces can be classified as

Contact Forces
1. Muscular Force
The force that comes into play because of the action of muscles is called muscular force. For example:
- Human beings use muscular force in order to walk.
- The expansion and contraction of the lungs are because of muscular force
- Movement of food along the food pipe
- Animals can also exit muscular forces; that's why they can move from one place to another
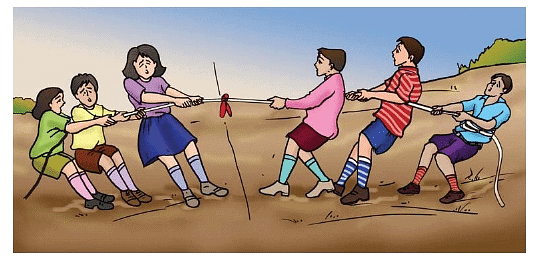 Muscular Force applied in Tug-of-War
Muscular Force applied in Tug-of-War
 Muscular Force applied by Animals
Muscular Force applied by Animals
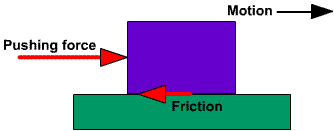
2. Frictional Force
It is the force that is exerted by the surface over an object whenever the object moves on the surface. The force of friction has the following characteristics:
- The force of friction always acts in the opposite direction of the motion of the object.
- It leads to the generation of heat as two surfaces come in contact with each other. For example, when we rub our hands together, heat is produced as a result of friction between our hands.
- The frictional force also leads to wear and tear on the surfaces of objects that come in contact with each other. For example, soles of shoes often get worn out due to friction force that acts between them and the ground as we walk.
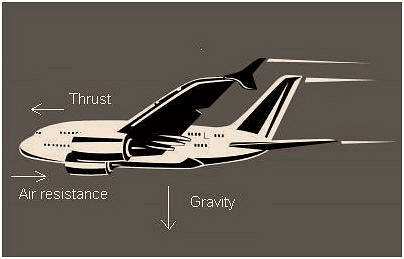
3. Air Resistance
Whenever an object moves or flies in the air, it experiences a force called air resistance.
Non-Contact Forces
1. Magnetic Force
- The force exerted by any magnetic object is called magnetic force.
- We know that, like magnetic poles always repel each other, that is, they push each other away.
- When opposite poles of a magnet attract each other, we can say that they are pulling each other towards themselves.
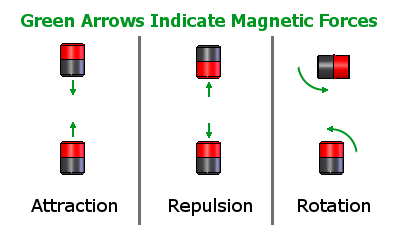 Magnetic Force
Magnetic Force
2. Electrostatic Force
- The force exerted by a charged particle is called electrostatic force.
- We know that like charges always repel or push each other away.
- Similarly, opposite charges always attract or pull each other towards themselves.
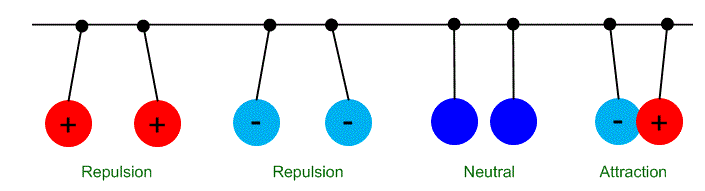 Electrostatic Forces
Electrostatic Forces
3. Gravitational force
- It is an attractive force that is applied by the Earth on all objects.
- It is also called the force of gravity or gravity that acts upon all the objects that are present on or near the Earth's surface.
- Gravity is a property exhibited by every object present in the universe and not only the Earth. Hence, all the planets, the moons, and even the sun have a gravitational force of their own.
 Gravitational Force
Gravitational Force
Pressure
- Not only the magnitude of the force but the area upon which it acts also affects the changes it may bring upon an object.
- The force acting upon a unit area is called pressure.
- Hence, the pressure exerted by an object depends upon its surface area.
- If the surface is small, the amount of pressure applied is large, and vice-versa.
- The SI unit of Pressure is Pascal (Pa) or N/m2
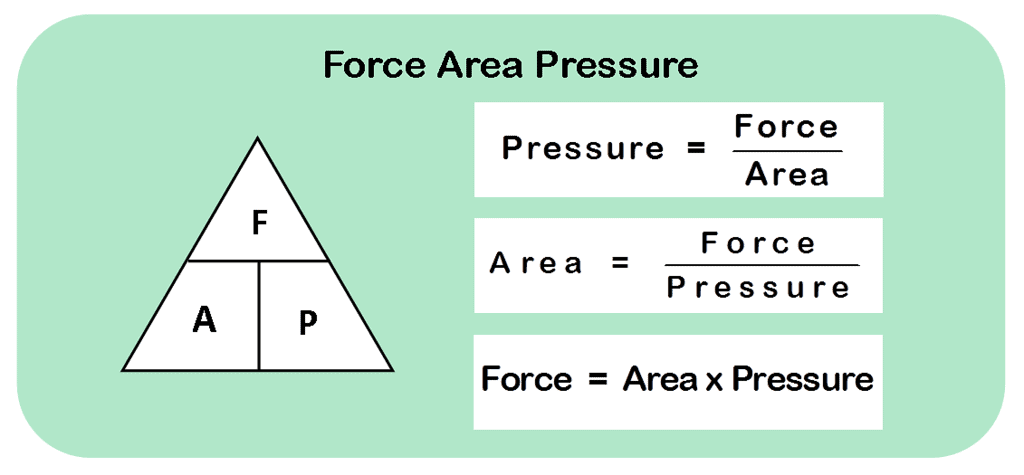 Relation between Force, Pressure and Area
Relation between Force, Pressure and AreaExamples of the relationship between the area and pressure
 Calculating Pressure for Different Areas
Calculating Pressure for Different Areas
- A needle has a pointed end that has a very small surface area. Hence when a large force is exerted upon the needle with a hammer, the pressure on the needle increases and it easily moves inside the wall.
- Shoulder bags always have broad straps rather than thin straps in order to minimize the pressure that would be exerted on the shoulders of the carrier due to the gravitational force acting upon the bag.
- Tools that are used for cutting and piercing always have sharp edges because as a person would apply a force on the tool, its sharp edges would exert more pressure due to less surface area and the object would cut down easily.
- The two tires of a tractor are wider because it minimizes the pressure exerted by the tractor on the ground. As a result, it becomes easier to move the tractor on a muddy field.
- Camel can walk easily over the sand because it has wide feet which allow them to walk on sand easily. Human beings, on the other hand, cannot as walk easily on the sand as their feet have less surface area and therefore, our feet sink in the sand.
The pressure exerted by liquids and gases
- Liquids exert pressure on the walls of the container in which they are put in.
- The pressure that a liquid exerts on the bottom of the container is dependent upon the height of the liquid in the container.
- The liquid exerts equal pressure on different points on the walls of the container having the same depth.
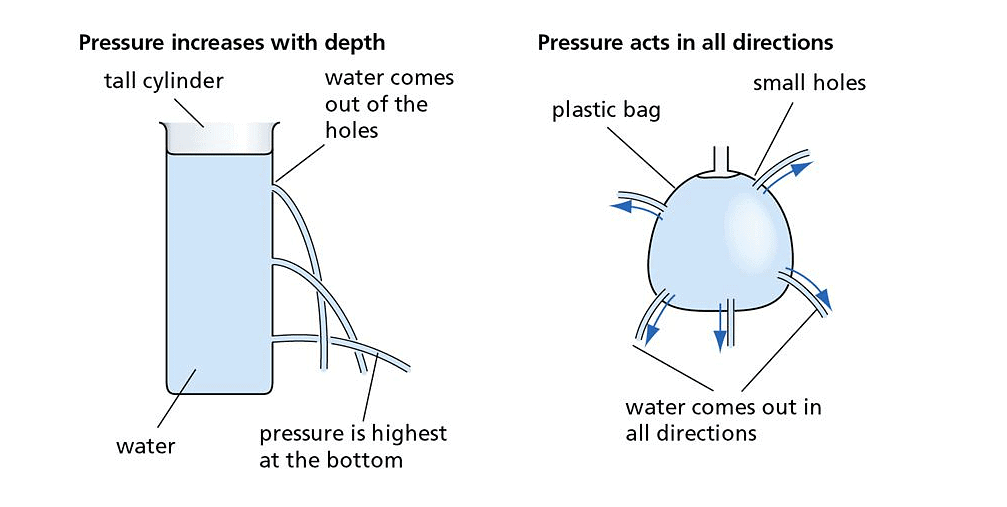 Pressure Exerted by Liquids
Pressure Exerted by Liquids
- Similarly, gases also exert pressure on the walls of the container. The molecules of a gas of higher kinetic energy collide with walls applying large force, and as a result, these molecules apply pressure on the walls of the container.
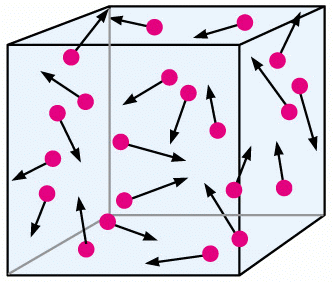
Atmospheric Pressure
- A layer of gases is present around the earth’s surface. The air present in the atmosphere exerts pressure on the earth which is called atmospheric pressure.
- The value of atmospheric pressure at the sea level is 101325 Pascal.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, so as one moves closer to the Earth's surface (from higher altitudes), pressure increases.
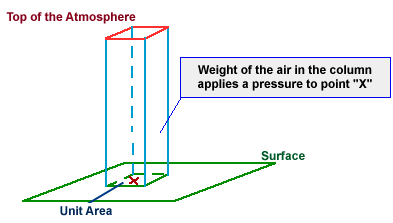 Atmospheric Pressure Demonstration
Atmospheric Pressure Demonstration
The amount of atmospheric pressure upon us is quite large due to the large surface area of the atmosphere around the earth but we do not experience any of its effects.
- This is so because the pressure of the air inside our body is equal to the atmospheric pressure. There are also fluids present in our body that exert pressure inside our body. Hence, our bodies easily obtain a balance with the atmospheric pressure.
However, sometimes at higher altitudes where the atmospheric pressure is low as compared to that at the Earth’s surface (low altitudes), nose bleeding occurs.
- This is so because, at that time, the blood pressure in our body becomes higher than the atmospheric pressure outside us.
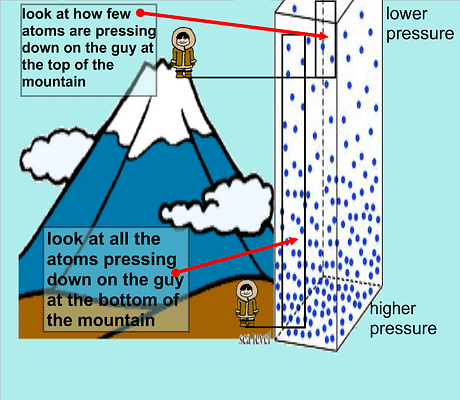
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Force and Pressure Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 8
| 1. What is the relationship between force and pressure? |  |
| 2. What are examples of contact forces that can affect pressure? |  |
| 3. How does force change the state of motion of an object? |  |
| 4. Can pressure change the shape of an object? |  |
| 5. What are examples of non-contact forces that can affect pressure? |  |






















