Sound Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 11
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Production of Sound |

|
| Propagation of Sound |

|
| Speed of Sound in Different Media |

|
| Reflection of Sound |

|
Introduction
Sound is a form of energy causing a hearing sensation. Other energy forms include mechanical and light energy.Energy conservation is the transformation, not creation or destruction, of energy. Sound production involves energy utilization.
Production of Sound
- Sound is generated by vibrations (e.g., clapping hands).
- Various methods produce sound: plucking, scratching, blowing, etc.
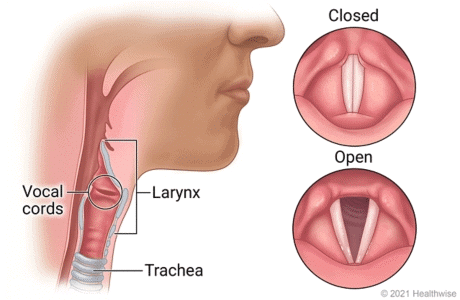
- Vibrations in vocal cords produce human voice.
- Sound in musical instruments comes from specific vibrating parts.
Propagation of Sound
Sound travels through mediums (solid, liquid, gas). It involves particle vibrations in the medium, which transmit the sound.- Waves: Disturbances moving through mediums.
- Sound waves: Mechanical waves characterized by particle motion.
Propagation of sound in Air:
Vibrations create high-pressure compressions and low-pressure rarefactions.
Wavelength (λ): Distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions.
Formula: Speed (ν) = Frequency (ƒ) × Wavelength (λ).
Sound Waves as Longitudinal Waves
- In longitudinal waves, particle movement is parallel to wave propagation.
- Slinky example demonstrates longitudinal wave properties.
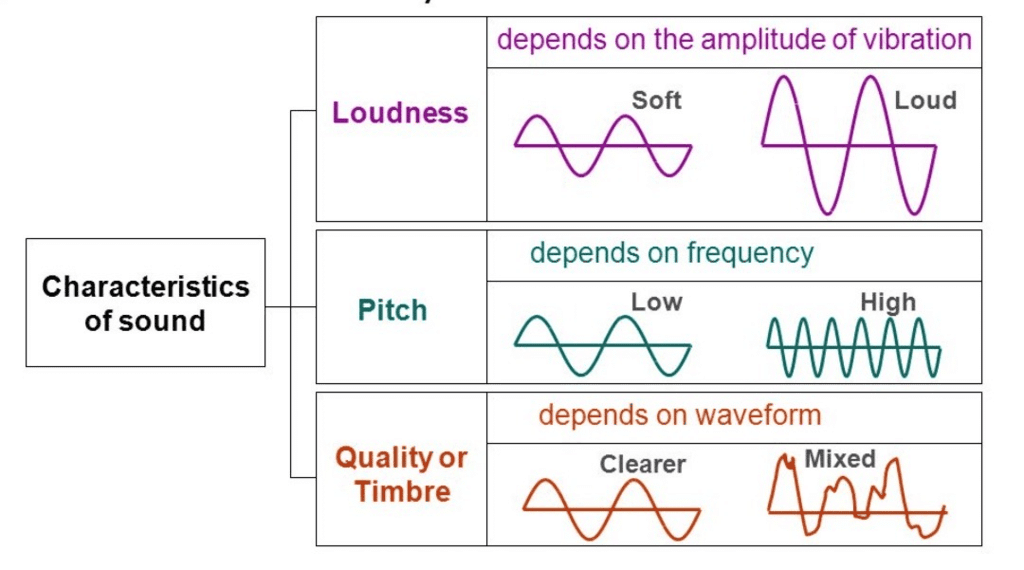
Characteristics of a Sound Wave
- Frequency: Number of oscillations per unit time (Hertz).
- Amplitude: Maximum disturbance magnitude in the medium.
- Speed: Distance a point on the wave travels per unit time.
- Loudness related to amplitude, pitch to frequency.
- Quality (Timbre): Quality differentiating sounds with same pitch and loudness.
- Pitch: Higher frequency means higher pitch of the produced sound.
- Intensity: Energy passing through a unit area per second.
Speed of Sound in Different Media
Speed varies with medium and temperature. Faster in solids, slower in gases.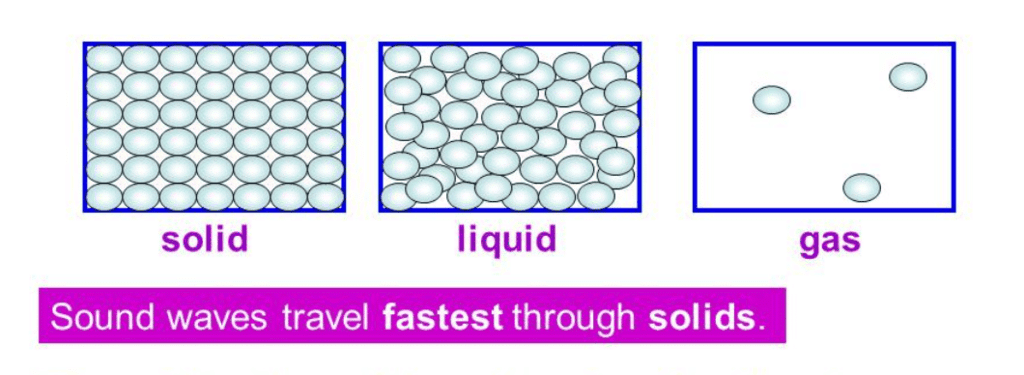 Note: Speed of sound increases with increase in temperature.
Note: Speed of sound increases with increase in temperature.
Range of Hearing
- Human audible range: 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
- Infrasound: Below 20 Hz : Used by animals like whales and elephants.
- Ultrasound: Above 20 kHz : Used by bats, dolphins, and for industrial and medical applications.
Age and species affect hearing range.
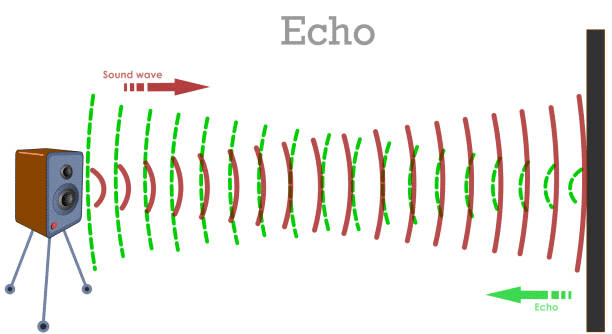
Reflection of Sound
Sound waves obey the law of reflection (angle of incidence = angle of reflection).Echo
Reflected sound heard after 0.1 seconds.
Minimum distance for an echo: 17.2 m (for air at 22°C).
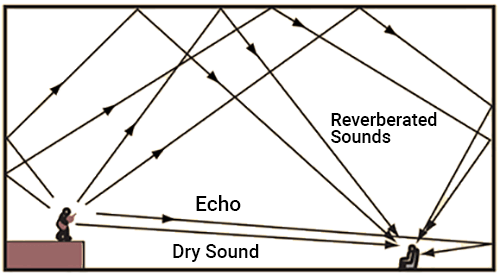
Reverberation
Continuous reflection causes prolonged sound.
Reduced using sound-absorbing materials like curtains or fibreboard.
Applications of Multiple Reflections
1. Megaphones and Loudhailers: Direct sound using conical shapes.
2. Stethoscopes: Reflect sound to amplify body sounds.
3. Auditoriums: Curved ceilings distribute sound evenly.
4. Rolling Thunder: Repeated reflections of sound.
Applications of Ultrasound
1.Cleaning: Removes dust and grease from hard-to-reach areas.
2. Detecting Cracks: Identifies flaws in metal blocks.
3. Echocardiography: Creates images of the heart using reflected ultrasonic waves.
4. Ultrasonography:
- Images internal organs.
- Detects abnormalities (e.g., stones, tumours).
- Useful during pregnancy for checking fetal development.
5. Kidney Stone Treatment: Breaks stones into smaller fragments for natural expulsion.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Sound Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 11
| 1. What is the definition of sound in physics? |  |
| 2. How is sound produced? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of sound? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves in the context of sound? |  |
| 5. How does the medium affect the speed of sound? |  |
















