Important Questions: Locating Places on the Earth | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1. What is a map, and what are its main types?
Answer: A map is a visual representation of an area showing features like mountains, rivers, cities, and roads. The main types of maps are:
- Physical Maps: Show natural features like mountains, rivers, and lakes.
- Political Maps: Show boundaries of countries, states, and cities.
- Thematic Maps: Focus on specific information, such as population density or climate zones.
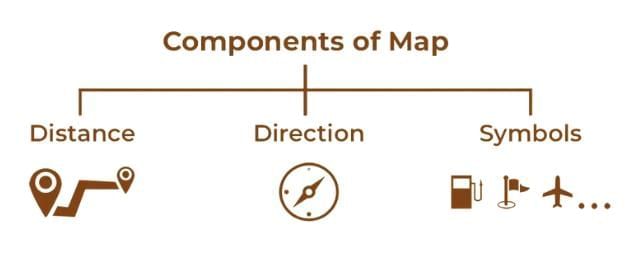
Q2. What are the key components of a map? Explain each briefly.
Answer: The key components of a map are:
- Distance: Represented by a scale, which shows the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground (e.g., 1 cm = 500 meters).
- Direction: Indicated by cardinal directions (North, South, East, West) and intermediate directions (Northeast, Southeast, Southwest, Northwest), often shown by a north arrow.
- Symbols: Pictures or shapes representing features like forests, roads, or cities, explained in the map’s legend or key.
Q3. What is the difference between a globe and a map?
Answer: A globe is a three-dimensional, spherical model of the Earth that accurately shows proportions and distances. A map is a flat, two-dimensional representation of an area, which is more convenient but less accurate due to distortions.
Q4. What are latitudes and longitudes, and how do they help locate places?
Answer:
- Latitudes: Imaginary horizontal lines running parallel to the Equator, measuring distance north or south (0° to 90°). The Equator is at 0° latitude.
- Longitudes: Imaginary vertical lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring distance east or west (0° to 180°) from the Prime Meridian (0° longitude).
Together, latitude and longitude form coordinates (e.g., 23.5°N, 74°W) to pinpoint exact locations on Earth.
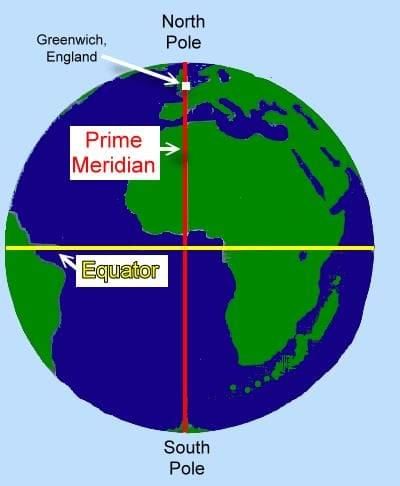
Q5. What are the Equator and Prime Meridian? How do they divide the Earth?
Answer:
- Equator: An imaginary line at 0° latitude that circles the Earth, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- Prime Meridian: An imaginary line at 0° longitude passing through Greenwich, England, dividing the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Q6. What are climate zones, and how are they related to latitude?
Answer: Climate zones are areas of the Earth with distinct climates based on latitude:
- Torrid Zone: Near the Equator (hot climate).
- Temperate Zones: Between the tropics and polar circles (moderate climate).
- Frigid Zones: Near the poles (very cold climate).
Q7. What is the significance of the Ujjayinī meridian in ancient Indian astronomy?
Answer: The Ujjayinī meridian, also called madhya rekhā, was an ancient Indian prime meridian passing through Ujjain, used as a reference for astronomical calculations. Indian astronomers, like Varāhamihira, used it to study latitude, longitude, and time, showcasing India’s advanced astronomical knowledge.
Q8. How is local time determined by longitude?
Answer: Local time is determined by a place’s longitude because the Earth rotates 15° every hour. Places with the same longitude have the same local time. Moving east from the Prime Meridian adds one hour per 15°, while moving west subtracts one hour per 15°.
Q9. What are time zones, and why do we need standard time?
Answer: Time zones are regions of the Earth divided by 15° of longitude, each with a standard time differing by about one hour from neighboring zones. Standard time is adopted within a country to avoid confusion from multiple local times, ensuring consistency (e.g., Indian Standard Time is GMT +5:30).
Q10. What is the International Date Line, and how does it affect the date?
Answer: The International Date Line is an imaginary line at approximately 180° longitude. Crossing it eastward subtracts a day (e.g., Monday to Sunday), while crossing westward adds a day (e.g., Sunday to Monday). It deviates to avoid splitting countries into different days.
Q11. Why do some countries have multiple time zones?
Answer: Large countries like Russia, Canada, and the USA have multiple time zones because they span wide longitudinal ranges, causing significant time differences across their regions. For example, Russia has 11 time zones, requiring adjustments when traveling across the country.
Q12. What is a map’s scale, and why is it important?
Answer: A map’s scale is the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground (e.g., 1 cm = 500 meters). It is important because it helps measure real-world distances accurately, making maps useful for navigation and planning.
Q13. What is the role of a map’s legend or key?
Answer: The legend or key explains the symbols used on a map, such as a tree for a forest or a dotted line for a road, helping users understand the map’s features.
Q14. How does the Earth’s rotation affect time zones?
Answer: The Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, or 15° per hour, from west to east. This causes different longitudes to experience different local times. Time zones are set every 15° to standardize time, with each zone differing by about one hour.
Q15. Define the following key terms: Hemisphere, Meridian, Coordinate.
Answer:
- Hemisphere: One half of the Earth, divided by the Equator (Northern/Southern) or Prime Meridian (Eastern/Western).
- Meridian: An imaginary line running from the North Pole to the South Pole, used to measure longitude.
- Coordinate: A pair of numbers (latitude and longitude) used to pinpoint a location on Earth.
|
45 videos|310 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Locating Places on the Earth - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What are the different methods used to locate places on Earth? |  |
| 2. How does the concept of latitude and longitude work? |  |
| 3. Why is the Equator considered an important reference line? |  |
| 4. What role do maps play in locating places on Earth? |  |
| 5. How has GPS technology changed the way we locate places? |  |