Class 5 Maths Chapter 2 Important Question Answers - Chapter 2 - Shapes and Angles
Q1: What is the difference between a closed shape and an open shape?
Ans: The difference between a closed shape and an open shape lies in whether the shape is fully connected or not:
1. Closed Shapes:
- A closed shape is a shape where all sides or lines are connected, with no openings. It encloses a specific area, meaning there is no gap between the endpoints.
- Examples: Circle, triangle, square, rectangle.
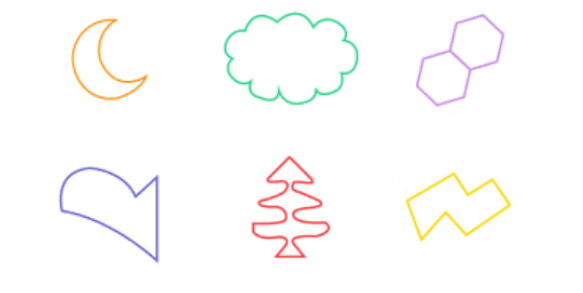 Examples of Closed Shapes
Examples of Closed Shapes
2. Open Shapes:
- An open shape has at least one side or part that is not connected, leaving a gap or opening. It does not enclose a specific area.
- Examples: A curved line, a V-shape, or a path with endpoints that don't meet.
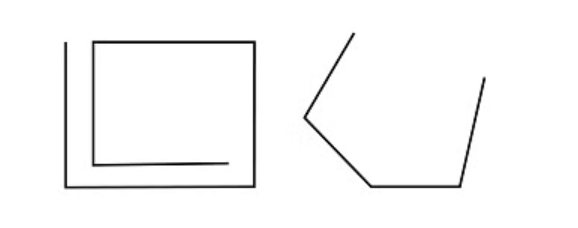 Examples of Open Shapes
Examples of Open Shapes
Q2: Imagine you are making a slide for the playground. How would you make a fast slide? Draw a 'fast' slide and a 'slow' slide.
Ans: To make a fast slide, you need to make it steep. A steeper slide means the angle between the slide and the ground is larger. So a 'fast' slide will be drawn more upright, while a 'slow' slide will be drawn longer and flatter.
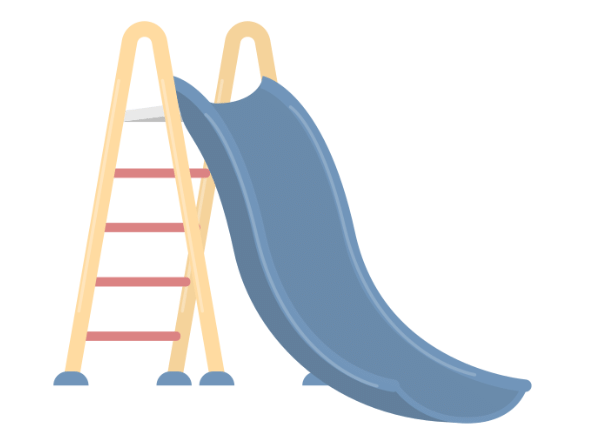 Fast Slide: Steeper Slope
Fast Slide: Steeper Slope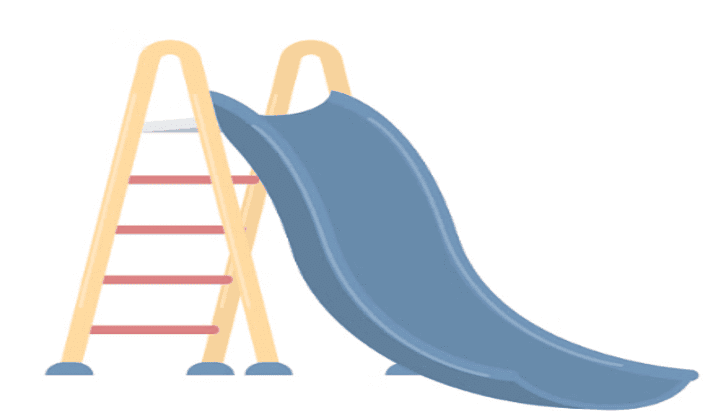 Slow Slide: Flatter Slope
Slow Slide: Flatter Slope
Q3: True or False: There are no edges in a spherical shape.
Ans: True.
A spherical shape, like a ball, has no edges. An edge is a straight line where two faces meet, but a sphere is completely smooth and round with no flat surfaces or sharp corners. It has a continuous, curved surface, so it doesn't have any edges, vertices or angles.
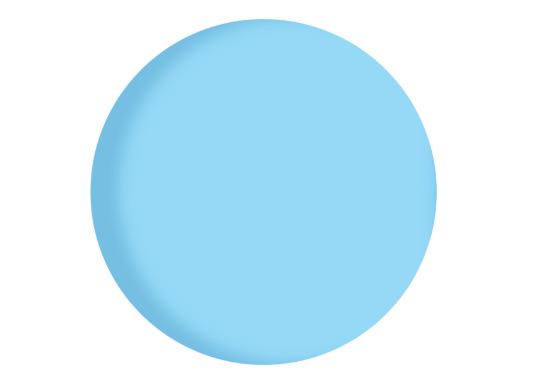 A Spherical Shape
A Spherical Shape
Q4: Construct the following angles using a 'D': 45°
Ans: Place the D on a piece of paper and follow the steps:
Step 1: Draw a line segment OB.
Step 2: Place the protractor ('D') at point O.
Step 3: In the outer circle of the protractor, look for 45 degrees reading, and with a pencil mark a dot and name it A.
Step 4: Join the point O with point A.
You have ∠AOB = 45°
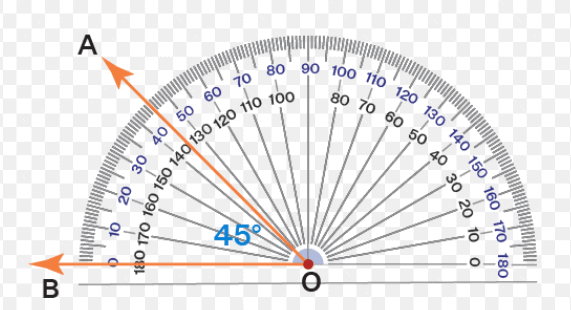
Q5: Construct the following angles using set-squares: 90°
Ans: Place 45° set-square as shown in the figure.
Draw two rays BC and BA along the edge from the vertex of 90° angle.
The angle so formed is 90° angle.
∠ABC = 90°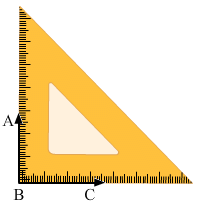
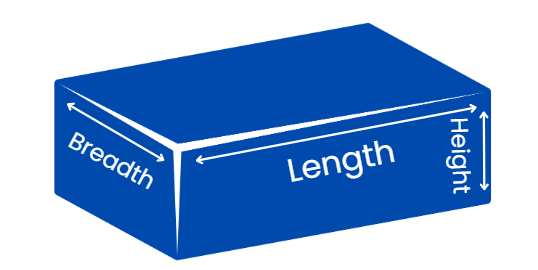
Q6: What is the shape of your instrumental box?
Ans: Consider an instrumental box shown in the image below. Hence, from the image, we can see that the shape of the instrumental box is cuboid.
Q7: What is the angle made by the hour and the minute hands in the following images given below?
(a) Less than 45 degrees
(b) More than 45 degrees but less than 90 degrees
(c) More than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
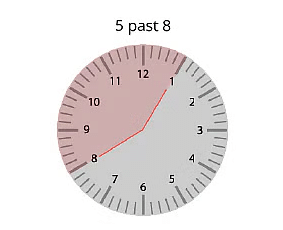
Ans: (c) More than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
By looking at the hour clock, we can see that the angle made by the clock in the question more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
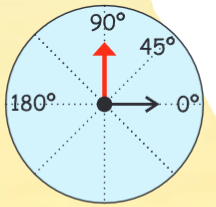
Q8: You are standing in a class-room facing north. In what direction are you facing after making a quarter turn to the right?
Ans: Right now you are standing facing the North. A quarter turn means turning 90° to the right. This means that you will now be facing east.
|
31 videos|192 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Class 5 Maths Chapter 2 Important Question Answers - Chapter 2 - Shapes and Angles
| 1. What are the different types of angles in geometry? |  |
| 2. How do I measure an angle using a protractor? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of angles in a triangle? |  |
| 4. Can you define complementary and supplementary angles? |  |
| 5. What is a right angle and how can I identify it? |  |
















