Important Questions: Timeline and Sources of History | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What do geologists study?
Ans: Geologists study the physical features of the Earth, including soil, stones, hills, mountains, rivers, seas, and oceans.
Q2: What types of remains do archaeologists dig up?
Ans: Archaeologists dig up tools, pots, toys, bones, teeth, and parts of houses left by previous cultures.

Q3: What is the most widely used calendar in the world today?
Ans: The Gregorian calendar
Q4: What does 'AD' stand for in the Western calendar system?
Ans: Anno Domini
Q5: What does a dotted line on a timeline indicate?
Ans: It indicates a skipped period of time to keep the timeline concise.
Q6: What do epigraphists study?
Ans: Epigraphists study ancient inscriptions.
Q7: When did the last Ice Age start and end?
Ans: It started over 100,000 years ago and ended about 12,000 years ago.
Q8: What crops did people begin to grow after the Ice Age?
Ans: Cereals and grains.
Q9: What tools did early humans use to make life easier?
Ans: Stone axes and arrowheads.
Q10: How long have modern humans, Homo sapiens, been on Earth?
Ans: About 300,000 years.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q11: Who examines fossils? Define fossils.
Ans: Palaeontologists examine fossils, which are remains of ancient plants and animals. Fossils are impressions or remains of plants and animals preserved in soil or rock layers.

Q12: Why is studying Earth’s history important?
Ans: Studying Earth's history is crucial as it helps us understand how life has changed over time. It also teaches us about the environment and how to protect it for the future.
Q13: Why do different cultures have different calendars?
Ans: Different cultures have different calendars because they celebrate important events and festivals based on their own history and beliefs. Each calendar reflects what is important to that culture.
Q14: How do we count centuries and millenniums?
Ans: We count centuries and millenniums both forwards (CE) and backwards (BCE). A century is 100 years and a millennium is 1,000 years. For example, the 21st century is from 2001 to 2100, and the 1st millennium BCE is from 1000 BCE to 1 BCE.
Q15: What happened when the Ice Age ended?
Ans: When the Ice Age ended, the weather became warmer, and the ice melted. This made rivers and oceans fill with water, which helped people and animals find food and water more easily.
Long Answer Type Questions
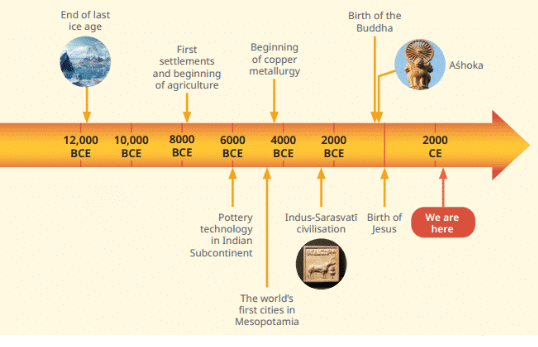
Q1: Explain how timelines help us understand the past with examples of events.
Ans:
- Timelines show the order of past events clearly.
- They stretch from early human times, 300,000 years ago, to now, marking big moments.
- For example, the last Ice Age ended 12,000 years ago, then farming began around 10,000 years ago, and cities rose in Mesopotamia by 4000 BCE.
- Gautama Buddha’s birth around 560 BCE comes before Jesus Christ’s at 1 CE, and India’s independence in 1947 CE follows.
- Without a year zero, 560 BCE to 2024 CE is 2,583 years (560 - 2024 - 1).
- This sequence helps us see how hunting led to farming, then towns, linking yesterday to today step by step.
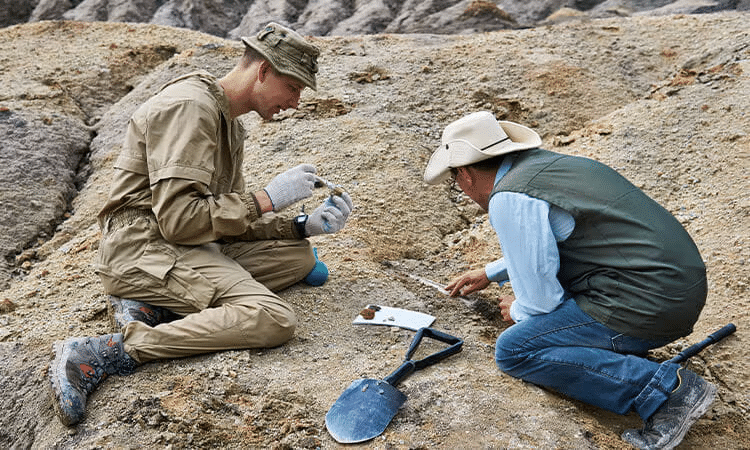
Q2: Describe how experts uncover history using different methods.
Ans:
- Experts dig into the past in unique ways.
- Geologists study Earth’s features like mountains and rivers to learn its story.
- Paleontologists examine fossils—old bones or plant remains—to understand ancient life.
- Anthropologists look at human societies, from early groups to now, exploring cultures.
- Archaeologists unearth tools, pots, and bones to piece together how people lived.
- Together, they use these clues, plus science like genetics or climate studies, to rebuild history.
- In recent times, newspapers and TV have added more details.
- Each method fits pieces into the puzzle, showing how humans and Earth changed over millions of years.
Q3: Discuss how time is measured in history with examples of eras and centuries.
Ans:
- Time in history uses years, centuries, and millennia, counted with the Gregorian calendar.
- The years prior to the birth of Jesus Christ are referred to as BCE (Before Common Era) and the years after his birth are referred to as CE (Common Era).
- For instance, the emergence of Mahajanpadas in India occurred around six hundred years before the birth of Jesus Christ, so it can be dated as 600 BCE. Similarly, India won its independence from the British around 1947 years after Jesus' birth and hence, it's dated as 1947 CE.
- A century is 100 years—2024 CE is in the 21st century (2001–2100), while 300 BCE to 201 BCE is the 3rd century BCE.
- A millennium is 1,000 years—the 3rd millennium CE runs 2001–3000.
- No year zero means 1 BCE jumps to 1 CE.
- This system tracks events, showing Buddha lived over 2,500 years before us.
Q4: Explore how sources like objects and stories reveal the past.
Ans:
- Sources like objects and stories unlock the past vividly.
- Old coins, tools, or pots show how people worked and lived—archaeologists find these buried clues.
- Rock paintings from caves, with animals or humans, hint at early beliefs and hunts.
- Family tales or diaries share personal histories, like a grandparent’s life.
- For bigger events, inscriptions or newspapers tell of kings or wars.
- Sometimes sources clash, so historians pick the truest ones.
- Science, like studying old bones’ genetics, adds fresh facts.
- These bits—pots, paintings, words—fit together, building a picture of life long ago, from daily tasks to big changes.
Q5: Explain how early humans adapted and grew into farming communities.
Ans:
- Early humans, around 300,000 years ago, faced tough times, living in caves or shelters.
- They hunted animals and gathered plants, using fire and stone tools like axes.
- Rock paintings show their life and beliefs.
- After the last Ice Age ended 12,000 years ago, warming melted ice, swelling rivers with fertile soil.
- By 10,000 years ago, they settled near rivers, growing grains and taming animals like goats.
- Villages formed, sharing land and food—no one owned it alone.
- Later, pottery and metal tools improved life, turning hamlets into towns.
- These steps from roaming to farming built the roots of the bigger societies we see later.
|
46 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Timeline and Sources of History - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What is the significance of timelines in history? |  |
| 2. How do primary and secondary sources differ in historical study? |  |
| 3. Why is it important for students to learn about historical timelines in Class 6? |  |
| 4. What types of questions are typically asked in history exams for Class 6? |  |
| 5. How can students effectively prepare for history exams focusing on timelines and sources? |  |

















