Important Questions: Transport & Communication | Geography Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the total length of roads in India?
Ans: India has a total of 42 lakh kms of roads.
Q2: Which is the longest National Highway?
Ans: The longest National Highway in India is National Highway no 7, stretching from Varanasi to Kanniyakumari, covering 2,369 km.
Q3: What is the total length of railways in India?
Ans: The total length of railways in India is 1,15,000 km.
Q4: When was Prasar Bharti set up?
Ans: Prasar Bharti was established in the year 1997.
Q5: When was the first telecast by Doordarshan started?
Ans: The first telecast by Doordarshan started on 15 September 1959.
Q6: Which states has the highest and the lowest density of metalled roads in India ?
Ans:
- The Highest road density—Kerala (387 per 100 sq. km.)
- The lowest road density Jammu & Kashmir— (3.5 km per 100 sq. km.)
Q7: Name the two categories of air transport in India.
Ans: International and domestic.
Q8: Identify the Indian seaport which provides port facilities to its landlocked neighbour countries. Name any one such country.
Ans: Kolkata Seaport and Nepal Sea Port.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q9: What are the disadvantages of road transport?
Ans:
- Road transport is costly.
- It results in air pollution.
- Heavy goods cannot be taken to long distances.
- Road transport is more accident-prone.
Q10: Name four national highways mentioning their terminals.
Ans:
- Sher Shah Suri Marg. National Highway No. 1 (Delhi to Amritsar).
- National Highway No. 3 (Between Agra and Mumbai).
- National Highway No. 7 (Between Varanasi and Kanniyakumari).
- National Highway No. 2 (Between Delhi and Kolkata).
Q11: Describe the two main types of air services in India.
Ans: The air services in India are of two types: international and domestic. Air India provides international air services for both passengers and cargo traffic to 35 destinations from four focal points—Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata. Air India carried 3.83 million passengers in 2000-01.
Major international air routes are Delhi-Rome-Frankfurt, Mumbai-London, Delhi-Moscow, Kolkata-Tokyo, Kolkata-Perth, Mumbai-London-New York. Indian Airlines, Alliance Air (subsidiary of Indian Airlines), private scheduled airlines, and air taxis provide domestic air services.
Indian Airlines operations also extend to the neighboring countries of Southeast Asia and West Asia. At present, there are two private scheduled airlines operating on the domestic network; 38 companies hold non-scheduled air taxi operator permits. Private operators presently cater to nearly 52.8% of the domestic air traffic. The share of private sector airways has increased rapidly after liberalization.
Q12: Describe the different means of communication.
Ans: Communication networks carry information from one place to another physically, like postal services, through wires like telegraph and telephone, or through airwaves like radio and television. Some communication systems work in cooperation with the transport system, like postal services. Others, however, function independently of the transport system, such as radio.
Q13: Write a note on Akashvani.
Ans: Akashvani : Radio is an effective means of mass communication in the country. Radio broadcasting started in India in 1927 with two private transmitters located at Mumbai and Kolkata. All India Radio (AIR) was constituted in 1936. It is also known as Akashvani. At the time of Independence there were six radio stations. At present, the All India Radio has 208 stations and 327 transmitting centres. These stations and transmitting centres provide services to 99 per cent of the population and 90 per cent of the area of the country. Private parties also have set up about 100 FM radio stations. All India Radio broadcastes a variety of programmes like information, education and entertainment.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q14: Describe the major oil and gas pipelines of India.
Ans:
- Naharkatiya Barauni pipeline. Oil India Limited constructed the first pipeline of 1,152 km from Naharkatiya oilfield in Assam to Barauni refinery in Bihar via Noonmati (1962-68).
- Haldia-Kanpur pipeline. To transport refined petroleum products. Barauni-Kanpur pipeline was laid down in 1966. Haldia-Maurigram-Rajbandh pipeline was constructed later.
- Ankleshwar-Koyali pipeline. Extensive network of pipelines has been constructed in the Gujarat region. First pipeline connected the Ankleshwar oilfield to Koyali refinery (1965). Later, Kalol-Sabarmati crude pipeline, the Navagaon-Kalol-Koyali pipeline and the Mumbai High-Koyali pipeline were laid.
- Ahmedabad-Koyali pipeline. Ahmedabad has been linked with Koyali by pipeline for transport of petroleum products.
- Ankleshwar-Vadodara pipeline. Gas pipelines have also been laid down between Khambhat and Dhuvaran, Ankleshwar and Uttaran, and Ankleshwar and Vadodara. Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL) operates over 4,200 km of pipeline in the country and supplies gas to power plants.
- HBJ gas pipeline. Construction of a cross country 1,750 km long Hazira-Bijapur-Jagdishpur (HBJ) pipeline has already been completed. This pipeline has now been extended from Bijapur to Dadri in Uttar Pradesh.
- Kandla-Delhi pipeline. GAIL is also implementing a 1,246 km long LPG pipeline project from Kandla/Jamnagar in Gujarat to Luni in Uttar Pradesh via Delhi.
- Mathura-Jalandhar pipeline. The Mathura refinery gets its crude from the Mumbai High through pipeline, which extends from Salaya on the Gulf of Kachchh to Mathura, Petroleum product supply pipeline exists between Mathura and Jalandhar via Delhi and Ambala, and between Mumbai and Pune for the transport of petroleum products.
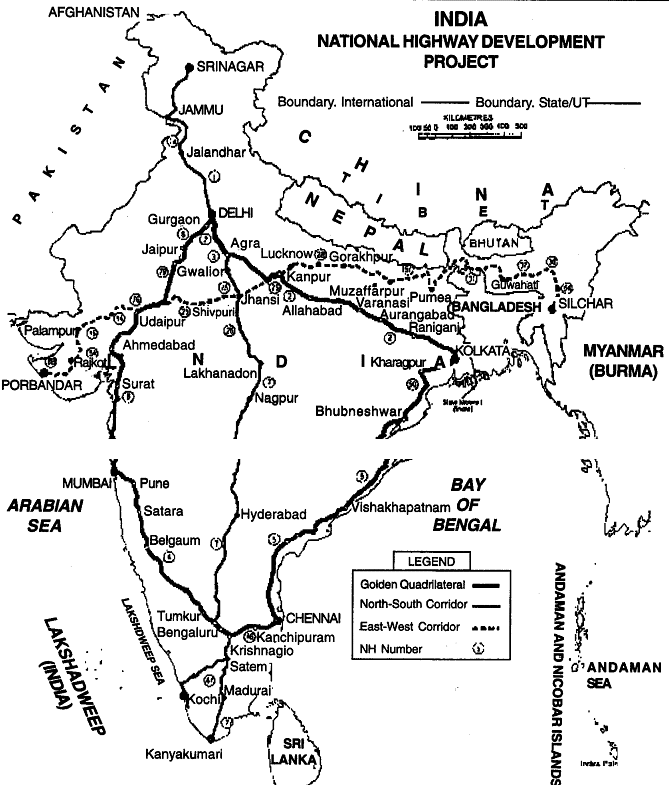
Q15: Describe the main features of development of railways in India.
Ans: Railways in India. The first railway line was constructed between Mumbai and Thane in the year 1853. It was only 34 km. long. Railways are the chief means of transport in India.
Main Characteristics:
- Indian Railways have a total length of 62,759 kms.
- It is the largest railway system in Asia and the fourth largest in the world.
- More than 18 lakh workers are engaged in Indian railways.
- Indian railways have about 12,670 trains which operate over 6,867 stations for a distance of 13 lakh kms.
- These railways carry 130 lakh passengers and 13 lakh tons freight daily.
- Railways have an investment of a capital of 8.0 crore rupees and yield an annual income of ? 21,000 crore.
- Indian railways have about 11,000 locomotives,38.0 coaches and 4 lakh wagons.
- Most of the railways are found in the level Gangetic plain.
- Railways have not been extensively developed in Jammu-Kashmir and Ladakh N.E. India, Western ghats, Chhotta Nagpur Plateau and Thar Desert (Rajasthan).
- In Southern India, construction of railways is retarded due to hilly areas and rivers.
- India has 4,259 diesel locomotives, 2,302 electric locomotives and 347 steam locomotives. The electric trains run over a distance of 11,772 kms.
Indian railways run of three gauges:
- Broad gauge—1.67 metres wide (49%)
- Metre gauge—1 metre wide (44%)
- Narrow gauge—0.76 metre wide (7%)
During year 1996-97, seven new rail zones have been created out of existing ones. The four following zones have been started:
- North-Central with headquarters at Allahabad.
- Central-Eastern with headquarters at Hajipur (Bihar).
- North-Western with headquarters at Jaipur.
- West-Southern with headquarters at Bangalore.
- Central with headquarters at Jabalpur.
- Eastern with headquarters at Bhubneshwar.
- S.E. Central Railway at Bilaspur.
Q16: “The triple transport system plays an important role in strengthening the social, political economic unity of India.” Explain.
Ans: Integrating role of transport. Means of transport are the lifeline of a country. A developed and efficient system of transport is vital for maintaining the sovereignty and economic unity of the country. Under the 20 years Nagpur Plan, a balanced and integrated transport system of rail, road and waterways has been aimed at. The different means of transport have played an integrating role in the political and economic unity of India.
- These have connected far flung areas with one another. Leh has been connected with Kanniyakumari, while Assam has been connected with Kutch.
- Means of transport distribute foodgrains, manufactured goods, raw materials and minerals to different parts of the country.
- Pipelines supply petroleum and gas to different areas.
- The commercialisation of agriculture, manufacturing growth of towns and cities have been achieved due to means of transport.
- The new road, railway lines have integrated the border areas with the rest of the country. Jawahar tunnel connects Kashmir valley with India.
- Railways line through gaps in the Vindhyan- Satpura hills and in Western Ghats have provided easy connection between the North and South.
- Ganga as a waterway has acted as a unifying agent right from U.P. to West Bengal. Thus, each means of transport has played its own role in a unified system of transport.
|
50 videos|273 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Transport & Communication - Geography Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the importance of transport and communication in humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How does transport contribute to the growth of the humanities/arts industry? |  |
| 3. How does communication technology impact the humanities/arts field? |  |
| 4. How do advancements in transportation affect the accessibility of cultural heritage sites? |  |
| 5. What role does communication play in preserving indigenous art forms and languages? |  |





















