Important River Systems of India | General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1 PDF Download
Introduction
Most of India's rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal, while some originate in the western parts of the country and empty into the Arabian Sea. The northern areas of the Aravalli range, parts of Ladakh, and the dry regions of the Thar Desert have inland drainage systems. All major rivers in India come from one of three main watersheds:
1. The Himalaya and the Karakoram range
2. The Chota Nagpur plateau and the Vindhya and Satpura ranges
3. The Western Ghats
Here are the major river systems in India:
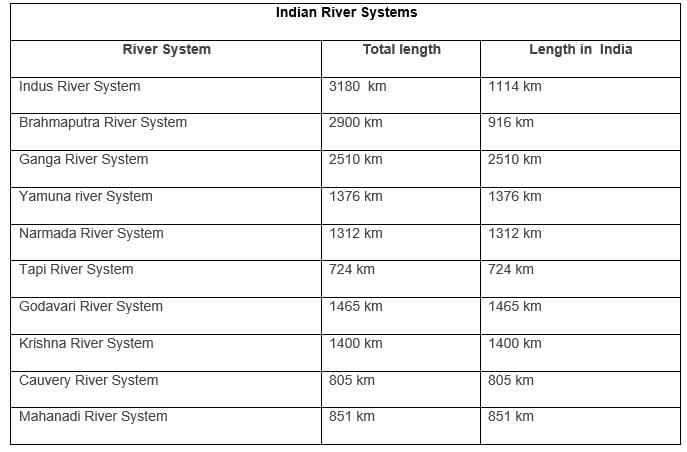
The Indus River System
- The Indus River begins at the northern slopes of the Kailash range in Tibet, close to Lake Mansarovar.
- It has many tributaries in both India and Pakistan, stretching about 2897 km in total until it reaches the Arabian Sea near Karachi, with approximately 700 km of its length located in India.
- The river enters India in the region of Jammu and Kashmir, creating a beautiful gorge.
- In the Kashmir area, it connects with several tributaries, including the Zaskar, Shyok, Nubra, and Hunza.
- While flowing through Leh, it moves between the Ladakh Range and the Zaskar Range.
- It cuts through the Himalayas at a deep gorge of 5181 m near Attock, which is located north of Nanga Parbat.
- The main tributaries of the Indus River in India include the Jhelum, Ravi, Chenab, Beas, and Sutlej.
The Brahmaputra River System
- The Brahmaputra river starts from Mansarovar Lake, which is also where the Indus and Sutlej rivers begin.
- It is about 3848 kilometers long, making it slightly longer than the Indus River.
- A majority of its length runs outside of India.
- The river flows in an eastward direction along the Himalayas.
- When it reaches a place called Namcha Barwa, it takes a U-turn and enters India in the state of Arunachal Pradesh.
- In India, it is referred to as the Dihang River.
- Within India, the river flows through the states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam and is joined by several smaller rivers called tributaries.
- The Brahmaputra has a braided channel for most of its course in Assam.
- In Tibet, the river is known as the Tsangpo.
- In the Tibetan region, it carries less water and has lower amounts of silt.
- However, in India, the river flows through an area with a lot of rainfall, resulting in it carrying large quantities of water during rainy seasons and significant amounts of silt.
- The Brahmaputra is one of the largest rivers in India in terms of water volume.
- It is known to cause disasters in both Assam and Bangladesh.
Ganga River System
The Ganga begins as the Bhagirathi from the Gangotri glacier.Before reaching Devprayag in the Garhwal Division, several rivers merge into the Alaknanda:
- Mandakini
- Pindar
- Dhauliganga
- Bishenganga
The Pindar River originates from East Trishul and Nanda Devi and joins the Alaknanda at Karan Prayag.
The Mandakini river converges with the Alaknanda at Rudraprayag.
At Devprayag, the waters from the Bhagirathi and the Alaknanda combine and are then known as the Ganga.
The Concept of Panch Prayag
- Vishnuprayag: where the Alaknanda meets the Dhauli Ganga
- Nandprayag: where the Alaknanda meets the Nandakini
- Karnaprayag: where the Alaknanda meets the Pindar
- Rudraprayag: where the Alaknanda meets the Mandakini
- Devprayag: where the Alaknanda meets the Bhagirathi - GANGA
The main tributaries of the Ganga include:
- Yamuna
- Damodar
- Sapta Kosi
- Ram Ganga
- Gomati
- Ghaghara
- Son
The Ganga travels a distance of 2525 km from its source before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
Yamuna River System
- The Yamuna River is the largest tributary of the Ganga River.
- It originates from the Yamunotri glacier, located at the Bandarpoonch peak in Uttarakhand.
- The main tributaries joining the Yamuna include the Sin, Hindon, Betwa, Ken, and Chambal rivers.
- The Tons River is the largest tributary of the Yamuna.
- The river's catchment area extends to the states of Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
Narmada River System
- The Narmada River is located in central India, originating from the Amarkantak Hill in Madhya Pradesh.
- It traditionally separates North India from South India.
- The Narmada, along with the Tapti and Mahi rivers, is one of the few rivers in India that flows from east to west.
- The Narmada flows through Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra before draining into the Arabian Sea in the Bharuch district of Gujarat.
Tapi River System
- The Tapi River, also known as Tapti, is a significant river in central India, flowing from east to west.
- It originates in the Eastern Satpura Range of southern Madhya Pradesh.
- The river drains historic regions such as Madhya Pradesh’s Nimar region, East Vidarbha, and Maharashtra’s Khandesh, before emptying into the Gulf of Cambay in the Arabian Sea.
- The Tapi River basin primarily lies in eastern and northern Maharashtra, with parts in Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
- Major tributaries include the Waghur, Aner, Girna, Purna, Panzara, and Bori rivers.
Godavari River System
- The Godavari River is the second-longest river in India, often called the Dakshin (South) Ganga or Vriddh (Old) Ganga.
- It is a seasonal river, experiencing dry periods in summer and widening during monsoons.
- Originating from Trimbakeshwar near Nasik in Maharashtra, the Godavari flows southeast through Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Orissa, draining into the Bay of Bengal.
- The river creates a fertile delta at Rajahmundry.
- Significant tributaries include the Pranahita (formed by the Penuganga and Warda rivers), Indravati, Bindusara, Sabari, and Manjira rivers.
- Asia’s largest rail-cum-road bridge, linking Kovvur and Rajahmundry, is situated on the Godavari River.
Krishna River System
- The Krishna River is one of India’s longest rivers, originating from Mahabaleshwar in Maharashtra.
- It flows through Sangli and empties into the Bay of Bengal, passing through Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Major tributaries include the Tungabhadra (formed by the Tunga and Bhadra rivers from the Western Ghats), Dudhganga, Koyna, Bhima, Mallaprabha, Dindi, Ghataprabha, Warna, Yerla, and Musi rivers.
Cauvery River System
- The Cauvery River originates from Talakaveri in the Western Ghats, a popular pilgrimage and tourist destination in Karnataka’s Kodagu district.
- The river flows through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu before draining into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Cauvery is vital for irrigation and has historically supported ancient kingdoms and modern cities in South India.
- Major tributaries include the Arkavathy, Shimsha, Hemavati, Kapila, Honnuhole, Amaravati, Lakshmana Kabini, Lokapavani, Bhavani, Noyyal, and Tirtha rivers.
Mahanadi River System
- The Mahanadi River originates from the Satpura Range in central India and flows eastward into the Bay of Bengal.
- It drains parts of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
- The Hirakud Dam, the largest dam on the Mahanadi, is a key feature of the river system.
|
64 videos|153 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Important River Systems of India - General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1
| 1. What are the major river systems of India? |  |
| 2. How does the Ganga River System contribute to agriculture in India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Indus River System historically? |  |
| 4. Which river system is known for its unique geographical features and biodiversity? |  |
| 5. How do the Narmada and Tapi River Systems differ in terms of their flow direction? |  |





















