Class 1 Exam > Class 1 Notes > General Knowledge for Young Learners > India’s Neighbouring Countries – Border States, Trade, Relations
India’s Neighbouring Countries – Border States, Trade, Relations | General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Neighbouring Countries of India |

|
| Neighbouring Countries of India Overview |

|
| List of Neighbouring Countries of India With Capital |

|
| Neighbouring Countries of India - Facts |

|
Neighbouring Countries of India
India shares a lengthy land border of over 15,106.7 kilometers with six countries: Pakistan to the west, China and Nepal to the north, Bhutan to the northeast, and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. This diverse range of neighbours positions India as a key player in South Asian geopolitics.
In addition to its land borders, India boasts a coastline of 7,516.6 kilometers, granting it access to the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean. This coastal stretch not only connects India to international waters but also plays a crucial role in trade routes linking the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia. Major ports such as Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata facilitate significant trade and cultural exchanges, reinforcing India’s position in the global economy.
Neighbouring Countries of India Overview
India shares its borders with nine countries: seven land borders ( Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Afghanistan. and two maritime borders ( Sri Lanka and the Maldives ). This geographical knowledge is vital for competitive exams, especially in the General Awareness section.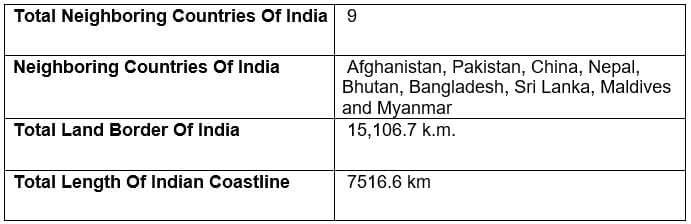
List of Neighbouring Countries of India With Capital
India shares its borders with nine countries, each possessing unique geographical, cultural, and economic relationships with India. Below is a detailed list of neighbouring countries, along with their capitals, border lengths, and the Indian states they share borders with.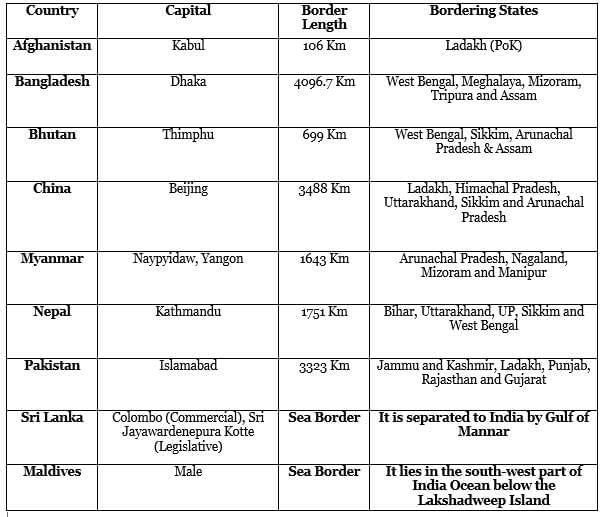
Neighbouring Countries of India - Facts
India-China Relations
- India and China have a long history of cultural and trade exchanges.
- In 1954, they signed the Panchsheel Agreement, promoting mutual respect and peaceful coexistence.
- However, a border conflict in 1962 created ongoing territorial disputes.
India-Pakistan Relations
- India and Pakistan share a history rooted in the 1947 partition of British India.
- Despite cultural similarities, tensions have risen due to conflicts like the 1965 war and the Kargil conflict in 1999.
- Both countries keep diplomatic channels open to reduce tensions and promote stability.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- SAARC was established in 1985 to foster regional cooperation and development in South Asia.
- Comprising eight member states, including India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, SAARC addresses issues like poverty, education, and climate change.
- While it aims to promote peace and collaboration, political disagreements among members have sometimes limited its effectiveness.
India-Bangladesh Relations
- India played a crucial role in supporting Bangladesh’s independence in 1971, leading to strong bilateral ties.
- The two countries collaborate closely on political, economic, and cultural fronts.
- They work together on trade, water-sharing agreements, and counterterrorism to ensure regional peace and stability.
India-Sri Lanka Relations
- India and Sri Lanka share deep historical and cultural ties, influencing their bilateral relationship.
- Both countries have strong connections through religion, language, and trade.
- Although issues related to the Indian-origin Tamil population in Sri Lanka have caused some tension, overall relations remain positive.
- Cooperation in defense, trade, and infrastructure development has strengthened their partnership, with a focus on resolving differences through diplomatic means.
The document India’s Neighbouring Countries – Border States, Trade, Relations | General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1 is a part of the Class 1 Course General Knowledge for Young Learners.
All you need of Class 1 at this link: Class 1
|
64 videos|153 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on India’s Neighbouring Countries – Border States, Trade, Relations - General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1
| 1. What are the neighbouring countries of India? |  |
Ans. The neighbouring countries of India are Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. Each of these countries shares a land border with India.
| 2. What are the capitals of India’s neighbouring countries? |  |
Ans. The capitals of India’s neighbouring countries are as follows:
- Pakistan: Islamabad
- China: Beijing
- Nepal: Kathmandu
- Bhutan: Thimphu
- Bangladesh: Dhaka
- Myanmar: Naypyidaw
| 3. What are the major border states of India that share boundaries with its neighbouring countries? |  |
Ans. The major border states of India that share boundaries with neighbouring countries include:
- Jammu and Kashmir (with Pakistan and China)
- Himachal Pradesh (with China)
- Uttarakhand (with China and Nepal)
- Sikkim (with China and Bhutan)
- West Bengal (with Bangladesh and Nepal)
- Assam (with Bangladesh and Myanmar)
- Arunachal Pradesh (with China)
- Meghalaya (with Bangladesh)
- Tripura (with Bangladesh)
- Mizoram (with Myanmar)
| 4. How does India maintain trade relations with its neighbouring countries? |  |
Ans. India maintains trade relations with its neighbouring countries through various trade agreements and initiatives. These include bilateral trade agreements that facilitate the exchange of goods, services, and investment. Additionally, India engages in regional cooperation organizations like SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) to enhance trade and economic ties. Each neighbouring country has specific trade protocols to streamline customs and tariffs.
| 5. What is the significance of India's relations with its neighbouring countries? |  |
Ans. India's relations with its neighbouring countries are significant for several reasons, including regional stability, economic cooperation, and cultural exchanges. Strong relations help in addressing security concerns, managing border disputes, and promoting trade. Additionally, fostering good neighbourly relations is essential for collaborative efforts in tackling issues like terrorism, climate change, and natural disasters in the region.
Related Searches




















