Integer Answer Type Questions: Moving Charges & Magnetism | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
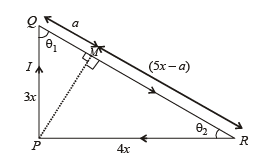
Q.1. A steady current I goes through a wire loop PQR having shape of a right angle triangle with PQ = 3x, PR = 4x and QR = 5x. If the magnitude of the magnetic field at P due to this loop is 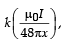 find the value of k.
find the value of k.
Ans. 7
Solution.
The right angled triangle is shown in the figure. Let us drop a perpendicular from P on QR which cuts QR at M.
The magnatic field due to currents in PQ and RP at P is zero.
The magnetic field due to current in QR at P is
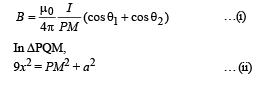
In ΔPRM,
16x2 = PM2 + (5x – a)2 … (iii)
⇒ 7 x2 = 25 x2- 10xa ⇒ 10xa = 18x2
⇒ a = 1.8 x … (iv)
From (ii) & (iv),
9 x2 = PM2+ (1.8x)2
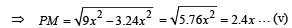
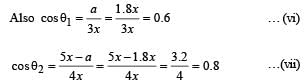
From (i), (v), (vi) and (vii),
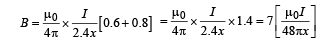
Comparing it with B =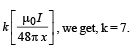
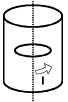
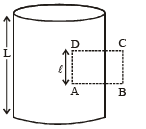
Q.2. A long circular tube of length 10 m and radius 0.3 m carries a current I along its curved surface as shown. A wire-loop of resistance 0.005 ohm and of radius 0.1 m is placed inside the tube with its axis coinciding with the axis of the tube. The current varies as I = I0cos(300 t) where I0 is constant. If the magnetic moment of the loop is Nμ0I0sin (300 t), then ‘N’ is
Ans. 6
Solution. Let us consider an amperian loop ABCD which is a rectangle as shown in the figure. Applying ampere’s circuital law we get
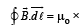 (current passing through the loop)
(current passing through the loop)
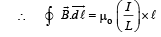
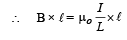
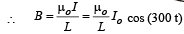
The magnetic moment of the loop = (current in the loop) × πr2
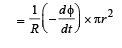
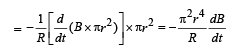
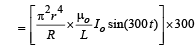
Comparing it with the expression given in the question we get
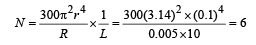
Q.3.A cylindrical cavity of diameter a exists inside a cylinder of diameter 2a as shown in the figure. Both the cylinder and the cavity are infinity long. A uniform current density J flows along the length. If the magnitude of the magnetic field at the point P is given by 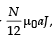 then the value of N is
then the value of N is
Ans.5
Solution. Current density J =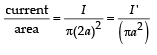
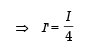
Let us consider the cavity to have current I' flowing in both the directions.
The magnetic field at P due to the current flowing through the cylinder
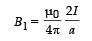
The magnetic field at P due to the current (I’) flowing in opposite direction is
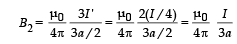
∴ The net magnetic field is
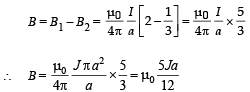
Q.4. Two parallel wires in the plane of the paper are distance X0 apart. A point charge is moving with speed u between the wires in the same plane at a distance X1 from one of the wires. When the wires carry current of magnitude I in the same direction, the radius of curvature of the path of the point charge is R1. In contrast, if the currents I in the two wires have directions opposite to each other, the radius of curvature of the path is R2. If 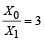 the value of
the value of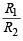 is
is
Ans. 3
Solution. 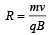
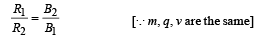
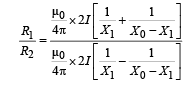
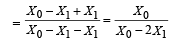
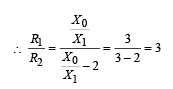
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Integer Answer Type Questions: Moving Charges & Magnetism - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What are moving charges in the context of magnetism? |  |
| 2. How are moving charges affected by a magnetic field? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between moving charges and magnetic fields? |  |
| 4. How do moving charges behave in a magnetic field? |  |
| 5. How are moving charges and magnetism related to the JEE Advanced exam? |  |





















