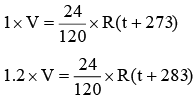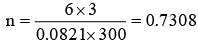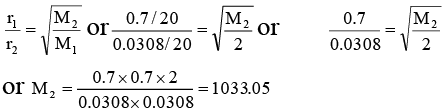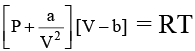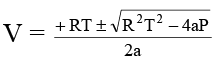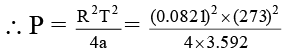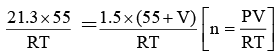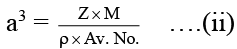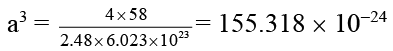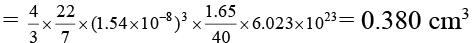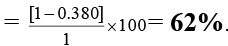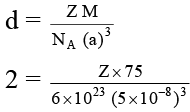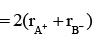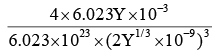Integer Answer Type Questions for JEE: States of Matter | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. The pressure exerted by 24 gm of an ideal gas at temp t° C in a vessel of volume V litre in one atm. When the temperature is increased by 10° C at the same volume, the pressure increases by 20%. Calculate the volume V. (Molecular wt. of gas = 120).
Ans. 820 ml.
Given: P1 = 1 atm. , w = 24gm, T1 = (t + 273) K
V1 = V ltr.
P2 = 1 + 20/100 = 1.2 atm., T2 = (t + 283) K, w = 24gm.
V2 = V ltr.
so t = – 223° C =
t = – 223° C + 273 = 50 K
so V = 24/120 x 0.082 x 50 ⇒ 0.82 ltr = 820 ml.
Q.2. At 27°C, hydrogen is leaked through a tiny hole into a vessel for 20 minutes. Another unknown gas at the same temperature and pressure as that of H2 is leaked through the same hole for 20 minutes. After the effusion of the gases the mixture exerts a pressure of 6 atmosphere. The hydrogen content of the mixture is 0.7 mole. If the volume of the container is 3 litre, what is the molar mass of the unknown gas?
Ans. 1033
For calculation of moles of unknown gas
The ideal gas equation is PV = nRT. With the help of given data.
6 × 3 = n × 0.0821 × 300
∴ Total number of moles of H2 and the unknown gas (gas mixture) = 0.7308
∴ No. of moles of the unknown gas
= Total no. of moles of gas mixture – no. of moles of H2
= 0.7308 – 0.7 = 0.0308
For Calculation of molecular mass
According to Graham’s Law of diffusion of gases
Thus, the molecular mass of unknown gas = 1033.05 ≌ 1033.
Q.3. If volume occupied by CO2 molecules is negligible, then calculate the pressure exerted by one mole of CO2 gas at 273 K. Given that a = 3.592 atm litre2 mol-2 for CO2.
Ans. 35
For 1 mole:
if b is negligible, P = RT/V - a/V2
or PV2- RTV + a = 0
The equation is quadratic in V, thus
Since, V has one value at given P and T, thus numerical value of discriminant = 0
or R2T2 = 4aP
= 34.96 atm ≌ 35 atm.
Q.4. A large irregularly-shaped closed tank is first evacuated and then connected to a 55 litre cylinder containing compressed nitrogen gas. The gas pressure in the cylinder, originally at 21.3 atm, falls to 1.5 atm after it is connected to the evacuated tank. Calculate the volume of the tank in litres.
Ans. 726
Let the volume of the tank be V litres.
As the number of moles of N2 before and after connecting it to the tank will be same,
(moles of N2 before connection) (moles of N2 after connection)
∴ V = 726 litres.
Q.5. Potassium fluoride (KF) has NaCl structure. Its density is 2.48 g cm-3 and its molar mass is 58 g mol-1. Compute the distance in picometer between K+ and F- ions in KF. (Given that (155.318)1/3 = 5.375)
Ans. 269 Pm.
Since NaCl has fcc structure, therefore, KF has also fcc structure and thus, its rank is 4. Again, in a face centred cubic lattice the distance between the cation and anion is equal to the sum of their radii, which is equal to half of the edge length of the unit cell. That is,
r+ + r- =a/2 ...(i)
The edge length is calculated by the formula
We know:
Z = 4,M = 58 g mol-1
ρ = 2.48 g cm-3, Av. No. = 6.023 × 1023 mol-1
On substituting the known data in equation (ii), we get,
a = 5.375 × 10-8 cm = 5.375 × 10-10 m
∴ = 537.5 × 10-12 m = 537.5 pm
On putting the value of a in equation (i), we get,
r+ + r- = a/2 = 537.5/2 = 268.7≌ 269 pm.
Q.6. The density of solid argon is 1.65 g/ml at -233°C. If the argon atom is assumed to be sphere of radius 1.54 × 10-8 cm, what percentage of solid argon is apparently empty space?
Ans. 62%
Volume of one atom of Ar = 4/3 πr3
Also, number of atoms in 1.65 g or one ml = 1.65/40 × 6.023 × 1023
∴ Total volume of all atoms of Ar in solid state = 4/3 πr3 × 1.65/40 × 6.023 × 1023
Volume of solid argon = 1 cm3
∴ % empty space
Q.7. The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight 75g/mol is 5 Å which crystallizes in cubic lattice. If the density is 2 g/cc then find the radius of metal atom. ( NA = 6 × 1023). Give the answer in pm.
Ans. 217 Pm.
Let ‘Z’ be the number lattice points per unit cell.
∴ Density of the metal whose M = 75 g mol-1 and a = 5 Å is given by
On solving, Z = 2
∴ The metal has BCC unit cell in which
4r = √3 a[∵ 1 Å = 100 pm]= 216.5 ≌ 217 pm.
Q.8. A compound AB has a rock salt type of structure (with A : B = 1 : 1). The formula weight of AB is 6.023Y g mol–1 and the closest A–B distances is Y1/3 nm. If this crystal contains 0.2% Frenkel defect; calculate the density of the lattice in Kg m–3.
Ans. 5 Kg m–3.
AB has rock salt structure A : B = 1 : 1 i.e. FCC structure (Z = 4) and formula weight of AB is 6.023Y g having closest distance (between A–B) = Y1/3 nm.
Therefore, edge length of unit cell
= 2 × Y1/3 × 10–9 m
Density of AB =
= 5 Kg m–3.
Q.9. How large a balloon could you fill with 4g of He gas at 22°C and 720 mm of Hg?
Ans. 25.565 litre
Given, P = 720 / 760 atm, T = 295K, w = 4g
and m = 4 for He
PV = w / M RT
= 720 / 760 × V = 4/4 × 0.0821 × 295
∴ V = 25.565 litre
Q.10. A 20g chunk of dry ice is placed in an empty 0.75 litre wire bottle tightly closed what would be the final pressure in the bottle after all CO2 has been evaporated and temperature reaches to 25°C?
Ans. 15.828 atm
w = 20g dry CO2 which will evaporate to develop pressure
m = 44, V = 0.75 litre, P = ? T = 298K
PV = W / m RT
P × 0.75 = 20 / 44 5 0.0821 × 298
P = 14.228 atm
Pressure inside the bottle = P + atm pressure = 14.828 + 1 = 15.828 atm
|
481 docs|964 tests
|