Integer Answer Type Questions: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. Based on VSEPR theory, the number of 90 degree F–Br–F angles in BrF5 is (2010)
Ans. (0)
Sol. According to VSEPR theory, number of electron pairs around central atom (Br) are 6.
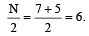 (Five are bond pairs and one is lone pair ) Its geometry is octahedral but due to lone pair –bond pair repulsion, the four fluorine atoms at corner are forced towards the upper fluorine atom thus reducing F–Br–F angle from 90° to 84.8°.
(Five are bond pairs and one is lone pair ) Its geometry is octahedral but due to lone pair –bond pair repulsion, the four fluorine atoms at corner are forced towards the upper fluorine atom thus reducing F–Br–F angle from 90° to 84.8°.
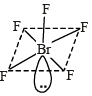
Q.2. The total number of lone-pairs of electrons in melamine is (JEE Adv. 2013)
Ans. (6)
Sol. Structure of melamine is as follows :
Total no. of lone pairs of electron is ‘6’.
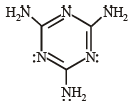
Q.3. A list of species having the formula XZ4 is given below.
XeF4, SF4, SiF4, BF4–, BrF4–, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, [FeCl4]2–, [CoCl4]2– and [PtCl4]2–.
Defining shape on the basis of the location of X and Z atoms, the total number of species having a square planar shape is (JEE Adv. 2014)
Ans. (4)
Sol.
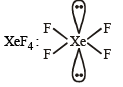 Square planar (sp3d2)
Square planar (sp3d2)
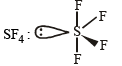 See-saw (sp3d)
See-saw (sp3d)
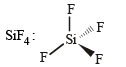 Tetrahedral (sp3)
Tetrahedral (sp3)
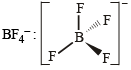 Tetrahedral (sp3)
Tetrahedral (sp3)
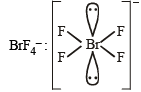 Square planar (sp3d2)
Square planar (sp3d2)
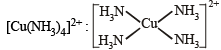 Square planar (dsp2)
Square planar (dsp2)
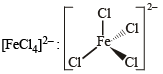 Tetrahedral (sp3)
Tetrahedral (sp3)
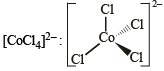 Tetrahedral (sp3)
Tetrahedral (sp3)
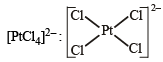 Square planar (dsp2)
Square planar (dsp2)
4. Among the triatomic molecules/ions, BeCl2, N3–, N2O, NO2+, O3, SCl2, ICl2– , I3– and XeF2, the total number of linear molecule(s)/ion(s) where the hybridization of the central atom does not have contribution from the d-orbital(s) is [Atomic number : S = 16, Cl = 17, I = 53 and Xe = 54] (JEE Adv. 2015)
Ans. (4)
Sol.

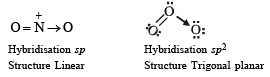


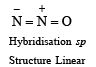
Only BeCl2, N3–, N2O and NO2 are linear with sp-hybridisation.
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Integer Answer Type Questions: Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What is a chemical bond? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of chemical bonds? |  |
| 3. How does the octet rule apply to chemical bonding? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds? |  |
| 5. How do intermolecular forces affect the properties of substances? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















