Internal Audit | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding an Internal Audit |

|
| Benefits of Conducting an Internal Audit |

|
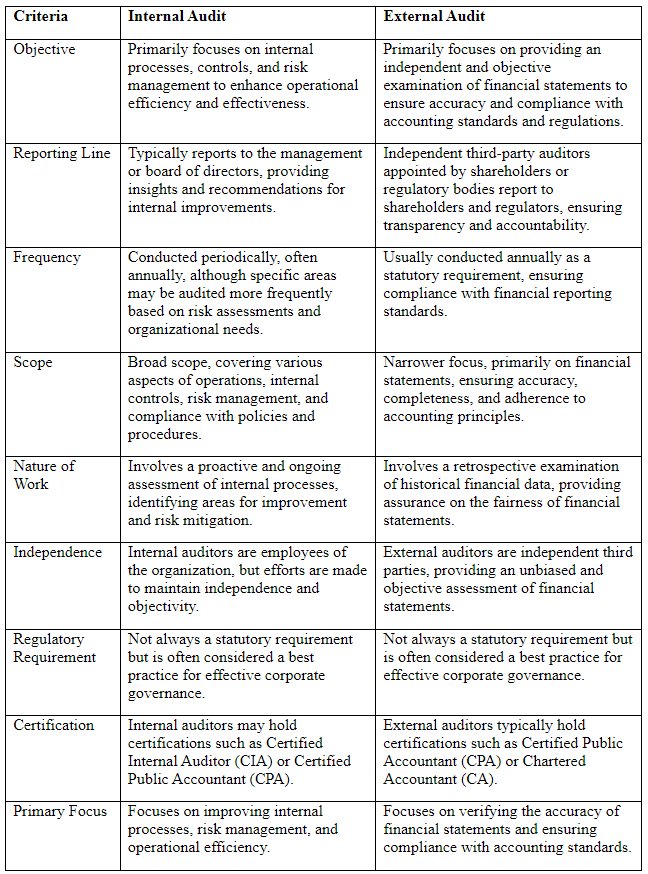
| Difference Between Internal Audit and External Audit |

|
| Objectives of Internal Audit and External Audit |

|
Understanding an Internal Audit
An internal audit is a thorough assessment conducted by an internal auditor to evaluate all aspects of a business. The main goal is to pinpoint any potential discrepancies and implement necessary actions to enhance operational efficiency.
The internal audit primarily focuses on reviewing risk management, operations, accounting, financial reporting, and internal control measures.
Internal audits are typically carried out at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Benefits of Conducting an Internal Audit
An internal audit provides various advantages, including:
- Enhancing effective organizational management: Internal audits play a crucial role in recognizing and rectifying any faulty processes, leading to an overall enhancement in operational efficiency.
- Assessing performance and making informed decisions: Regular internal audits allow management to evaluate performance and make well-informed choices regarding operational improvements.
- Promoting employee accountability: Internal audits help employees stay alert about their duties, thus increasing their efficiency.
- Identifying areas for improvement: By pinpointing areas that need enhancement, internal audits enable better resource allocation, which ultimately benefits the organization.
Difference Between Internal Audit and External Audit
Objectives of Internal Audit and External Audit
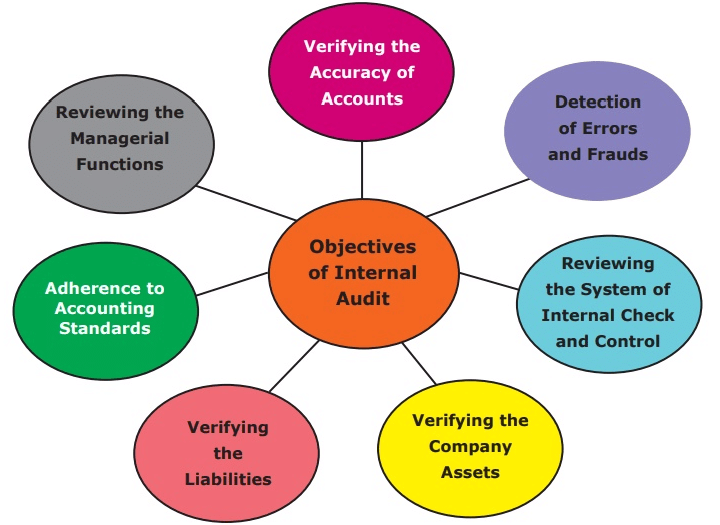
Objectives of Internal Audit
The aims of internal auditing are delineated as follows:
Risk Management:
- Identification and evaluation of potential risks in the organization.
- Providing recommendations for effective strategies to minimize risks.
Operational Efficiency:
- Assessment of internal processes, systems, and controls for optimal performance.
Compliance:
- Ensuring adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies to prevent legal issues.
Internal Controls:
- Reviewing and implementing safeguards to protect assets and prevent fraud.
- Ensuring accuracy in financial reporting.
Continuous Improvement:
- Offering suggestions for enhancing operations, controls, and risk management.
- Contributing to overall organizational performance improvement.
Financial Management:
- Examining financial processes for accurate reporting and resource utilization.
Information Systems:
- Evaluating information system effectiveness and security to safeguard data integrity.
Strategic Alignment:
- Assessing activities to ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
- Providing insights on strategic risks.
Fraud Prevention:
- Identifying and mitigating the risk of fraudulent activities.
Management Support:
- Offering objective insights to aid in informed decision-making.
Objectives of External Audit

Financial Statement Accuracy: Assure shareholders and creditors that financial statements accurately reflect the company's financial position.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Ensure that financial statements adhere to relevant accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
- Independence and Objectivity: Maintain impartiality to boost audit process credibility and provide an unbiased assessment of financial data.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Verify that the organization complies with laws and regulations to mitigate legal risks.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Enhance trust among investors, creditors, and the public through an objective evaluation of the company's financial health.
- Detection of Fraud or Misstatements: Identify any significant misstatements or fraudulent activities in financial reports to prevent irregularities.
- Going Concern Assessment: Evaluate the organization's ability to sustain operations and disclose any concerns regarding its viability.
- Management Accountability: Hold management responsible for accurate and fair financial reporting, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Audit Opinions: Provide an opinion on whether financial statements are presented fairly and comply with accounting standards.
- Shareholder Protection: Safeguard shareholders' interests by independently verifying the organization's financial health and the reliability of its financial statements.
Conclusion
Internal audit is crucial for fostering transparency, accountability, and efficiency within an organization. It involves a structured review and assessment of processes to pinpoint areas needing enhancement, minimize the risk of fraud and errors, and ensure alignment with organizational goals and regulatory standards. The insights derived from internal audits aid in informed decision-making and empower management to continually bolster internal controls.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Internal Audit - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are the benefits of conducting an internal audit? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between internal audit and external audit? |  |
| 3. What are the objectives of internal audit and external audit? |  |
| 4. How can an internal audit help an organization in decision-making? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for organizations to conduct both internal and external audits? |  |




















