Introduction: Active & Passive | English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction
Voice, in grammar, refers to the form of a verb that indicates whether the subject performs the action or receives the action's result from others. Sometimes, the subject directly performs the action, while at other times, it is acted upon indirectly.
For instance:
- Direct action by the subject: "He takes tea."
- Indirect action by the same subject: "Tea is taken by him."
There are two primary types of voice: Active and Passive.
Active Voice: When using the active voice, the subject carries out the action.
Examples:
- "God loves all men."
- "Birds build nests."
- "Dog eats bones."
These sentences illustrate the subject as the performer of the action, signifying the active voice.
Passive Voice: In the passive voice, the action verb acquires an object.
Examples:
- "All men are loved by God."
- "Nests are built by birds."
- "Bones are eaten by the dog."
These sentences represent the passive voice. Passive voice construction is employed in English:
- To emphasize the action rather than the doer.
- When the doer is unknown.
- When it is more convenient.
NOTE: To convert active voice into passive voice, relocate the object from the active voice to the subject position and use the appropriate 'be' verb (is/am/are/was/were/has been/have been/shall be/will be).
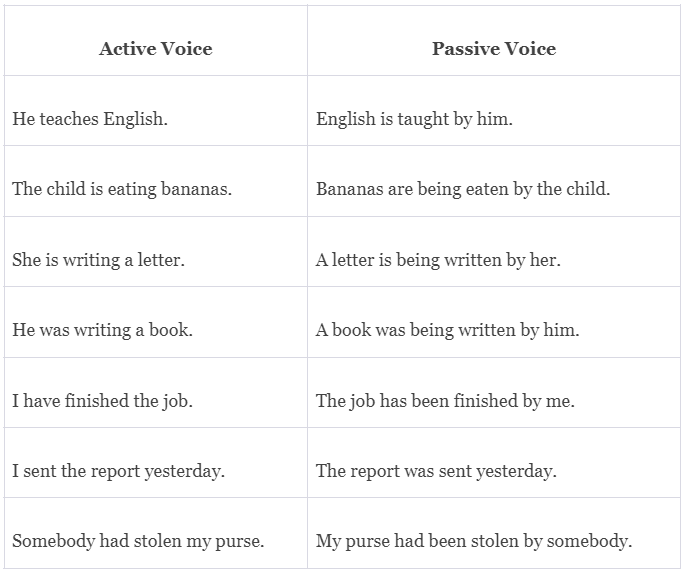
How to form passive forms of verbs?
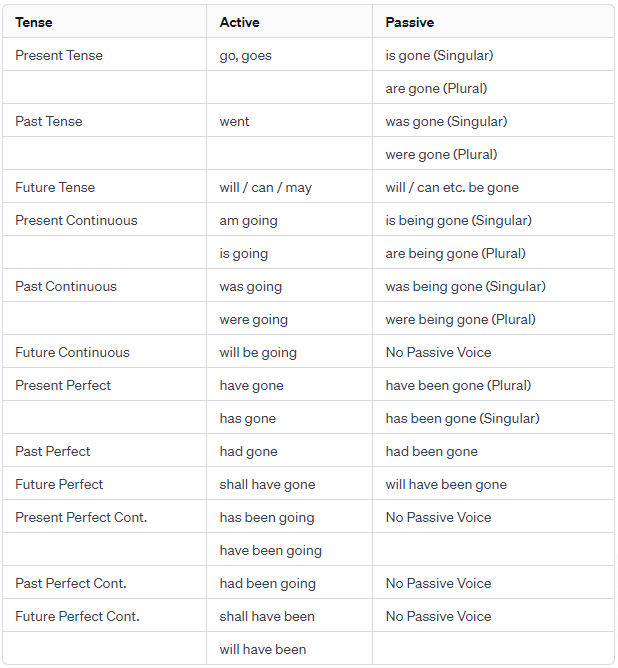
Changes of Pronouns :
Rules for changing Active Voice into Passive Voice
1. As mentioned earlier, the structure of sentence will be reversed in Passive Voice. The places of the Subject and the object will interchange. The subject will shift to the place of Object and the object will take the place of Subject in Passive Voice.
Example :
- Active Voice : He buys a camera.
- Passive Voice : A camera is bought by him.
2. Only Past Participle Form or 3rd form of verb (e.g. eaten etc) will always be used as main verb in Passive voices for all tenses. No other form of verb will be used as main verb. It can be seen in all the examples given on this page.
3. The word “by” will be used before subject in the Passive voice.
Example :
- Active Voice : She drinks water.
- Passive Voice : Water is drunk byher.
4. Other words such as ‘with’ or ‘to’ may also be used instead of word ‘by’ depending upon the subject of the sentence. These words are used in a very few cases. The word ‘by’ is used in the most cases.
Examples:
- Active Voice : I know him.
- Passive Voice : He is known to me.
- Active Voice : Water fills a tub.
- Passive Voice : A tub is filled with water.
5. The auxiliary verb will be changed in Passive Voice depending upon the tense of sentence in its Active Voice. There are rules for changing the auxiliary for each tense which can also be studied on this website.
6. Subject may not be always mentioned in Passive Voice. A passive voice sentence can be written without having subject, if it gives clear idea about the subject. Read the following examples.
Examples :
- Active Voice : Women are not treated as equals.
- Passive Voice : Sugar is sold in kilograms.
Note: The above rules, except rule No. #5, are the basic rules for changing Active Voices into Passive Voice and apply to all type of sentences. The rule No. 5 is about the usage of auxiliary verbs in Passive Voices which differs for each tense of the sentence.
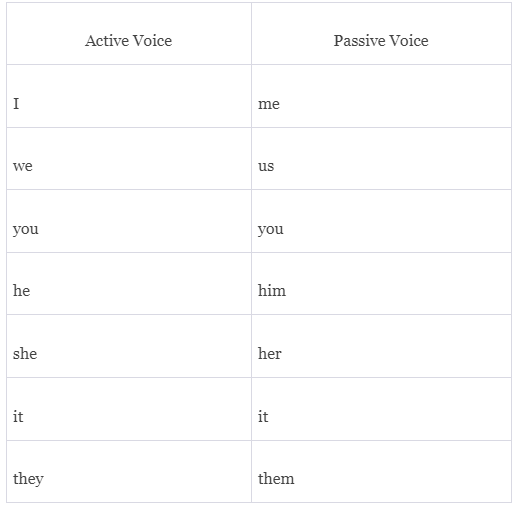
Passive Voice Transformation Rules for Imperative Sentences
An imperative sentence, which conveys a command, advice, or request, lacks a specific subject and addresses the listener. This type of sentence instructs, advises, or requests action without explicitly mentioning the subject. Consequently, imperative sentences in the passive voice also do not specify a subject.
Converting an imperative sentence from active to passive voice involves three key rules:
- The passive voice of an imperative sentence commences with the word "Let."
- In the passive voice of imperative sentences, the auxiliary verb "Be" is utilized.
The base form (1st form) of the verb, such as "write," transforms into the past participle (3rd form), like "written," for constructing the passive voice of an imperative sentence.
To better grasp these rules, consider the examples provided below:
- Passive Voice Examples for Imperative Sentences
Questions in the Passive
If the question in the Active Voice begins with a Helping verb the Passive voice must also begin with a suitable helping verb. Supposing the question begins with ‘Wh or How’ form (what, when, how ...) the Passive Voice must begin with the same.
Sentences with Two Objects:
When a sentence contains both an Indirect Object and a Direct Object in the Active Voice, it can yield two variations of Passive Voice.

She brought me a cup of coffee. (AV)
- I was brought a cup of coffee by her. (PV) (or)
- A cup of coffee was brought [to] me by her. (PV)
The teacher teaches us grammar. (AV)
- We are taught grammar by the teacher. (PV) (or)
- Grammar is taught [to] us by the teacher. (PV)
Consider Complement:
- They made him king. (AV)
- He was made king by them. (PV)
Infinitive and Gerund:
- I want to shoot the tiger. (AV)
- I want the tiger to be shot. (PV)
- I remember my father taking me to the theatre. (AV)
- I remember being taken to the theatre by my father. (PV)
Active Voice into Passive Voice:
When transforming Passive Voice into Active Voice, the rules of the Active Voice should be applied in reverse order. In instances where the Passive Voice sentence lacks a subject or agent, the appropriate subject must be provided.
To ascertain whether a given sentence is in the passive voice, it should contain one of the following constructions:
- is, was, are, were, am + past participle
- be + past participle
- being + past participle
- been + past participle
- Let ...be + past participle
Changing Passive Voice to Active Voice.

Passive Voice / Impersonal Passive
Here are the sentences rephrased in passive voice, including both with and without the inclusion of the 'by' phrase:
They say that might is right.
- Passive with 'by' phrase: It is said by them that might is right.
- Impersonal Passive: It is said that might is right.
One finds mosquitoes everywhere.
Passive with 'by' phrase: Mosquitoes are found by one everywhere.
Impersonal Passive: Mosquitoes are found everywhere.
He gave us a cheque.
- Passive with 'by' phrase: A cheque was given to us by him.
- Impersonal Passive: A cheque was given to us.
The sentences are transformed into passive voice with and without the 'by' phrase, showcasing both the traditional passive construction and the impersonal passive form where the emphasis is on the action or process rather than the doer or agent.
|
145 videos|268 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: Active & Passive - English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the difference between active voice and passive voice? |  |
| 2. How do you change a sentence from active voice to passive voice? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific rules for transforming imperative sentences into passive voice? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of how to transform a question into the passive voice? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of using passive voice in writing? |  |





















