Introduction and Types: Coded Inequality | Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams PDF Download
Reasoning Inequality – Concept and Basics
What is Reasoning Inequality?
When a group of elements are given with a certain coded relationship denoted by <, >, = ≤ or ≥, such type of questions fall under the category of reasoning Inequality.
To make the concept even more understandable, refer to the table given below:
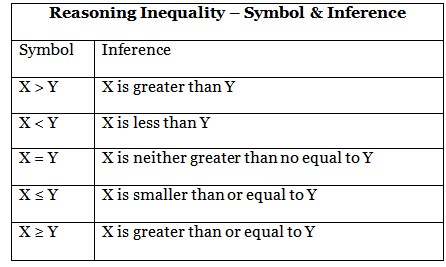
Once a candidate understands the meaning of each of the symbols mentioned above, answering questions based on reasoning inequality shall become easier.
 Another critical aspect that a candidate must know concerning the Inequality in reasoning is the order or the rank of these symbols.If in a question, P > Q ≥ R is given, the greater-than sign (>) will be of the highest order and P > R and not P ≥ R
Another critical aspect that a candidate must know concerning the Inequality in reasoning is the order or the rank of these symbols.If in a question, P > Q ≥ R is given, the greater-than sign (>) will be of the highest order and P > R and not P ≥ R
If in a question, P ≥ R = Q is given, in that case, P > Q or P = Q
If in a question, P < Q < R is given, then P < R
If in a question, P < Q > R is given, the no relation can be found between the terms
Similar conclusions can be drawn for other questions based on inequalities.
Types of Questions in Inequality
The questions based on inequality have to be solved with the help of cracking the coding relationship between the given elements but to make the questions more complex, a new pattern for reasoning inequality questions has come up.
Given below are the two patterns in which the Inequality questions in reasoning are asked:
- Direct Questions – In direct questions, the candidates are given the elements and the relationship between them is marked with the help of the signs, <, >, =, etc. For example A>B=C≤D
- Coded Questions – The new format of inequality questions which is now being asked in all major exams is that they denote each sing with a symbol. For example, they may give “A@B, where @ means that A is neither greater than nor equal to B”. In this case, the “=” sign has been denoted with the “@” sign. This pattern is now being followed for all major Government exams to make the questions complex and confusing.
Tips and Tricks to Solve Questions on Inequality
Every aspirant preparing for the competitive exams knows the value of time management to qualify any of these exams. So, any small tip or trick which can help you save some time in the final examination must be used to answer the questions.
Given below are such tips to help you answer the questions on Inequality and ace the reasoning ability section:
- To answer any inequality question, the most important thing is to be aware of the signs and their representation. Only then can you answer the questions without making errors
- If the statements given comprise a single element more than once, try to combine the statement so that no element is repeated. For example, “A > B > C, F < C, A = E”, all are a part of a single statement, so you can combine them to form, “E = A > B > C > F”
- At no point should you change the sign between two given elements. However, you can write H > E or E < H as both denote the same
- For coded inequalities, make sure that you make a table or any other diagram which mentions what sigh each code represents. This will save you some time as you shall not have to read the question again and again and spend time on it.
Solved Examples on Inequality
Directions (Q1-Q2): Answer the following questions based on the statement given below:
Statement: P < S < R < T > Q
Q1: Which sign should be filled in the blank for the conclusion given below?
Conclusion: P ___ T
(a) >
(b) <
(c) =
(d) ≤
Ans: (b)
Q2: Which of the given conclusions is incorrect based on the given statement?
(a) P < R
(b) S < T
(c) No relation between P & Q
(d) No relation between P & T
Ans: (c)
Directions (Q3-Q4): Based on the statements, answer the following questions.
‘P * Z’ means P is neither greater nor smaller than Z
‘P # Z’ means P is neither greater than nor equal to Z
‘P & Z’ means P is neither smaller than nor equal to Z
‘P + Z’ means P is not smaller than Z
‘P % Z’ means P is not greater than Z
Q 3. For the statement given below, which of the following options is correct?
Statement: A # C * F & R % T
(a) A & C
(b) F # T
(c) C * R
(d) C # F
Ans: (d)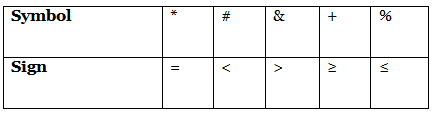
Statement: A # C * F & R % T
Conclusion: A < C = F > R ≤ T
A & C ↔ A > C
F # T ↔ F < T
C * R ↔ C = R
A % T ↔ A ≤ T
C # F ↔ C > R
And only C > R is correct based on the given equation
Q4: To prove that A > B in the given statement, which code should be filled in the blank?
Statement: C & B ____ F * E # A
(a) #
(b) *
(c) &
(d) %
Ans: (d)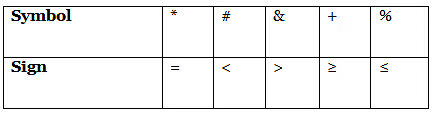
C & B ____ F * E # A
When % is placed in the blank, the statement becomes,
C & B % F * E # A
⇒ C > B ≤ F = E < A, which proves that A > B
|
73 videos|83 docs|121 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction and Types: Coded Inequality - Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams
| 1. What is a reasoning inequality and why is it important in exams? |  |
| 2. What are the types of coded inequalities? |  |
| 3. How can one solve reasoning inequality questions effectively in exams? |  |
| 4. Can reasoning inequalities be solved using mathematical operations? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid while solving reasoning inequality questions? |  |





















