Introduction of Computers | Computer Science for Class 7 PDF Download
Introduction

Computer is a programmable electronic device designed to accept data, perform prescribed mathematical and logical operation at high speed and display the result of these operation.
Data: Data is raw facts and figures, in other word; raw material which is not meaningful is called data. Data is not processed it does not form meaningful information.
Example: Taj Mahal, Shahajahan, 1632.
Information: Data represented in useful form is called information. It is the raw material that is processed to form meaningful information.
Example: Taj mahal was built by shahajahan in 1632.
The data after being processed becomes information. Conversion of data into information is called data processing.
Characteristics of Computer
Automation: Computer is an intelligent device. It can perform a job without human assistance. But computer is a machine, which cannot start the job themselves. We need to instruct the computer using coded instruction called programme.
Accuracy and reliability : Computer is highly accurate and reliable. However error can occur in computer but these errors are due to humans who writes the programme, thus computer error are caused due to incorrect input data or unreliable programme gives incorrect output. This is called as Garbage in garbage out (GIGO).
Storage: Computer can store massive amount of information depending on the storage capacity and then retrieve it whenever required.
Diligence: Unlike human being, computer does not show sign of fatigue, tiredness and lack of concentration. It performs first to last calculation from millions of calculation with same speed and accuracy.
No IQ: Computer has to be told what to do, how to do and in what sequence. We do it by instructing it using programmes. It does not work without instruction.
No Feeling and emotions: Computer does not have emotions and feeling as human do.
Power of remembering: Computer can recall any amount of information stored in its memory even after several years.
Speed: Computer is very fast device. It’s speed is measured in MIPS( Million instruction per second ). A computer is capable of performing 3MIPS.
Versatility: It means computer is capable of performing any task, provided the task can be reduced to finite logical steps.
Evolution of Computer
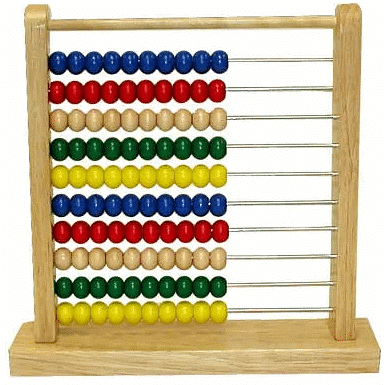
(i) First calculating device: Abacus was invented by Mesopotamians in around 3000 BC. It consists of beads on movable rods divided into two parts.
By using the place value of digits and position of beads in an Abacus , Addition & multiplication of numbers were performed. The Chinese further improved the abacus so that calculation could become easier.
 (ii) First mechanical adding machine: The First mechanical adding machine was Pascaline invented by Blaise Pascal in It was capable of performing addition and subtraction along with carry forward capability.
(ii) First mechanical adding machine: The First mechanical adding machine was Pascaline invented by Blaise Pascal in It was capable of performing addition and subtraction along with carry forward capability.
 (iii) Later using the technology of Blaise Pascal, Gattfried Leibnitz in 1673 invented first calculator for multiplication and division. The multiplication was performed by repetitive addition of numbers.
(iii) Later using the technology of Blaise Pascal, Gattfried Leibnitz in 1673 invented first calculator for multiplication and division. The multiplication was performed by repetitive addition of numbers.
(iv) Charles Babbage is called as the father of modern computer. He designed a “Difference Engine” in 1822 which could calculate various mathematical function like solving polynomial. In 1833, he designed Analytical Engine which could perform arithmetical operation (Addition, Subtraction, Division, Multiplication) and comparison.
Charles Babbage was unable to produce the making model of Analytical engine because of the unavaibility of engineering required to manufacture the machine at that time. But later it proved to be the basis of modern computer.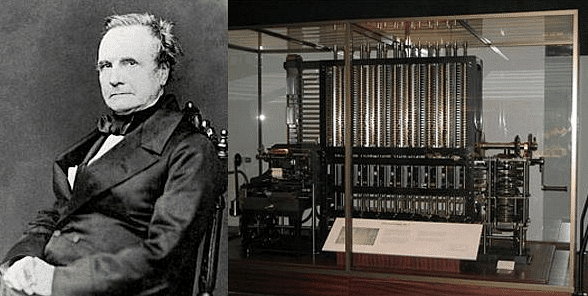
(v) Jacquard’s loom ( 1801 ): In order to make cotton weaving process automatic Joseph Marie Jacquard developed a programmable loom which used cards having holes punched on them.
(vi) Punch Card Machine: Herman Holterith come with the concept of punch card for speeding the collation job of American Census of 1880. Hollerith later founded Tabulating machine in 1896.
(vii) Mark I computer(1944): Mark I computers, also known as Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator.
- It is first fully automatic calculating machine .
- Designed by Howard Aiken in collaboration with IBM.
- It was an electro mechanical device based on technique of punched card.
(viii) ENIAC Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator (1943-1946 ):
- It is the First electronic computer.
- It was developed by professor J Presper Eckect and John Mauchly.
- In this Diode and Triode were used as a switch.
- The main drawback of ENIAC was to change the program, as its program was wired.
- Later Dr Jhon Von Neumann introduced “stored programme concept” to overcome this problem.
(ix) EDVAC Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer (1946- 1952 ):
- First stored programed computer.
- Developed by John von Neumann.
(x) EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer):
- It was developed by group of scientist of Cambridge University headed by professor Maurice Wilkes .
- First computer capable of storing instruction and data in memory.
(xi) UNIVAC Universal Automatic Computer (1951):
- It is First digital computer
- First computer that was commercially available for business and scientific application.
- First business use was by general Electric Corporation in 1954. After the success of UNIVAC I the IBM entered into in field of computer with IBM 701 computer.
After the success of UNIVAC I the IBM entered into in field of computer with IBM 701 computer.
Uses of Computer

Limitation of Computer
(i) Computer does not work on itself, it requires set of instructions to be provided, and else computer (Hardware) is waste.
(ii) Computer are not intelligent, they have to be instructed about each and every step which they have to perform
(iii) Computers cannot take decisions on its own, one has to program the computer to take an action if some conditional prevail.
(iv) Computers, unlike humans cannot learn by experience.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is considered the brain of the computer. It controls all parts of the computer including data processing (like storing data, retrieving data, executing data).
Control Unit
It performs all tasks except the data processing acts . It obtains the instructions from the memory, intercepts it and directs the following operation. It also communicates with the input and output devices. It is regulates the transfer of data.
ALU
The Arithmetic and Logic Unit is a circuit that performs arithmetic and logical functions.
The arithmetic function involves mathematical functions like subtraction, addition, division, multiplication, etc.,
The logical function involves functions like selecting, matching, sorting, etc.,
I/O Unit
The Input and output devices are the interface for the user and the computer to access the data from the user and provide the processed data to the user. The input devices like keyboard, mouse, joystick, barcode scanner, etc., is used to input the data into the computer. The computer processes the data and provides the data back to user through output devices like monitor, printer, graphic plotter, etc.,
Memory Unit
The computer’s memory unit consists of RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (read Only Memory). The RAM first gets instructions which then passes to the processor which processes and sends back. The Random access memory is also called as Read/Write memory, which is the temporary memory of a computer. The ROM is a special memory which is read only memory, writing and erasing is not possible by user without specialized equipment. Read only memory can be manufacturer-programmed or user-programmed only.
|
26 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction of Computers - Computer Science for Class 7
| $1. What is a computer and how does it work? |  |
| $2. What are the main components of a computer? |  |
| $3. What is the difference between hardware and software? |  |
| $4. What are the different types of computers? |  |
| $5. Why is it important to learn about computers in today's world? |  |


















