Introduction to Atomic Physics | Modern Physics for IIT JAM PDF Download
Individual carbon atoms are visible in this image of a carbon nanotube made by a scanning tunneling electron microscope.
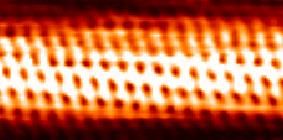
From childhood on, we learn that atoms are a substructure of all things around us, from the air we breathe to the autumn leaves that blanket a forest trail. Invisible to the eye, the existence and properties of atoms are used to explain many phenomena—a theme found throughout this text. In this chapter, we discuss the discovery of atoms and their own substructures; we then apply quantum mechanics to the description of atoms, and their properties and interactions. Along the way, we will find, much like the scientists who made the original discoveries, that new concepts emerge with applications far beyond the boundaries of atomic physics.
Discovery of the Atom:
How do we know that atoms are really there if we cannot see them with our eyes? A brief account of the progression from the proposal of atoms by the Greeks to the first direct evidence of their existence follows.
People have long speculated about the structure of matter and the existence of atoms. The earliest significant ideas to survive are due to the ancient Greeks in the fifth century BCE, especially those of the philosophers Leucippus and Democritus. (There is some evidence that philosophers in both India and China made similar speculations, at about the same time.) They considered the question of whether a substance can be divided without limit into ever smaller pieces. There are only a few possible answers to this question. One is that infinitesimally small subdivision is possible. Another is what Democritus in particular believed—that there is a smallest unit that cannot be further subdivided. Democritus called this the atom. We now know that atoms themselves can be subdivided, but their identity is destroyed in the process, so the Greeks were correct in a respect. The Greeks also felt that atoms were in constant motion, another correct notion.
The Greeks and others speculated about the properties of atoms, proposing that only a few types existed and that all matter was formed as various combinations of these types. The famous proposal that the basic elements were earth, air, fire, and water was brilliant, but incorrect. The Greeks had identified the most common examples of the four states of matter (solid, gas, plasma, and liquid), rather than the basic elements. More than 2000 years passed before observations could be made with equipment capable of revealing the true nature of atoms.
Over the centuries, discoveries were made regarding the properties of substances and their chemical reactions. Certain systematic features were recognized, but similarities between common and rare elements resulted in efforts to transmute them (lead into gold, in particular) for financial gain. Secrecy was endemic. Alchemists discovered and rediscovered many facts but did not make them broadly available. As the Middle Ages ended, alchemy gradually faded, and the science of chemistry arose. It was no longer possible, nor considered desirable, to keep discoveries secret. Collective knowledge grew, and by the beginning of the 19th century, an important fact was well established—the masses of reactants in specific chemical reactions always have a particular mass ratio. This is very strong indirect evidence that there are basic units (atoms and molecules) that have these same mass ratios. The English chemist John Dalton (1766–1844) did much of this work, with significant contributions by the Italian physicist Amedeo Avogadro (1776–1856). It was Avogadro who developed the idea of a fixed number of atoms and molecules in a mole, and this special number is called Avogadro’s number in his honor. The Austrian physicist Johann Josef Loschmidt was the first to measure the value of the constant in 1865 using the kinetic theory of gases.
Patterns and Systematics
The recognition and appreciation of patterns has enabled us to make many discoveries. The periodic table of elements was proposed as an organized summary of the known elements long before all elements had been discovered, and it led to many other discoveries. We shall see in later chapters that patterns in the properties of subatomic particles led to the proposal of quarks as their underlying structure, an idea that is still bearing fruit.
Knowledge of the properties of elements and compounds grew, culminating in the mid-19th-century development of the periodic table of the elements by Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907), the great Russian chemist. Mendeleev proposed an ingenious array that highlighted the periodic nature of the properties of elements. Believing in the systematics of the periodic table, he also predicted the existence of then-unknown elements to complete it. Once these elements were discovered and determined to have properties predicted by Mendeleev, his periodic table became universally accepted.
Also during the 19th century, the kinetic theory of gases was developed. Kinetic theory is based on the existence of atoms and molecules in random thermal motion and provides a microscopic explanation of the gas laws, heat transfer, and thermodynamics (see Introduction to Temperature, Kinetic Theory, and the Gas Laws and Introduction to Laws of Thermodynamics). Kinetic theory works so well that it is another strong indication of the existence of atoms. But it is still indirect evidence—individual atoms and molecules had not been observed. There were heated debates about the validity of kinetic theory until direct evidence of atoms was obtained.
The first truly direct evidence of atoms is credited to Robert Brown, a Scottish botanist. In 1827, he noticed that tiny pollen grains suspended in still water moved about in complex paths. This can be observed with a microscope for any small particles in a fluid. The motion is caused by the random thermal motions of fluid molecules colliding with particles in the fluid, and it is now called Brownian motion. (See [link].) Statistical fluctuations in the numbers of molecules striking the sides of a visible particle cause it to move first this way, then that. Although the molecules cannot be directly observed, their effects on the particle can be. By examining Brownian motion, the size of molecules can be calculated. The smaller and more numerous they are, the smaller the fluctuations in the numbers striking different sides.
The position of a pollen grain in water, measured every few seconds under a microscope, exhibits Brownian motion. Brownian motion is due to fluctuations in the number of atoms and molecules colliding with a small mass, causing it to move about in complex paths. This is nearly direct evidence for the existence of atoms, providing a satisfactory alternative explanation cannot be found.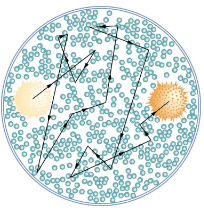
It was Albert Einstein who, starting in his epochal year of 1905, published several papers that explained precisely how Brownian motion could be used to measure the size of atoms and molecules. (In 1905 Einstein created special relativity, proposed photons as quanta of EM radiation, and produced a theory of Brownian motion that allowed the size of atoms to be determined. All of this was done in his spare time, since he worked days as a patent examiner. Any one of these very basic works could have been the crowning achievement of an entire career—yet Einstein did even more in later years.) Their sizes were only approximately known to be 1010 m based on a comparison of latent heat of vaporization and surface tension made in about 1805 by Thomas Young of double-slit fame and the famous astronomer and mathematician Simon Laplace.
Using Einstein’s ideas, the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Perrin (1870–1942) carefully observed Brownian motion; not only did he confirm Einstein’s theory, he also produced accurate sizes for atoms and molecules. Since molecular weights and densities of materials were well established, knowing atomic and molecular sizes allowed a precise value for Avogadro’s number to be obtained. (If we know how big an atom is, we know how many fit into a certain volume.) Perrin also used these ideas to explain atomic and molecular agitation effects in sedimentation, and he received the 1926 Nobel Prize for his achievements. Most scientists were already convinced of the existence of atoms, but the accurate observation and analysis of Brownian motion was conclusive—it was the first truly direct evidence.
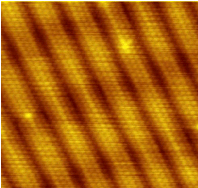
A huge array of direct and indirect evidence for the existence of atoms now exists. For example, it has become possible to accelerate ions (much as electrons are accelerated in cathode-ray tubes) and to detect them individually as well as measure their masses (see for a discussion of mass spectrometers). Other devices that observe individual atoms, such as the scanning tunneling electron microscope, will be discussed elsewhere. All of our understanding of the properties of matter is based on and consistent with the atom. The atom’s substructures, such as electron shells and the nucleus, are both interesting and important. The nucleus in turn has a substructure, as do the particles of which it is composed. These topics, and the question of whether there is a smallest basic structure to matter, will be explored in later parts of the text.
Individual atoms can be detected with devices such as the scanning tunneling electron microscope that produced this image of individual gold atoms on a graphite substrate.
|
52 videos|44 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Atomic Physics - Modern Physics for IIT JAM
| 1. What is atomic physics? |  |
| 2. What are the main areas of study in atomic physics? |  |
| 3. How is atomic physics relevant to everyday life? |  |
| 4. What experiments are conducted in atomic physics? |  |
| 5. How does atomic physics contribute to our understanding of the universe? |  |






















