Introduction to Goods and Service Tax (GST) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Meaning of GST
- Goods and Service Tax (GST) is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services.
- It is a nation-wide tax seeking to unify several indirect taxes.
- Based on the principle of ‘One Nation one Tax’.
- The GST Act was passed in the Parliament on 24th March, 2017.
- It came into effect from 1st July, 2017.
- Taxes Merged into GST: GST has replaced many indirect taxes levied by Centre and State Governments.
- Central level taxes that have merged into GST are as under:
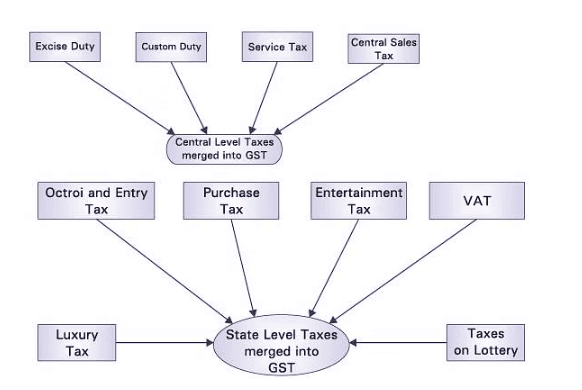
- State-level taxes that have been included in GST are listed below:
- GST Rate Structure:Goods and services are categorized into five different tax rates for GST collection:
- Essential Items such as food: 0%
- Common Use Items: 5%
- Standard Rate: 12%
- Maximum Goods and all services under the standard rate: 18%
- Luxury Items and tobacco: 28%
- GST is paid when purchasing goods and services, and it is collected from customers when selling goods and services.
- The GST paid on purchases is referred to as Input GST and is offset against the GST collected on sales, known as Output GST.
- Therefore, the GST paid on purchases (Input GST) is not considered a cost for the buyer but rather an asset, as it can be used to offset the GST collected from sales (Output GST).
- Similarly, the GST collected from sales (Output GST) is not treated as the seller's income but is regarded as a liability.
Important Notes
- Usually, GST Paid on buying goods and services (known as Input GST) is not considered a cost for the buyer. Instead, it is seen as an Asset because it can be offset against GST Collected (referred to as Output GST).
- However, there are specific situations where GST Paid cannot be offset against GST Collected. In these instances, GST Paidon the purchase of goods and services becomes a cost for the buyer. The situations where this occurs include:
- Food and Beverages Expenses (like restaurant bills).
- Payments for health insurance.
- Membership Fees for clubs, health centers, and fitness centers.
- Repairs and Maintenance of buildings.
- Purchases of Vehicles.
- Free gifts to Staff.
- Payments for goods and services for personal use.
- GST Paid (or Input GST) is Reversedin the following cases:
- Goods lost or stolen.
- Goods destroyed or written off.
- Goods given as free samples.
- Goods donated as gifts or charity.
- The following goods and services are exempt from the levy of GST:
- Payments of Wages and Salaries.
- Supply of Services to the government or embassies of other countries.
- Electricity and Water Bills.
- Educational Services.
- Health Services.
Objectives or Advantages of GST :
- Decrease in the Cost of Goods: The Cost of goods will decrease since tax on tax is eliminated in GST regime.
- Cascading Effect of Taxes: In the pre-GST regime, there were many indirect taxes levied by both centre and state.
- Excise Duty and VAT: Centre charged excise duty on goods manufactured and States charged VAT on the same goods.
- Tax on Tax: This led to a cascading effect of taxes.
- GST Benefits: GST avoids this cascading effect as the tax is calculated only on the value added at each stage of transfer of ownership.
- Ease of Doing Business: GST harmonizes tax administration between the Centre and the States which will improve the ease of doing business.
- Reduce Tax Evasion: Electronic return filing and assessment will reduce tax evasion and compliance cost.
- Transparency: Tax system becomes more transparent, regular and predictable.
Type of Taxes under GST:
- There are three types of taxes under GST:
- Central GST (CGST)
- State GST (SGST) or Union Territory GST (UTGST)
- Integrated GST (IGST)
- CGST and SGST are applied to sales made within the same state, known as intra-state sales.
- For example, if a dealer in Rajasthan sells goods worth ₹50,000 to another dealer or consumer in Rajasthan,
- Assuming the GST rate is 12%, this rate is split into:
- CGST at 6%
- SGST at 6%
- The total GST collected will be ₹6,000, with ₹3,000 going to the Central Government and ₹3,000 going to the Rajasthan Government.
- IGST applies to sales made between different states, known as inter-state sales.
- It is also charged on goods and services imported into India and exported out of India.
- For instance, if a dealer in Rajasthan sells goods worth ₹50,000 to a dealer in Madhya Pradesh,
- If the IGST rate is 12%, the seller will charge ₹6,000 as IGST.
- This entire amount of ₹6,000 will go to the Central Government.
Accounting Procedure:
In case of Intra-state supply of goods and services state)


In case of purchase returns, Input CGST A/c and Input SGST A/cs are credited because a t the time of purchase Input CGST A/c and Input SGST A/cs were debited .
In case of sales returns, Output CGST A/c and Output SGST A/cs are debited because at the time of sale Output CGST A/c and O utput SGST A/cs were credited.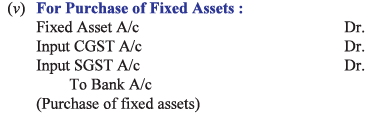

(vii) For Income (for example commission received)
(viii) For goods withdrawn by the Proprietor for personal use:
(ix) For goods given as free samples, loss of goods by fire or goods stolen:
(Goods distributed as free samples, goods stolen and goods destroyed by fire and Input CGST and Input SGST reversed)
(x) For Setting off Input CGST against Output CGST:
(xi) For setting off Input SGST against Output SGST:
(xii) For payment o f GST:
Practical Questions
Q1: Rohan, a Chartered Accountant has a registered office in Chandigarh. He also obtained registration in the state of West Bengal in respect of his newly opened branch office. Whether head office or branch office will be treated as deemed distinct person.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Yes, Office will be treated as deemed distinct person.
Q2: Vasu Ltd. Provides the following particulars relating to good supplied to it by Agni Ltd.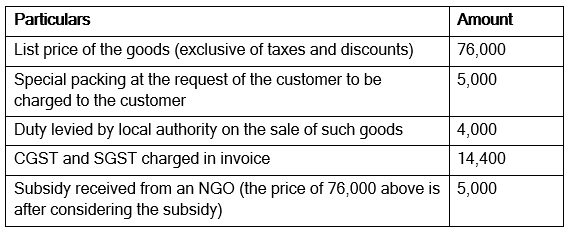 Vasu Ltd. Offers 3% discount of the list price of the goods which is recorded in theinvoice for the goods.
Vasu Ltd. Offers 3% discount of the list price of the goods which is recorded in theinvoice for the goods.
Determine the value of taxable supplies made by Vasu Ltd.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Value: 87,720
Q3: Vanika Advertisers conceptualized and designed the advertising campaign for a new product launched by New Moon Pvt. Ltd. for a consideration of Rs. 7,00,000. Vanika Advertisers owed Rs. 25,000 to one of its vendors in relation to the advertising service provided by it to New Moon Pvt. Ltd. Such liability of Vasu Advertisers was discharged by New Moon Pvt. Ltd. New Moon Pvt. Ltd. Delayed the payment of consideration and thus, paid Rs. 18,000 as interest.
Determine the value of taxable supply by Vasu Advertisers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Value: 7,43,000
Q4: Candy Rose Ltd., Mumbai, a registered supplier, is manufacturing chocolates and biscuits. It provides the following details of taxable inter-state supply made by it for the month of October, 20xx a) Tax levied by Municipal Authority: Rs. 24,000
a) Tax levied by Municipal Authority: Rs. 24,000
b) Packing charges: Rs. 12,000c)
c) Late fee paid by the recipient of supply for delayed payment of invoice: Rs. 5,000
Calculate the value of taxable supply made by M/s Candy Rose Ltd. for the month of October 20xx.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Value : Alternate 1: 13,06,000 Alternate 2: 13,11,000
Q5: M/s RT Ltd. supplied taxable goods from the factory after manufacture in the month of October 2017 for sale to a distributor for Rs. 8,00,000. However, he deposited the GST @ 12% of the goods on 10 Jan 2018 against show cause notice issued undersection 74 (when there is a fraud) of the CGST Act, 2017 by the Central tax Officer and passed the order accordingly. During the month of December 2017, M/s X Ltd. received goods worth Rs. 5,00,000by paying GST 12%.
(a) Find the Net GST deposited by M/s RT Ltd. into the Government account on 10 Jan 2018
(b) Your answer is different if M/s RT Ltd. paid GST @ 12% against show causenotice issued under section 73 (when there is no fraud)
(c) Rework, M/s RT Ltd. paid output tax by following self-assessment (i.e. whenthere is no show cause notice issued), what will the GST payable?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
a) Net GST Liability: CGST – 48,000, SGST – 48,000
b) Net GST Liability: CGST – 18,000, SGST – 18,000
c) Net GST Liability: CGST – 18,000, SGST – 18,000
Q6: Sharma Traders is a registered supplier of goods in Arunachal Pradesh. It purchasedgoods valued at Rs. 10,000 from Kiran Suppliers located within the same state. KiranSuppliers charged CGST and SGST separately in its invoice. Subsequently, SharmaTraders sold goods valuing Rs. 9,500 to Rashtogi Manufacturers located in ArunachalPradesh. 20% of the inputs purchased are still lying in the stock and there was noopening stock of the goods. Rate of CGST and SGST on supply and purchase of goods is 9% each.
Calculate the net GST payable by Sharma Traders and input tax credit (ITC) to be carried forward, if any.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Net GST Payable: CGST – Nil, SGST – Nil
ITC C/F: CGST – 45, SGST - 4
Q7: Determine the time of supply in the following independent cases, in case supply does not involve the movement of goods:
 View Answer
View Answer 
TOS:
1. 2nd OCT
2. 1st OCT
3. 4th NOV
Q8: Determine the time of supply from the following particulars:
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
TOS: Rs. 3,000 (6th May) & For Rs. 12,000 is 15th Sep
Q9: On July 7, 20xx, Y supplies 27 tonnes of a chemical to G at the rate of Rs. 88,000per ton. Compute the value of supply and GST liability for the following data:
- He charges additionally the following- freight: 3,12,000, packing charge: Rs.72,000, weighing charges: Rs. 30,000, inspection charges: Rs. 12,000.
- He also charges cost of an instrument of an instrument which is specially purchased by Y to manufacture this chemical: Rs. 1,10,000 (this instrument cannot be used for any other purpose).
- GST rate is 18%
- Inspection charges are directly borne by G and not included in the invoice.
- State Government has paid a subsidy of Rs. 40,00,000 to Y to set up chemical manufacturing plant in Patna.
- G is required to make payment within 15 days of supply. However, payment is made in October 2017 and for late payment, Y charges interest of Rs. 11,000.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Value: 29,23,000 and CGST: 2,63,070, SGST: 2,63,070
Q10: The Customs Authorities have confiscated smuggled gold from Mr. Jindal. Theconfiscated gold these goods Sold to Tanishq Jewellers of Delhi for Rs. 30,00,000.Applicable rate of GST is 18%. You are required to compute the following:
(i) Person liable to pay GST
(ii) Net GST liability
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
i) Tanishq Jewellers.
ii) 5,40,00
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Goods and Service Tax (GST) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is Goods and Services Tax (GST) and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of GST? |  |
| 3. How does GST affect pricing of goods and services? |  |
| 4. Who is required to register for GST? |  |
| 5. What are the key benefits of implementing GST? |  |






















