Investigating Rate of a Reaction | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
Investigating The Rate of a Reaction
- Determining the rate of a reaction involves measuring how rapidly reactants are consumed or products are formed.
- The chosen measurement method depends on the substances involved in the reaction.
- Various laboratory techniques exist for measuring reaction rates, all relying on a property that changes during the reaction, typically linked to reactant or product concentration.
- This property is often related to characteristics such as color, mass, or volume.
- Faster reactions may be simpler to measure once they are complete, although continuously measuring reaction rates as the process unfolds can yield more data.
- Three commonly employed techniques include measuring mass loss on a balance, quantifying the volume of gas produced, and observing color changes at the reaction's conclusion.
Investigating the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction
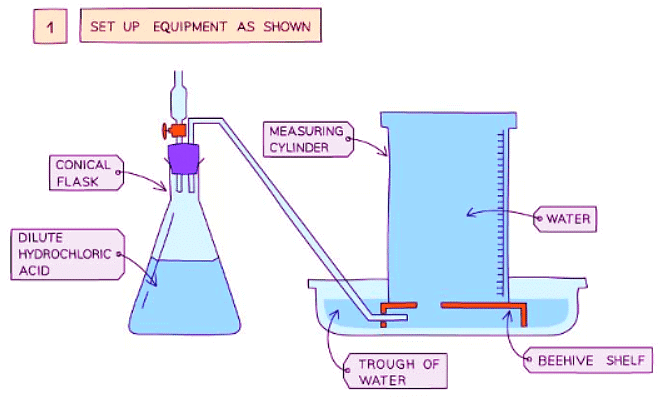
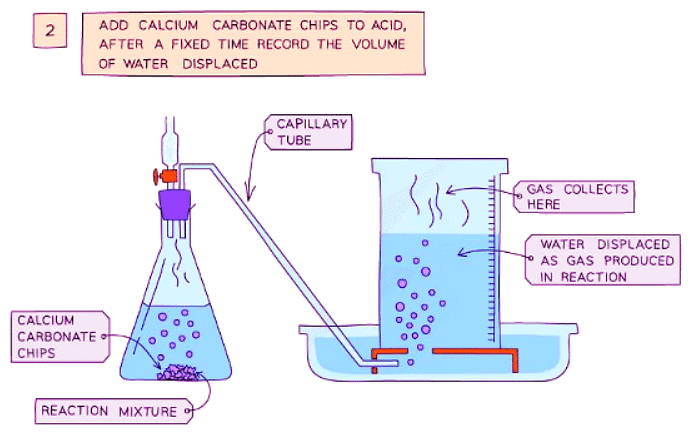
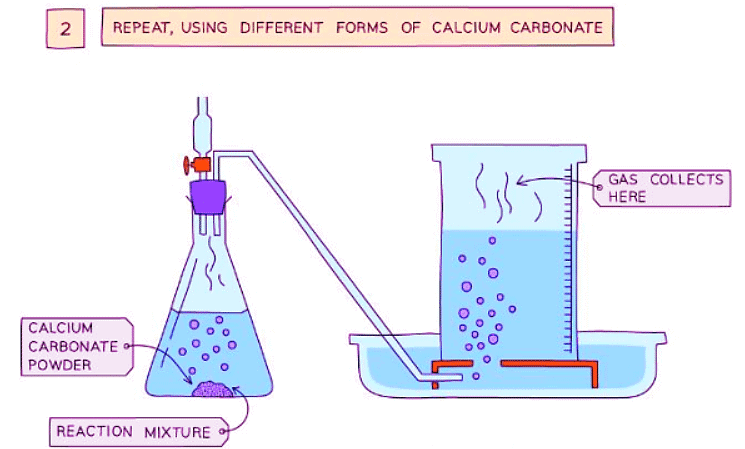
Diagram showing the process of downwards displacement to investigate the effect of the surface area of a solid on the rate of reaction.
Method
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid into a conical flask
- Use a delivery tube to connect this flask to a measuring cylinder upside down in a bucket of water (downwards displacement)
- Add calcium carbonate chips into the conical flask and quickly put the bung back into the flask
- Measure the volume of gas produced in a fixed time using the measuring cylinder
- Repeat with different sizes of calcium carbonate chips (lumps, crushed, and powdered)
Result
- Smaller sizes of chips cause an increase in the surface area of the solid, leading to an increased rate of reaction
- This is because more surface area of the particles is exposed to the other reactant, resulting in more frequent and successful collisions, thus increasing the rate of reaction
Effect of concentration of a solution on the rate of reaction
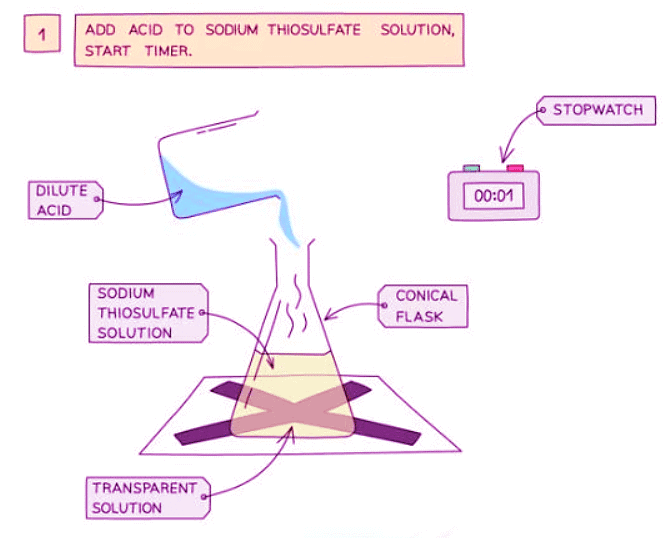
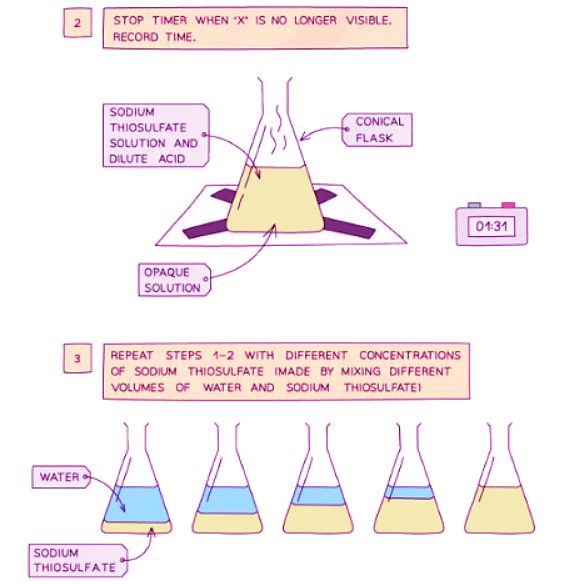
Diagram showing the apparatus needed to investigate the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction
Method
- Measure 50 cm3 of sodium thiosulfate solution into a flask
- Measure 5 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid into a measuring cylinder
- Draw a cross on a piece of paper and put it underneath the flask
- Add the acid into the flask and immediately start the stopwatch
- Look down at the cross from above and stop the stopwatch when the cross can no longer be seen
- Repeat using different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate solution (mix different volumes of sodium thiosulfate solution with water to dilute it)
Result
- With an increase in the concentration of a solution, the rate of reaction will increase.
- This is because there will be more reactant particles in a given volume, allowing more frequent and successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
Effect of temperature on the rate of reaction
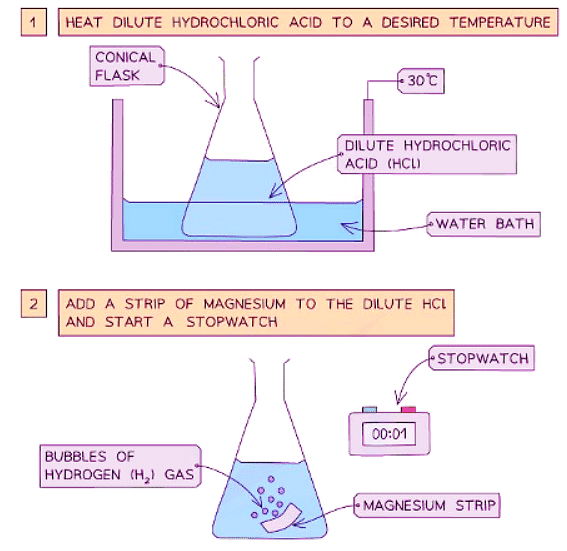
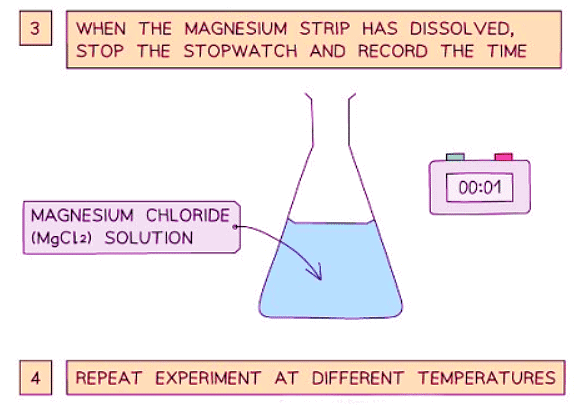
Diagram showing the apparatus needed to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction
Method
- Dilute hydrochloric acid is heated to a set temperature using a water bath.
- Add the dilute hydrochloric acid into a conical flask.
- Add a strip of magnesium and start the stopwatch.
- Stop the time when the magnesium fully reacts and disappears.
- Repeat the experiment at different temperatures and compare the results.
Result
- With an increase in temperature, the rate of reaction will increase.
- This is because the particles will have more kinetic energy than the required activation energy, leading to more frequent and successful collisions, which in turn increases the rate of reaction.
Effect of a catalyst on the rate of reaction
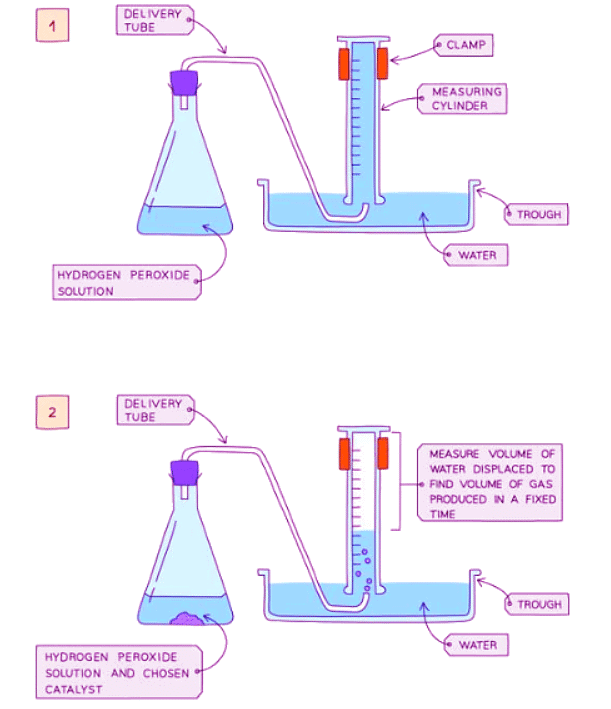
Diagram showing the apparatus needed to investigate the effect of a catalyst on the rate of reaction
Method
- Place hydrogen peroxide into a conical flask.
- Connect the flask to an upside-down measuring cylinder submerged in water using a delivery tube (downward displacement method).
- Introduce manganese(IV) oxide catalyst into the flask and promptly seal it with a bung.
- Measure the volume of gas generated within a specific time period using the measuring cylinder.
- Conduct the experiment again, this time excluding the manganese(IV) oxide catalyst, and compare the outcomes.
Result
- Employing a catalyst leads to a heightened reaction rate.
- The catalyst offers an alternate path necessitating less activation energy, enabling more colliding particles to meet the activation energy requirement for a reaction.
- This facilitates more frequent and successful collisions, thereby escalating the reaction rate.
Monitoring changes in mass
- When certain reactions occur, they generate gases that are released during the process.
- The produced gas can be collected and its volume can be tracked using various techniques.
- Alternatively, the reaction can be conducted in an open flask on a balance to measure the decrease in the mass of the reactant.
- Cotton wool is commonly inserted into the flask's opening to allow gas to escape while preventing any materials from being expelled from the flask, especially in cases of vigorous reactions.
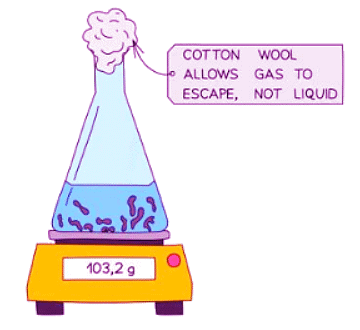
Diagram showing the set-up for measuring the rate of reaction by loss in mass
- This approach may not be suitable for gases like hydrogen with a low relative formula mass (M r) as the decrease in mass could be too minimal to measure accurately.
Evaluating Investigations of Rates of Reactions
- When studying reaction rates, several methods exist to conduct the same investigation.
- Effective experimental planning and design involve determining the most suitable method to employ.
- This requires understanding the advantages and disadvantages associated with the available methods.
Table showing some Examples of Advantages and Disadvantages of Methods of Investigating Rates of Reaction
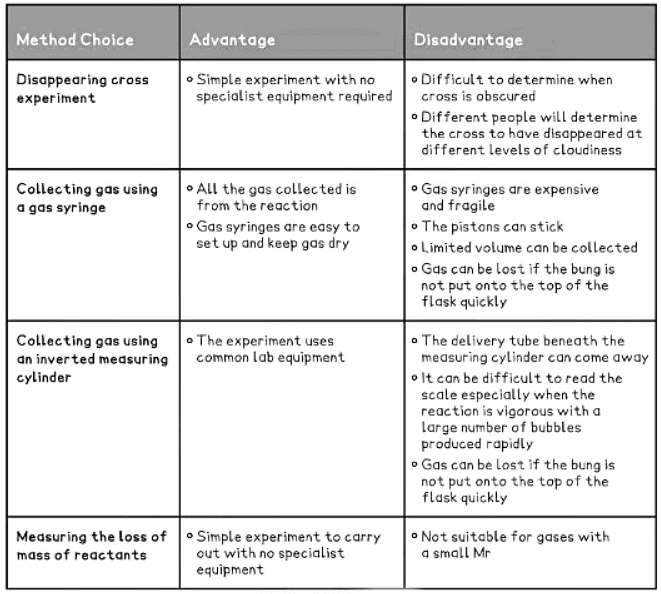
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Investigating Rate of a Reaction - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. How can reaction rates be measured in a chemical reaction? |  |
| 2. What is the effect of particle size on the rate of a reaction? |  |
| 3. How does concentration affect the rate of a reaction? |  |
| 4. What impact does temperature have on the rate of a reaction? |  |
| 5. How does the presence of a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction? |  |





















