Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > Ionic Bonds
Ionic Bonds | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
The Formation of Ions
Ionic Bonding
- An ion is formed when an atom undergoes a process of gaining or losing electrons, resulting in an electrical charge.
- Atoms adjust their electron count to achieve stability, typically by acquiring a full outer electron shell, a configuration that enhances stability.
- This adjustment ensures that the electron arrangement of the ion mirrors that of noble gases such as helium or neon.
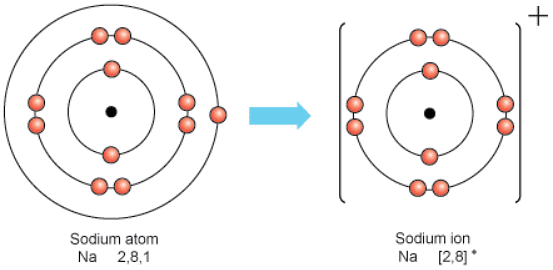
Ionisation of Metals and Non-metals
- Metals: All metals can lose electrons to other atoms to become positively charged ions, known as cations.
- Non-metals: All non-metals can gain electrons from other atoms to become negatively charged ions, known as anions.
What is Ionic Bonding?
Ionic Bonding Definition
- Ionic bonding occurs when metal atoms interact with non-metal atoms, resulting in the formation of ionic compounds.
- Metal atoms undergo electron loss, which is then gained by non-metal atoms to create positively and negatively charged ions.
- The attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms a strong ionic bond that holds the compound together.
Ionic Bonding Examples
- Dot-and-cross diagrams are visual tools representing the electron arrangements in ionic or covalent compounds.
- These diagrams use dots and crosses to depict outer-shell electrons, with brackets indicating evenly spread charges and ion charges noted in the top right corner.
Dot and Cross Diagrams
- Electrons in dot and cross diagrams are represented as dots and crosses.
- In a dot and cross diagram:
- Only the outer electrons are depicted.
- The charge of the ion is evenly distributed, shown using brackets.
- The charge on each ion is indicated at the top right-hand corner.
- Only the outer electrons are typically shown.
- The charge of the ion is evenly spread, demonstrated by brackets.
- The charge on each ion is written at the top right-hand corner.
Question for Ionic BondsTry yourself: What is the process that occurs when metal atoms interact with non-metal atoms, resulting in the formation of ionic compounds?View Solution
Ionic Bonds between Group I & Group VII Elements
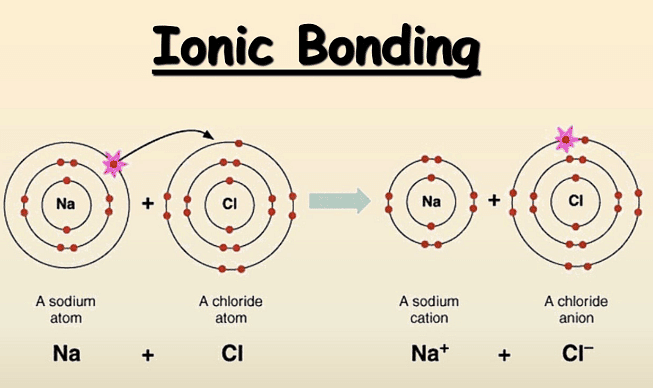
Ionic bonding occurs between elements from Group I and Group VII, such as Sodium and Chlorine forming Sodium Chloride (NaCl).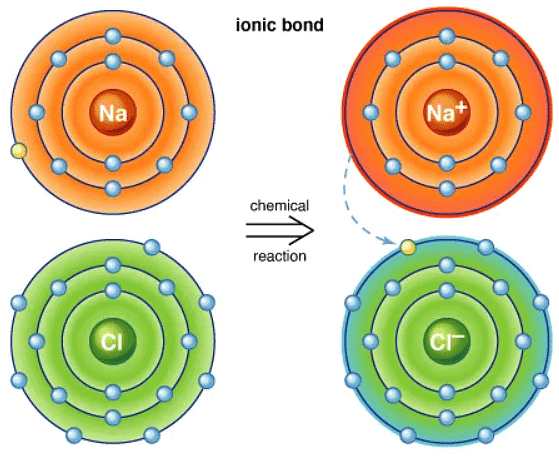
Process of Ionic Bond Formation
- Sodium, as a Group I metal, loses one outer electron to achieve a full outer electron shell.
- This loss leads to the formation of a positively charged sodium ion with a charge of +1.
- Chlorine, being a Group VII non-metal, gains an electron to complete its outer electron shell.
- The gained electron transforms Chlorine into a negatively charged chloride ion with a charge of -1.
- The resulting oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces.
Characteristics of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds exhibit no overall charge due to the balance of positive and negative charges.
- They are held together by strong ionic bonds formed from the attraction between ions of opposite charges.
In summary, Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between Group I and Group VII elements, leading to the formation of stable ionic compounds like Sodium Chloride.
Formula of Ionic Compound
- The formula of an ionic compound like sodium chloride (NaCl) represents the ratio of the ions present in the compound.
Question for Ionic BondsTry yourself: What is the result of the ionic bond formation between sodium and chlorine?View Solution
The document Ionic Bonds | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Ionic Bonds - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What is the process of ion formation? |  |
Ans. Ion formation occurs when an atom gains or loses electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Atoms can either lose electrons to become positively charged cations or gain electrons to become negatively charged anions.
| 2. How do Group I elements form ionic bonds with Group VII elements? |  |
Ans. Group I elements have one valence electron, while Group VII elements have seven valence electrons. Group I elements will easily lose their electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, while Group VII elements will readily gain one electron. This transfer of electrons results in the formation of ionic bonds between these groups.
| 3. What is the significance of ionic bonding in Year 11 chemistry? |  |
Ans. Understanding ionic bonding is crucial in Year 11 chemistry as it lays the foundation for comprehending the behavior of compounds formed between metals and nonmetals. This knowledge is essential for predicting chemical reactions and understanding the properties of different substances.
| 4. Can you provide an example of an ionic bond between a Group I and Group VII element? |  |
Ans. An example of an ionic bond formed between a Group I and Group VII element is the compound formed between sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) to create sodium chloride (NaCl). Sodium loses an electron to chlorine, resulting in the formation of Na+ cation and Cl- anion.
| 5. How do ionic bonds differ from covalent bonds in terms of electron sharing? |  |
Ans. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another to achieve stability, leading to the formation of ions. In contrast, covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Related Searches





















