PH, Buffer Solutions, Solubility & Solubility Product | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
17. Calculation of pH of Acidic Buffer Solution
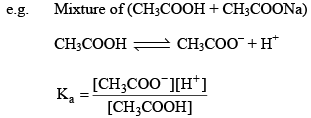
Since most of CH3COO– comes from salt (CH3COONa) and hence conc. of CH3COO– will be conc. of CH3COONa.
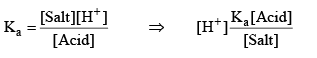
Taking (–ve) log both side
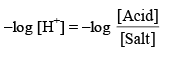
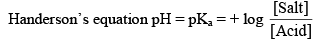
Illustration: Find pH of solution contains 0.1 M (100 ml) CH3COOH and mixed with 0.1 M, 50 ml NaOH. Ka = 10–5.
Solution: Here, an acid and base are mixed. So, first of all, Acid–Base react ion take place.
MIlimoles of CH3COOH = 10 mmol
Milimoles of NaOH = 5 mmol
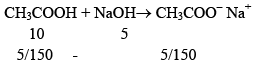
Now, solution is having weak acid CH3COOH and it’s salt having common ion. So, this solution is buffer solution ⇨ Acidic Buffer
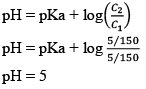
18. Basic Buffer
A mixture containing equimolar solutions of ammonium hydroxide and its almost completely dissociated salt, ammonium chloride, constitutes another good basic buffer.The mixture contains undissociated NH4OH as well as NH4+ and Cl– ions. The buffer action of this mixture many now be considered. If a strong acid is added. The H+ ions added are neutralized by the base NH4OH
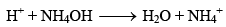
If a strong base is added, the OH– ions added are neutralized by NH4+ ions forming very slightly dissociated NH4OH.
19. Calculation of pH of Basic Buffer Solution
e.g. Mixture of (NH4OH + NH4Cl)
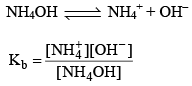
Since most of NH4+ ions comes salt (NH4Cl) so we take NH4+ conc. of salt (NH4Cl).
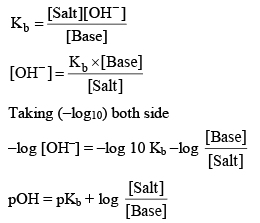
Hence pH = 14 –pOH at 14°C, Kw = 1 × 10–14 mol/litre.
Illustration:0.1 M, 100 ml NH4OH is titrated with 0.1 M, H2SO4 solution. Calculate the pH if kb = 10–5
(a) Nothing is added
(b) 25 ml, H2SO4 is added
(c) 0.1 M, 20 ml NaOH is mixed in resulting solution for made in part b.
(d) Find the pH if 0.1M, 10 ml H2SO4 is added in part b.
Solution
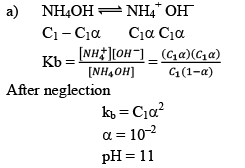
b) When an acid H2SO4 is added with NH4OH (a base), Acid-Base reaction takes place.
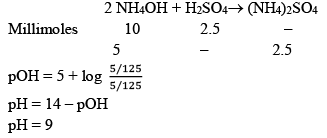
c) In part b we are having a weak base and its salt when NaOH is added it will React with (NH4)2SO4.
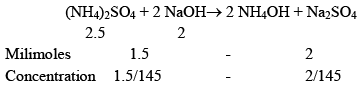
Now, the solution is having weak base and it’s salt, hence Buffer
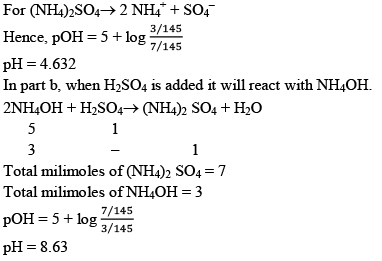
20. Salt Buffer
A salt buffer is a solution of a salt which itself can act as a buffer. Such salt is the salt of a weak acid and weak base.
For example,
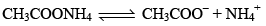
When an acid is added, it reacts with CH3COO– to produce CH3COOH and when a base is added, it reacts with NH4+ to produce NH4OH.
21. Buffer Capacity or Buffer Index
Buffer capacity of a solution is defined in terms of buffer index which is the change in the concentration of Buffer acid (or base) required for change of it’s pH value by one, keeping
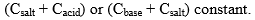
Let there be a buffer solution of volume 1 litre with ‘x’ mole of acid and ‘S’ moles of ‘salt’
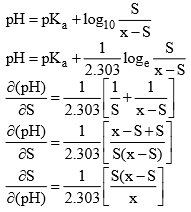
Maximum value of Buffer Index
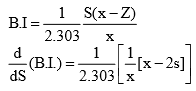
For maximum value of Buffer index
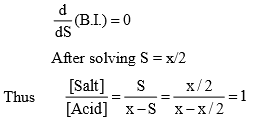
Hence max. value of Buffer index occurs when 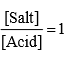
22. Buffer Range
It is difficult to give an exact limit into which a buffer can be used it in generally accepted that a solution has useful buffer capacity provided that the value of [Salt]/[Acid] lie within the range of 10 to 0.1. Hence from Henderson equation.
pKa + log 0.1 < pH < pKa + log10 10
pKa – 1 < pH < pKa + 1
Outside this range the Buffer capacity it too small to be of any practical application.
23. Hydrolysis of Salt
Salts are strong electrolytes when dissolved in water, they dissociated almost completely into cations or anions. If anion reacts with water it is called as anionic hydrolysis.

If cation reacts with water it is called as cationic hydrolysis.

“The phenomenon of the interaction of anions and cations of the salt with H+ and OH– ions furnished by water yielding acidic or alkaline solution is known as salt hydrolysis.
For the study of hydrolysis salts are divided into 4 groups.
Hydrolysis of salt of strong Acid or weak base:
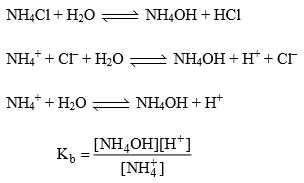
Relation B/w Kh, Kb and Kw:
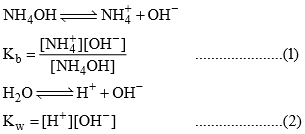
Dividing (2) ÷ (1)
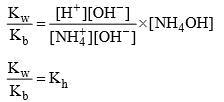
Degree of hydrolys
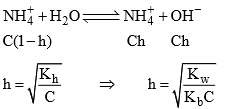
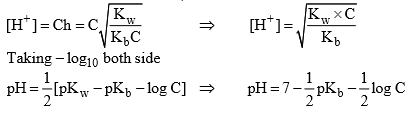
Hydrolysis of salt of weak acid and strong base:
CH3COONa is a salt of weak acid (CH3COOH) and strong base (NaOH). After hydrolysis resultant solution will be basic due to presence of strong base (NaOH)/
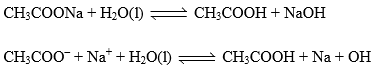
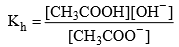
Relation between, Kh, Kw and Ka
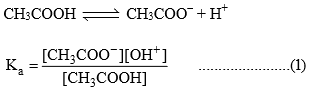

Dividing equation (2) ÷ (1)
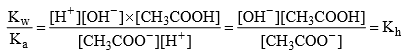
Degree of Hydrolysis
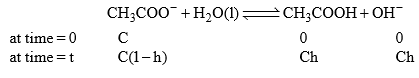
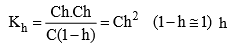 should be smaller than 0.1 than 1 – h = 1
should be smaller than 0.1 than 1 – h = 1
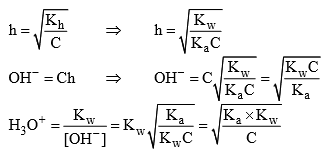
Taking (- ve) log both side
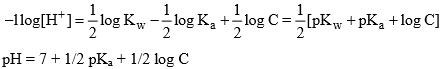
pH will be more than 7, hence resultant solution will be basic in nature.
Hydrolysis of salt of Weak Acid and Weak Base:
Let’s take the salt CH3COONH4 made of salt of weak acid (CH3COOH) and Weak base (NH4OH).
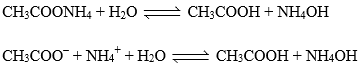
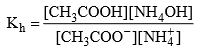
Relation between, Kh, Kw, Ka and Kb
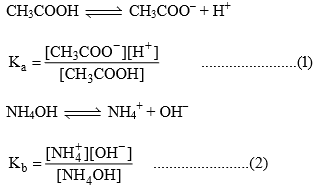
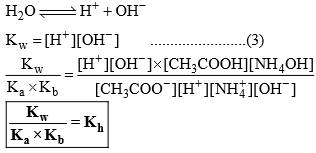
Degree of Hydrolysis
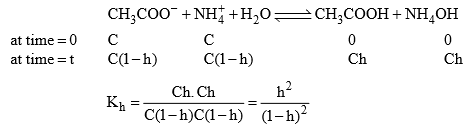
If h ≤ 0.1, 1 – h ≌ 1
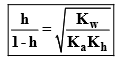
The acetic acid formed would partially decompose to give CH3COO– and H+. But because of common ion effect (that is, due to the unhydrolyzed CH3COO–) it is possible to neglect the acetate ion coming from CH3COOH.
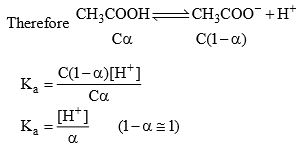
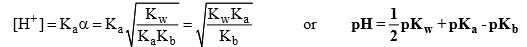
This expression is independent of conc. of the salt.
(i) if Ka = Kb, pH = 7 solution will be neutral
(ii) if Ka > Kb, pH < 7, acidic solution
(iii) if Ka < Kb then pH > 7, alkaline solution
In the hydrolysis of salt of weak acid and a weak base such as NH4CN, CH3COONH4. Both the ions are hydrolyzed, if we assume Ka ≌ Kb, then the hydrolysis of the cation and anion of the salt occur approximately to equal extent for a salt which has Ka < Kb. it would be expected at the first glance that CN– ions hydrolyzed to a much greater extent than 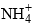 ions. However, the hydrolysis of CN– ion produced OH– ions according to the equation.
ions. However, the hydrolysis of CN– ion produced OH– ions according to the equation.
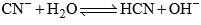
Which can react with 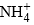 ions as
ions as
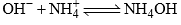
This latter reaction causes equilibrium in the from reaction to be displaced to the right. Because OH– ions are removed from the solution. Also the production of OH– by the former reaction displaces the latter reaction to the right. Therefore the hydrolysis of one ion drags the hydrolysis of the other ion along so that both the hydrolysis are fairly extensive far in extant from each other so it is fairly safe to assume 
Illustration: What is the pH of 0.4 M aqueous solution of NaCN, given that the pkb (CN–) is 70.
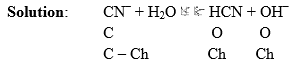
pKb(CN–) is given means equilibrium constant of this reaction is given. This reaction expresses the basicity of CN– ion.
pKb = - log Kb
4.7 = - log Kb
Kb = 1.9 × 10–5
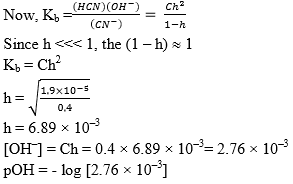
pOH = 2.55
pH = 11.45
Illustration: Find out the Kh of a centimolar solution of NH4Cl. If the dissociation constant for NH4OH is 10–6 and Kw = 10–14. Find the degree of hydrolysis and pH of solution.
Solution: NH4Cl is a salt of strong acid and weak base.
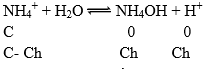
Equilibrium constant 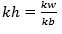
Kb = 10–6
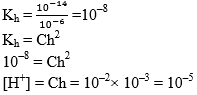
pH = 5
24. Case IV: Salts of Strong Acid + Strong Base
e.g., NaCl, KNO3,………..etc.
This category of salts not undergo salt hydrolysis
25. Solubility and Solubility Product
A solution which remain in contact with excess of the solute is said to be saturated. The amount of a solute, dissolved in a given volume of a solvent (in 1 litre) to forma saturated solution at a given temperature, it termed as the solubility of the solute in the solvent at that temperature.
Molar Solubility:
No. of moles of solute dissolved in per litre of solution
Solubility Product:
In a saturated of a salt, there exists a dynamic equilibrium between the excesss of the solute and ions furnished by that parts of the solute which has gone in solution. The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt is given as product of the conc. of the ions raised to the power equal to the no. of times the in occur in the equation after the dissociation of the electrolyte.
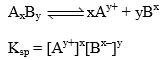
Let the solubility of AxBy is S then
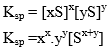
The principle of solubility product is applicable for sparingly soluble salt.
26. Common-ion Effect on Solubility
The common ion present in the solution decrease the solubility of a given compound e.g. The solubility of BaSO4 in Na2SO4 solution is smaller than in an aqueous solution.
Consider saturated solution of AgCl. If a salt having either of the ion common to AgCl say KCl is added to it, then
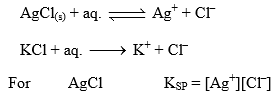
[Cl–] Increases in solution due to presence of KCl and thus to have KSP constant, [Ag+] will decrease or AgCl will precipitate out from solution, i.e., solubility of AgCl will decrease with increasing concentration of KCl in solution.
Let 0.1 M KCl(aq.) solution with AgCl(aq.). If solubility of AgCl is s mol litre–1, then
For AgCl KSP = [Ag+][Cl–]
KSP = s(s + 0.1)
s being small in comparison to 0.1 and thus may be neglected therefore,
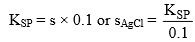
Where s is solubility of AgCl in presence of 0.1 M KClaq.
27. Ionic Product
For a solution of a salt at a specified concentration, the product of the concentration of the ions, each raised to the proper power, is called as the ionic product for a saturated solution in equilibrium with excess of solid, the ionic product is equal to solubility product.
At equilibrium, ionic product = solubility product
If ionic product is less than solubility product it means solution is unsaturated means more salt can be dissolve in it.
If ionic product greater than solubility it means solution is holding more salt than can dissolve in it, therefore ppt started till, until or unless ionic product becomes equal to Ksp.
|
84 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on PH, Buffer Solutions, Solubility & Solubility Product - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is a buffer solution and how does it work? |  |
| 2. How do buffer solutions maintain a stable pH? |  |
| 3. What is solubility and how is it determined? |  |
| 4. What is the solubility product and how is it calculated? |  |
| 5. How does temperature affect solubility and the solubility product? |  |





















