Irodov Solutions: Diffraction of Light- 1 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.97. A plane light wave falls normally on a diaphragm with round aperture opening the first N Fresnel zones for a point P on a screen located at a distance b from the diaphragm. The wavelength of light is equal to 2n,. Find the intensity of light /0 in front of the diaphragm if the distribution of intensity of light I (r) on the screen is known. Here r is the distance from the point P.
Ans.
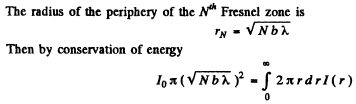
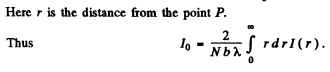
Q.98. A point source of light with wavelength λ = 0.50 p,m is located at a distance a = 100 cm in front of a diaphragm with round aperture of radius r = 1.0 mm. Find the distance b between the diaphragm and the observation point for which the number of Fresnel zones in the aperture equals k = 3.
Ans. By definition
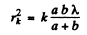
for the periphery of the kth zone. Then
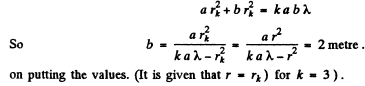
Q.99. A diaphragm with round aperture, whose radius r can be varied during the experiment, is placed between a point source of light and a screen. The distances from the diaphragm to the source and the screen are equal to a = 100 cm and b = 125 cm. Determine the wavelength of light if the intensity maximum at the centre of the diffraction pattern of the screen is observed at r1 = 1.00 mm and the next maximum at r2 = 1.29 mm
Ans. Suppose maximum intensity is obtained when the aperture contains k zones. Then a minimum will be obtained for k + 1 zones. Another maximum will be obtained for k + 2 zones. Hence
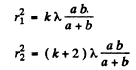
Thus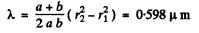
On putting the values.
Q.100. A plane monochromatic light wave with intensity l0 falls normally on an opaque screen with a round aperture. What is the intensity of light I behind the screen at the point for which the aperture (a) is equal to the first Fresnel zone; to the internal half of the first zone; (b) was made equal to the first Fresnel zone and then half of it was closed (along the diameter)?
Ans. (a) When the aperture is equal to the first Fresnel Zone
The amplitude is Ax and should be compared with the amplitude y when the aperture is very wide. If I0 is the intensity in the second case the intensity in the first case will be 4lo
When the aperture is equal to the internal half of the first zone Suppose Ain and Aout are the amplitudes due to the two halves o f the first Fresnel zone. Ain and Aout differ in phase by 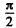 because only half the Fresnel zone in involved. Also in magnitude
because only half the Fresnel zone in involved. Also in magnitude
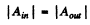 then
then
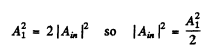
Hence following the aigument of the first case.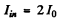
(b) The aperture was made equal to the first Fresnel zone and then half of it was closed along a diameter. In this case the amplitude of vibration is 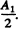 Thus
Thus
I = l0 .
Q.101. A plane monochromatic light wave with intensity Iofalls normally on an opaque disc closing the first Fresnel zone for the observation point P. What did the intensity of light I at the point P become equal to after (a) half of the disc (along the diameter) was removed; (b) half of the external half of the first Fresnel zone was removed (along the diameter)?
Ans. (a) Suppose the disc does not obstruct light at all. Then
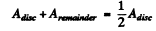
(because the disc covers the first Fresnel zone only).
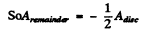
Hence the amplitude when half of the disc is removed along a diameter
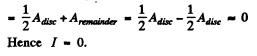
(b) In this case
We write 
where 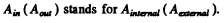 The factor i takes account of the
The factor i takes account of the 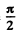 phase difference between two halves of the first Fresnel zone. Thus
phase difference between two halves of the first Fresnel zone. Thus
On the other hand 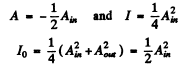
so 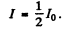
Q.102. A plane monochromatic light wave with intensity /0 falls normally on the surfaces of the opaque screens shown in Fig. 5.20. Find the intensity of light I at a point P
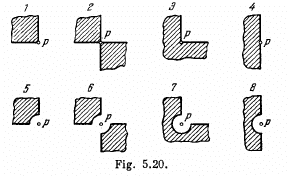
(a) located behind the corner points of screens 1-3 and behind the edge of half-plane 4;
(b) for which the rounded-off edge of screens 5-8 coincides with the boundary of the first Fresnel zone. Derive the general formula describing the results obtained for screens 1-4; the same, for screens 5-8.
Ans. W hen the screen is fully transparent, the. amplitude of vibrations is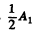 (with intensity
(with intensity
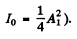
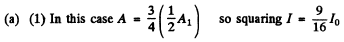
(2) In this case 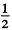 of the plane is blacked out so
of the plane is blacked out so
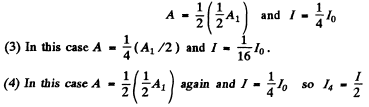
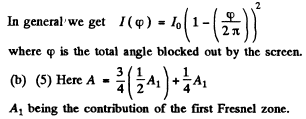
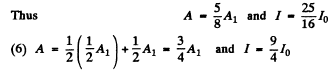
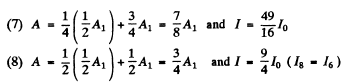
In 5 to 8 the first term in the expression for the amplitude is the contribution of the plane part and the second term gives the expression for the Fresnel zone part. In general in (5) to
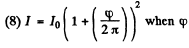 is the angle covered by the screen.
is the angle covered by the screen.
Q.103. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.60 1.t.m falls normally on a sufficiently large glass plate having a round recess on the opposite side (Fig. 5.21). For the observation point P that recess corresponds to the first one and a half Fresnel zones. Find the depth h of the recess at which the intensity of light at the point P is (a) maximum; (b) minimum; (c) equal to the intensity of incident light.
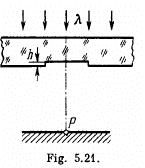
Ans. We would require the contribution to the amplitude of a wave at a point from half a Fresnel zone. For this we proceed directly from the Fresnel Huyghens principle. The complex amplitude is written as
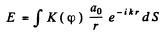
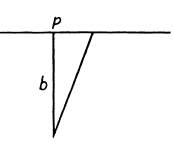

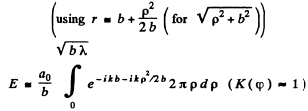
For the first Fresnel zone 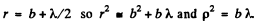
Thus
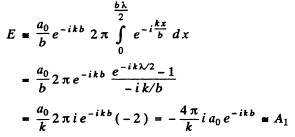
For the next half zone
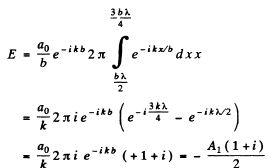
If we calculate the contribution of the full 2nd Fresnel zone we will get - Av If we take account of the factors K (φ) and 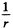 which decrease monotonically we exp ect the contribution to change to - A2. Thus we write for the contribution of the half zones in the 2nd Fresnel zone as
which decrease monotonically we exp ect the contribution to change to - A2. Thus we write for the contribution of the half zones in the 2nd Fresnel zone as
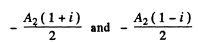
The part lying in the recess has an extra phase difference equal to 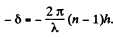 Thus the full amplitude is (note that the correct form is
Thus the full amplitude is (note that the correct form is 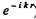
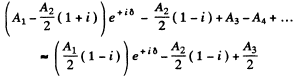
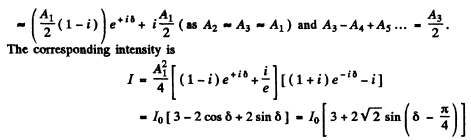
(a) For maximum intensity sin
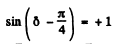
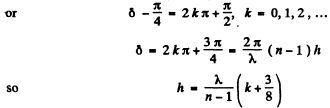
(b) For minimum intensity
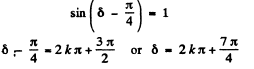
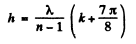
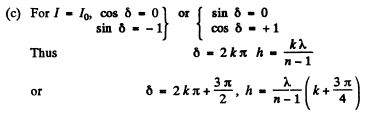
Q.104. A plane light wave with wavelength λ and intensity Io falls normally on a large glass plate whose opposite side serves as an opaque screen with a round aperture equal to the first Fresnel zone for the observation point P. In the middle of the aperture there is a round recess equal to half the Fresnel zone. What must the depth h of that recess be for the intensity of light at the point P to be the highest? What is this intensity equal to?
Ans. The contribution to the wave amplitude of the inner half-zone is
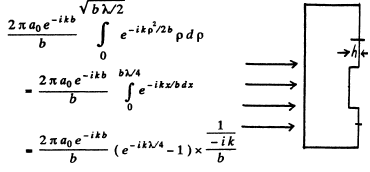
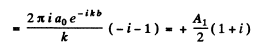
With phase factor this becom es 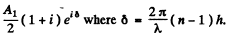 The contribution of
The contribution of
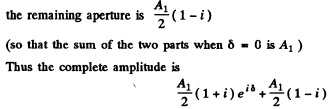
and the intensity is
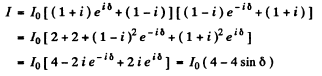
Here 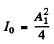 .s the intensity of the incident light which is the same as the intensity due to an aperture of infinite extent (and no recess). Now
.s the intensity of the incident light which is the same as the intensity due to an aperture of infinite extent (and no recess). Now
l is maximum when 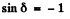
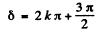
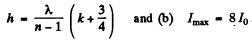
Q.105. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.57 um falls normally on a surface of a glass (n = 1.60) disc which shuts one and a half Fresnel zones for the observation point P. What must the minimum thickness of that disc be for the intensity of light at the point P to be the highest? Take into account the interference of light on its passing through the disc.
Ans. We follow Ihe argument of 5.103. we find that the contribution of the first Fresnel zone is
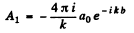
For the n ext h a lf zone it i 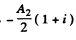
(The contribution of the remaining part of the 2nd Fresnel zone will be 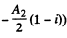
If the disc has a thickness h, the extra phase difference suffered by the light wave in passing through' the disc will be
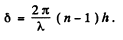
Thus the amplitude at P will be
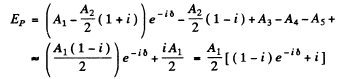
The corresponding intensity will be
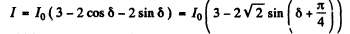
The intensity will be a maximum when
or 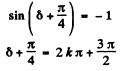
i.e 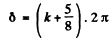
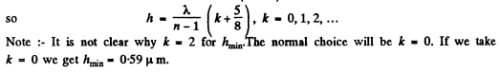
Q.106. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.54 um goes through a thin converging lens with focal length f = 50 cm and an aperture stop fixed immediately after the lens, and reaches a screen placed at a distance b = 75 cm from the aperture stop. At what aperture radii has the centre of the diffraction pattern on the screen the maximum illuminance?
Ans. Here the focal point acts as a virtual source of light. This means that we can take spherical waves conveiging towards F. Let us divide these waves intofresnel zones just after they emerge from the stop. We write 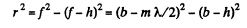
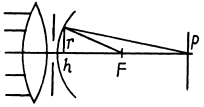
Here r is the radius of the mth fresnel zone and A is the distance to the left of the foot of the perpendicular. Thus
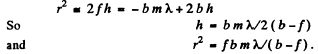
The intensity maxima are observed when an odd number of Fresnel zones are exposed by the stop. Thus
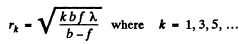
Q.107. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a round aperture. At a distance b = 9.0 m from it there is a screen showing a certain diffraction pattern. The aperture diameter was decreased η = 3.0 times. Find the new distance b' at which the screen should be positioned to obtain the diffraction pattern similar to the previous one but diminished η times.
Ans. or the radius of the periphery of the kth zone we have
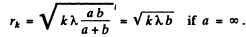
If the aperture diameter is reduced η times it will produce a similar deftraction pattern (reduced η times) if the radii of the Fresnel zones are also η times less. Thus

Q.108. An opaque ball of diameter D = 40 mm is placed between a source of light with wavelength λ = 0.55 um and a photographic plate. The distance between the source and the ball is equal to a = 12 m and that between the ball and the photographic plate is equal to b = 18 m. Find:
(a) the image dimension y' on the plate if the transverse dimension of the source is y = 6.0 mm;
(b) the minimum height of irregularities, covering the surface of the ball at random, at which the ball obstructs light.
Note. As calculations and experience show, that happens when the height of irregularities is comparable with the width of the Fresnel zone along which the edge of an opaque screen passes
Ans. (a) If a point source is placecd before an opaque ball, the diffraction pattern consists of a bright spot inside a dark disc followed by fringes. The bright spot is on the line joining the point source and the centre of the ball. When the object is a finite source of transverse diamensiony, every point of the source has its corresponding image on the line joining that point and the centre of the ball. Thus the transverse dimension of the image is given by
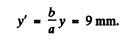
(b) The minimum height of the irregularities covering the surface of the ball at random, at which the ball obstructs light is^according to the note at the end of the problem, corn* parable with the width of the Fresnel zone along which the edge of opaque screen passes. SO
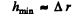
Tofind Δr we note that
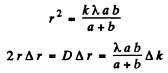
Where D = diameter of the disc (= diameter of the last Fresnel zone) and Δk = 1 Thus
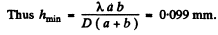
Q.109. A point source of monochromatic light is positioned in front of a zone plate at a distance a = 1.5 m from it. The image of the source is formed at a distance b = 1.0 m from the plate. Find the focal length of the zone plate.
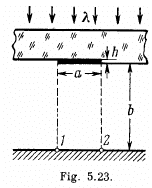
Ans.


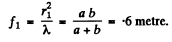
This is the principle focal length. Other maxima are obtained when
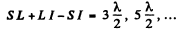
These focal lengths are also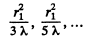
Q.110. A plane light wave with wave- length λ = 0.60 um and intensity I, falls normally on a large glass plate whose side view is shown in Fig. 5.22. At what height h of the ledge will the intensity of light at points located directly below be
(a) minimum;
(b) twice as low as I0 (the losses due to reflection are to be neglected).
Ans. Just below the edge the amplitude of the wave is given by
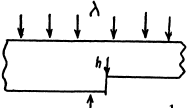
Here the quantity in the brackets is the contribution of various Fresnel zones; the factor 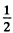 is to take account of the division of the plate into two parts by the ledge; the phase factor 5 is given by
is to take account of the division of the plate into two parts by the ledge; the phase factor 5 is given by
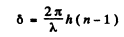
and takes into account the extra length traversed by the waves on the left.
Using 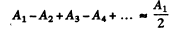
we get 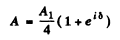
and the corresponding intensity is
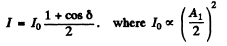
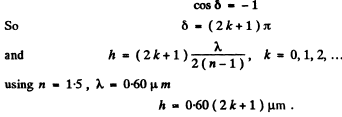
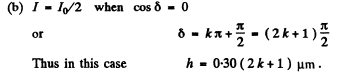
Q.111. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on an opaque half-plane. A screen is located at a distance b = 100 cm behind the half-plane. Making use of the Cornu spiral (Fig. 5.19), find: (a) the ratio of intensities of the first maximum and the neighbouring minimum; (b) the wavelength of light if the first two maxima are separated by a distance Δx = 0.63 mm.
Ans. (a) From the Cornu’s spiral, the intensity of t^e first maximum is given as
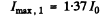
and the intensity of the first minimum is given by
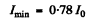
so the required ratio is
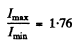
(b) The value of the distance x is related to the parameter v in Fresnel's integral by
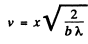
For the first two maxima the distances x1 , x 2 are related to the parameters v1, v2 by
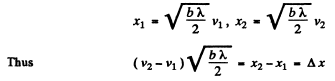
or 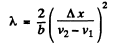
From the Cornu’s spiral the positions of the maxima are
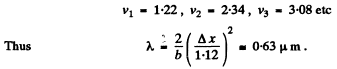
Q.112. A plane light wave with wavelength 0.60 pm falls normally on a long opaque strip 0.70 mm wide. Behind it a screen is placed at a distance 100 cm. Using Fig. 5.19, find the ratio of intensities of light in the middle of the diffraction pattern and at the edge of the geometrical shadow.
Ans. We shall use the equation written down in 5.103, the Fresnel-Huyghens formula.
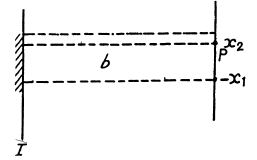
Suppose we want tofind the intensity at P which is such that the coordinates of the edges (x-coordinates) with respect to P are x2 and - x1. Then, the amplitude at P is
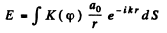 (1)
(1)
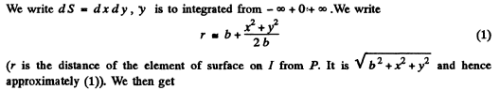
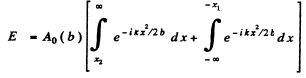
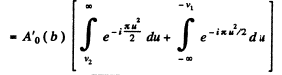
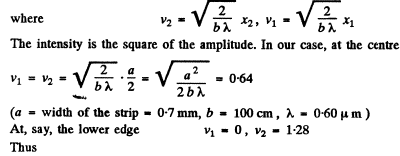
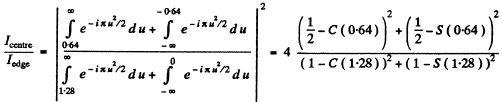
where
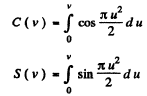
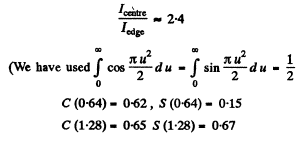
Rough evaluation of the integrals using cornu’s spiral gives
Q.113. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a long rectangular slit behind which a screen is positioned at a distance b = 60 cm. First the width of the slit was adjusted so that in the middle of the diffraction pattern the lowest minimum was observed. After widening the slit by Δh = 0.70 mm, the next minimum was obtained in the centre of the pattern. Find the wavelength of light.
Ans. If the aperture has width A then the parameters ( v , - v ) associated w ith
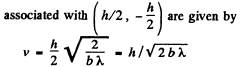
The intensity of light at O on the screen is obtained as the square of the amplitude A of the wave at O which is
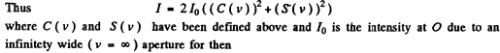
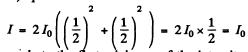
By definition v corresponds to the first minimum of the intensity. This means
when we increase 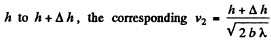 relates to the second
relates to the second
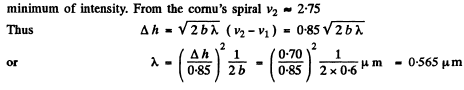
Q.114. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.65 p.m falls normally on a large glass plate whose opposite side has a long rectangular recess 0.60 mm wide. Using Fig. 5.19, find the depth h of the recess at which the diffraction pattern on the screen 77 cm away from the plate has the maximum illuminance at its centre.
Ans. Let a = width of the recess and
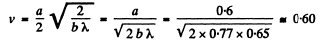
be die parameter along Cornu’s spiral corresponding to the half-width of the recess. The amplitude of the diffracted wave is given by
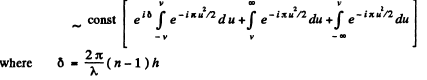
is the extra phase due to the recess. (Actually an extra phase e -lδ appears outside the recess. When we take it out and absorb it in the constant we get the expression written).
Thus the amplitude is
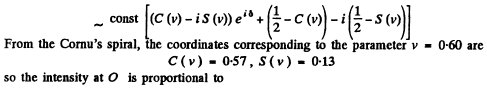
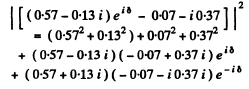
We write
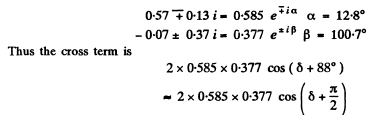
For maximum intensity
or 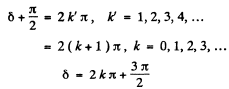
so 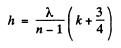
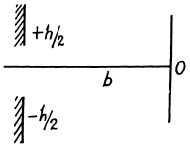
Q.115. A plane light wave with wavelength λ = 0.65 p.m falls normally on a large glass plate whose opposite side has a ledge and an opaque strip of width a = 0.30 mm (Fig. 5.23). A screen is placed at a distance b = 110 cm from the plate. The height h of the ledge is such that the intensity of light at point 2 of the
screen is the highest possible. Making use of Fig. 5.19, find the ratio of intensities at points 1 and 2.
Ans.
Using the method of problem 5.103 we can immediately write down the amplitudes at 1 and 2. We get :
At 1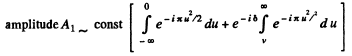
At 2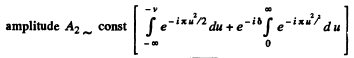
where 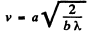
is the parameter of Cornu’s spiral and constant factor is common to 1 and 2. With the usual notation
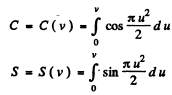
and the result 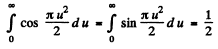
We find the ratio of intensities as
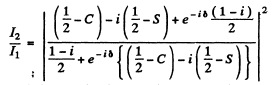
(The constants in A1 and A2 must be the same by symmetry)
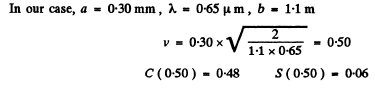
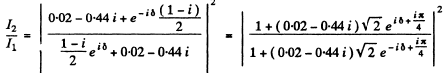
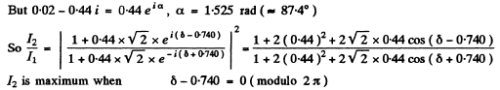
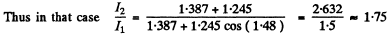
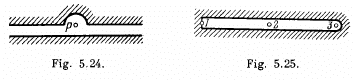
Q.116. A plane monochromatic light wave of intensity Io falls normally on an opaque screen with a long slit having a semicircular

cut on one side (Fig. 5.24). The edge of the cut coincides with the boundary line of the first Fresnel zone for the observation point P. The width of the slit measures 0.90 of the radius of the cut. Using Fig. 5.19, find the intensity of light at the point P.
Ans. 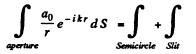
The contribution of the full 1st Fresnel zone has been evaluated in 5.103. The contribution of the semi-circle is one half of it and is
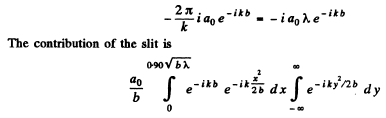
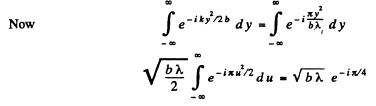
Thus the contribution of the slit is
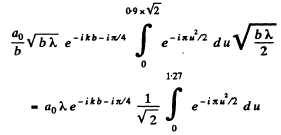
Thus the intensity at the observation point P on the screeii is
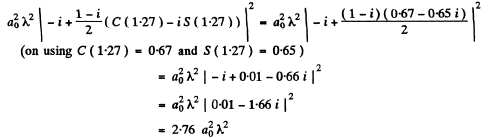

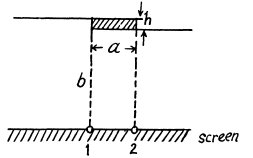
Q.117. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on an opaque screen with a long slit whose shape is shown in Fig. 5.25. Making use of Fig. 5.19, find the ratio of intensities of light at points 1, 2, and 3 located behind the screen at equal distances from it. For point 3 the rounded-off edge of the slit coincides with the boundary line of the first Fresnel zone.
Ans. From the statement of the problem we know that the width of the slit = diameter of the first Fresnel  where b is the distance of the observation point from the slit
where b is the distance of the observation point from the slit
We calculate the amplitudes by evaluating the integral of problem 5.103 We get
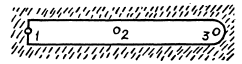
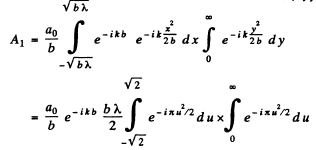
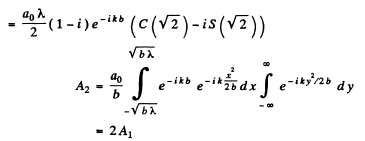
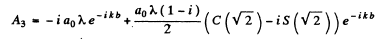
where the contribution of the 1st half Fresnel zone (in A3, first term) has been obtained from the last problem.
Thus
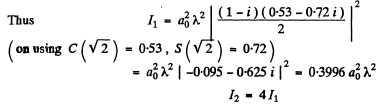
So 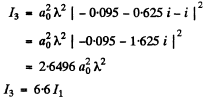
Thus
Q.118. A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on an opaque screen shaped as a long strip with a round hole in the middle. For the observation point P the hole corresponds to half the Fresnel zone, with the hole diameter being η = 1.07 times less than the width of the strip. Using Fig. 5.19, find the intensity of light at the point P provided that the intensity of the incident light is equal to I0
Ans.
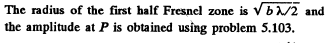
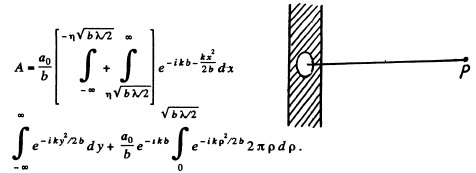
We use
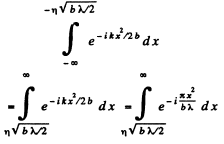
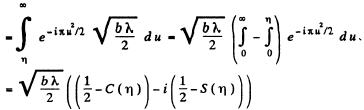
Thus
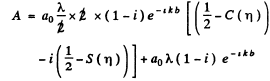
where we have used
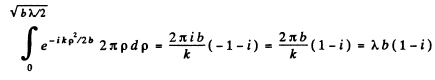
Thus the intensity is
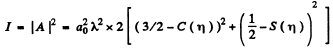
From Cornu’s Spiral,
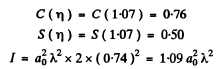
As before
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Diffraction of Light- 1 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is diffraction of light? |  |
| 2. How does the diffraction of light occur? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of diffraction of light? |  |
| 4. What are some real-life examples of diffraction of light? |  |
| 5. How is the diffraction of light related to the study of optics? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















